|
PRKD3
Serine/threonine-protein kinase D3 (PKD3) or PKC-nu is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PRKD3'' gene. Protein kinase C (PKC) is a family of serine- and threonine-specific protein kinases that can be activated by calcium and the second messenger diacylglycerol. PKC family members phosphorylate a wide variety of protein targets and are known to be involved in diverse cellular signaling pathways. PKC family members also serve as major receptors for phorbol esters, a class of tumor promoters. Each member of the PKC family has a specific expression profile and is believed to play a distinct role. The protein encoded by this gene is one of the PKC family members. This kinase can be activated rapidly by the agonists of G protein-coupled receptor G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Kinase C
In cell biology, Protein kinase C, commonly abbreviated to PKC (EC 2.7.11.13), is a family of protein kinase enzymes that are involved in controlling the function of other proteins through the phosphorylation of hydroxyl groups of serine and threonine amino acid residues on these proteins, or a member of this family. PKC enzymes in turn are activated by signals such as increases in the concentration of diacylglycerol (DAG) or calcium ions (Ca2+). Hence PKC enzymes play important roles in several signal transduction cascades. In biochemistry, the PKC family consists of fifteen isozymes in humans. They are divided into three subfamilies, based on their second messenger requirements: conventional (or classical), novel, and atypical. Conventional (c)PKCs contain the isoforms α, βI, βII, and γ. These require Ca2+, DAG, and a phospholipid such as phosphatidylserine for activation. Novel (n)PKCs include the δ, ε, η, and θ isoforms, and require DAG, but do not require Ca2+ for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine- And Threonine-specific Protein Kinase
A serine/threonine protein kinase () is a kinase enzyme, in particular a protein kinase, that phosphorylates the OH group of the amino-acid residues serine or threonine, which have similar side chains. At least 350 of the 500+ human protein kinases are serine/threonine kinases (STK). In enzymology, the term ''serine/threonine protein kinase'' describes a class of enzymes in the family of transferases, that transfer phosphates to the oxygen atom of a serine or threonine side chain in proteins. This process is called phosphorylation. Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes and is a very important posttranslational modification. The chemical reaction performed by these enzymes can be written as :ATP + a protein \rightleftharpoons ADP + a phosphoprotein Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are ATP and a protein, whereas its two products are ADP and phosphoprotein. The systematic name of this enzyme class is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
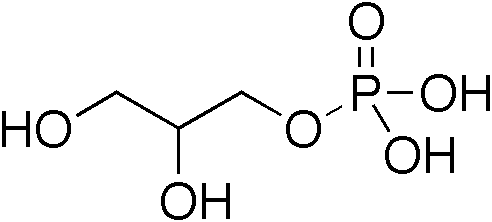
Diacylglycerol
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. DAGs can act as surfactants and are commonly used as emulsifiers in processed foods. DAG-enriched oil (particularly 1,3-DAG) has been investigated extensively as a fat substitute due to its ability to suppress the accumulation of body fat; with total annual sales of approximately USD 200 million in Japan since its introduction in the late 1990s till 2009. Production Diglycerides are a minor component of many seed oils and are normally present at ~1–6%; or in the case of cottonseed oil as much as 10%. Industrial production is primarily achieved by a glycerolysis reaction between triglycerides and glycerol. The raw materials for this may be either vegetable oils or animal fats. Food additive Diglycerides, generally in a mix with monoglycerides (E471), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phorbol Ester
Phorbol esters are a class of chemical compounds found in a variety of plants, particularly in the families Euphorbiaceae and Thymelaeaceae. Chemically, they are ester derivatives of the tetracyclic diterpenoid phorbol. Biological activity Protein kinase C (PKC) is a phorbol ester receptor. Phorbol esters can stimulate PKC in a similar way to diglycerides. Phorbol esters are known for their ability to promote tumors. In particular, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) is used as a biomedical research tool in models of carcinogenesis. Plants that contain phorbol esters are often poisonous Poison is a chemical substance that has a detrimental effect to life. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figuratively, with a broa .... References {{Chem-stub Diterpenes Carboxylate esters Cyclopentenes Plant toxins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein-coupled Receptor
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-(pass)-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptors, and G protein-linked receptors (GPLR), form a large group of evolutionarily-related proteins that are cell surface receptors that detect molecules outside the cell and activate cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times. Text was copied from this source, which is available under Attribution 2.5 Generic (CC BY 2.5) license. Ligands can bind either to extracellular N-terminus and loops (e.g. glutamate receptors) or to the binding site within transmembrane helices (Rhodopsin-like family). They are all activated by agonists although a spontaneous auto-activation of an empty receptor can also be observed. G protein-coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-cell Antigen Receptor
The B cell receptor (BCR) is a transmembrane protein on the surface of a B cell. A B cell receptor is composed of a membrane-bound immunoglobulin molecule and a signal transduction moiety. The former forms a type 1 transmembrane receptor protein, and is typically located on the outer surface of these lymphocyte cells. Through biochemical signaling and by physically acquiring antigens from the immune synapses, the BCR controls the activation of the B cell. B cells are able to gather and grab antigens by engaging biochemical modules for receptor clustering, cell spreading, generation of pulling forces, and receptor transport, which eventually culminates in endocytosis and antigen presentation. B cells' mechanical activity adheres to a pattern of negative and positive feedbacks that regulate the quantity of removed antigen by manipulating the dynamic of BCR–antigen bonds directly. Particularly, grouping and spreading increase the relation of antigen with BCR, thereby proving sensit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phospholipase C Gamma
Phospholipase C (PLC) is a class of membrane-associated enzymes that cleave phospholipids just before the phosphate group (see figure). It is most commonly taken to be synonymous with the human forms of this enzyme, which play an important role in eukaryotic cell physiology, in particular signal transduction pathways. Phospholipase C's role in signal transduction is its cleavage of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into diacyl glycerol (DAG) and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3), which serve as Second messenger system, second messengers. Activators of each PLC vary, but typically include heterotrimeric G protein subunits, protein tyrosine kinases, Small GTPase, small G proteins, Ca2+, and phospholipids. There are thirteen kinds of mammalian phospholipase C that are classified into six isotypes (β, γ, δ, ε, ζ, η) according to structure. Each PLC has unique and overlapping controls over expression and subcellular distribution. Variants Mammalian variants The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |