|
POU-homeodomain
POU (pronounced 'pow') is a family of proteins that have well-conserved homeodomains. Etymology The acronym POU is derived from the names of three transcription factors: * the Pituitary-specific Pit-1 * the Octamer transcription factor proteins Oct-1 and Oct-2 (octamer sequence is ATGCAAAT) * the neural Unc-86 transcription factor from ''Caenorhabditis elegans''. Diversity POU domain genes have been described in organisms as divergent as ''Caenorhabditis elegans'', ''Drosophila'', ''Xenopus'', zebrafish and human but have not been yet identified in plants and fungi. Comparisons of POU domain genes across the animals suggests that the family can be divided into six major classes (POU1-POU6). Pit-1 is part of the POU1 class, Oct-1 and Oct-2 are members of POU2, while Unc-86 is a member of POU4. The six classes diverged early in animal evolution: POU1, POU3, POU4, and POU6 classes evolved before the last common ancestor of sponges and eumetazoans, POU2 evolved in the Bilater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pituitary-specific Positive Transcription Factor 1
POU domain, class 1, transcription factor 1 (Pit1, growth hormone factor 1), also known as POU1F1, is a transcription factor for growth hormone. Function PIT1 is a pituitary-specific transcription factor responsible for pituitary development and hormone expression in mammals and is a member of the POU family of transcription factors that regulate mammalian development. The POU family is so named because the first 3 members identified were PIT1 and OCT1 (MIM 164175) of mammals, and Unc-86 of C. elegans (Herr et al., 1988). PIT1 contains 2 protein domains, termed POU-specific and POU-homeo, which are both necessary for high affinity DNA binding on genes encoding growth hormone (GH; MIM 139250) and prolactin (PRL; MIM 176760). PIT1 is also important for regulation of the genes encoding prolactin and thyroid-stimulating hormone beta subunit (TSHB; MIM 188540) by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH; MIM 257120) and cyclic AMP. upplied by OMIMref name="ncbi" /> Interactions Pituita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pituitary-specific Positive Transcription Factor 1
POU domain, class 1, transcription factor 1 (Pit1, growth hormone factor 1), also known as POU1F1, is a transcription factor for growth hormone. Function PIT1 is a pituitary-specific transcription factor responsible for pituitary development and hormone expression in mammals and is a member of the POU family of transcription factors that regulate mammalian development. The POU family is so named because the first 3 members identified were PIT1 and OCT1 (MIM 164175) of mammals, and Unc-86 of C. elegans (Herr et al., 1988). PIT1 contains 2 protein domains, termed POU-specific and POU-homeo, which are both necessary for high affinity DNA binding on genes encoding growth hormone (GH; MIM 139250) and prolactin (PRL; MIM 176760). PIT1 is also important for regulation of the genes encoding prolactin and thyroid-stimulating hormone beta subunit (TSHB; MIM 188540) by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH; MIM 257120) and cyclic AMP. upplied by OMIMref name="ncbi" /> Interactions Pituita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eumetazoa
Eumetazoa (), also known as diploblasts, Epitheliozoa, or Histozoa, are a proposed basal animal clade as a sister group of the Porifera (sponges). The basal eumetazoan clades are the Ctenophora and the ParaHoxozoa. Placozoa is now also seen as a eumetazoan in the ParaHoxozoa. Several other extinct or obscure life forms, such as ''Iotuba'' and ''Thectardis'', appear to have emerged in the group. Characteristics of eumetazoans include true tissues organized into germ layers, the presence of neurons and muscles, and an embryo that goes through a gastrula stage. Some phylogenists once speculated the sponges and eumetazoans evolved separately from different single-celled organisms, which would have meant that the animal kingdom does not form a clade (a complete grouping of all organisms descended from a common ancestor). However, genetic studies and some morphological characteristics, like the common presence of choanocytes, now unanimously support a common origin. Traditionally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain
The immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) is the large polypeptide subunit of an antibody (immunoglobulin). In human genome, the IgH gene loci are on chromosome 14. A typical antibody is composed of two immunoglobulin (Ig) heavy chains and two Ig light chains. Several different types of heavy chain exist that define the class or isotype of an antibody. These heavy chain types vary between different animals. All heavy chains contain a series of immunoglobulin domains, usually with one variable domain (VH) that is important for binding antigen and several constant domains (CH1, CH2, etc.). Production of a viable heavy chain is a key step in B cell maturation. If the heavy chain is able to bind to a surrogate light chain and move to the plasma membrane, then the developing B cell can begin producing its light chain. The heavy chain doesn't always have to bind to a light chain. Pre-B lymphocytes can synthesize heavy chain in the absence of light chain, which then can allow the heavy ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin Light Chain
] The immunoglobulin light chain is the small Peptide, polypeptide subunit of an antibody (immunoglobulin). A typical antibody is composed of two immunoglobulin (Ig) heavy chains and two Ig light chains. In humans There are two types of light chain in humans: * kappa (κ) chain, encoded by the immunoglobulin kappa locus (IGK@) on chromosome 2 (locus: 2p11.2) * lambda (λ) chain, encoded by the immunoglobulin lambda locus (IGL@) on chromosome 22 (locus: 2q11.22) Antibodies are produced by B lymphocytes, each expressing only one class of light chain. Once set, light chain class remains fixed for the life of the B lymphocyte. In a healthy individual, the total kappa-to-lambda ratio is roughly 2:1 in serum (measuring intact whole antibodies) or 1:1.5 if measuring free light chains, with a highly divergent ratio indicative of neoplasm. The quotient of kappa divided by lambda, according to a novel polyclonal free light chain assay, ranges from 0.26 to 1.65. Both the kappa and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroendocrinology
Neuroendocrinology is the branch of biology (specifically of physiology) which studies the interaction between the nervous system and the endocrine system; i.e. how the brain regulates the hormonal activity in the body. The nervous and endocrine systems often act together in a process called neuroendocrine integration, to regulate the physiological processes of the human body. Neuroendocrinology arose from the recognition that the brain, especially the hypothalamus, controls secretion of pituitary gland hormones, and has subsequently expanded to investigate numerous interconnections of the endocrine and nervous systems. The endocrine system consists of numerous glands throughout the body that produce and secrete hormones of diverse chemical structure, including peptides, steroids, and neuroamines. Collectively, hormones regulate many physiological processes. The neuroendocrine system is the mechanism by which the hypothalamus maintains homeostasis, regulating reproduction, metab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
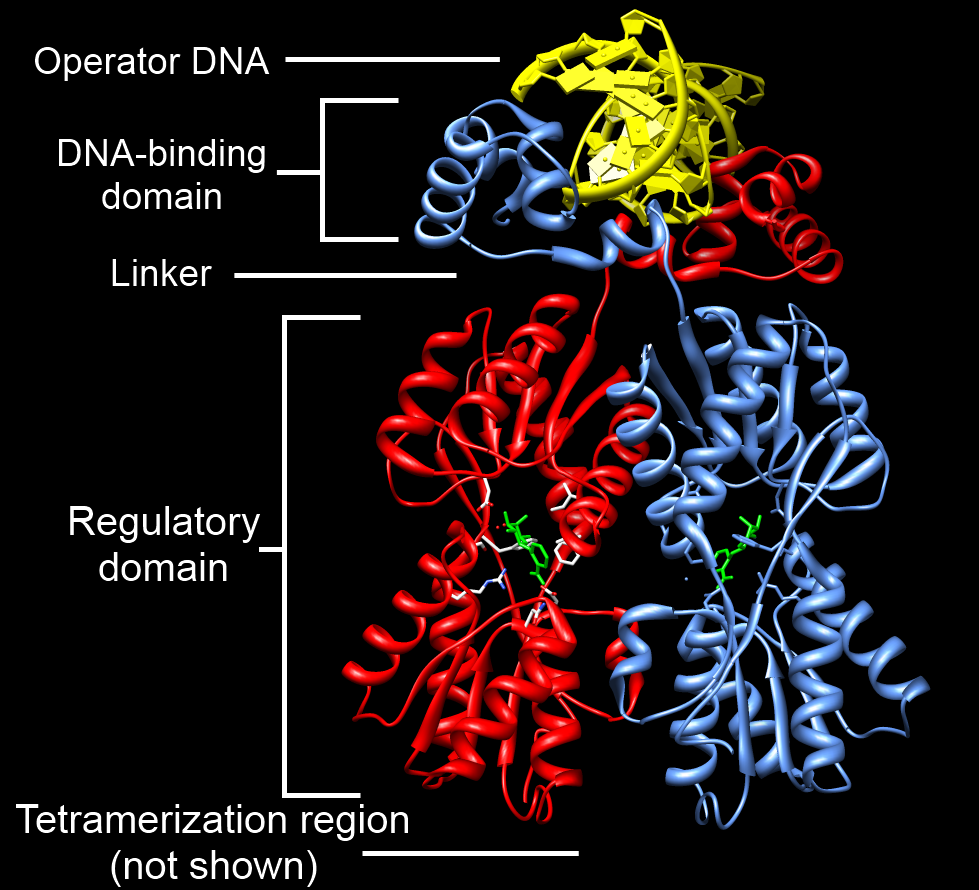
DNA Binding Domain
A DNA-binding domain (DBD) is an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. A DBD can recognize a specific DNA sequence (a recognition sequence) or have a general affinity to DNA. Some DNA-binding domains may also include nucleic acids in their folded structure. Function One or more DNA-binding domains are often part of a larger protein consisting of further protein domains with differing function. The extra domains often regulate the activity of the DNA-binding domain. The function of DNA binding is either structural or involves transcription regulation, with the two roles sometimes overlapping. DNA-binding domains with functions involving DNA structure have biological roles in DNA replication, repair, storage, and modification, such as methylation. Many proteins involved in the regulation of gene expression contain DNA-binding domains. For example, proteins that regulate transcription by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are expressed in the desired cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are up to 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of RNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Competence
In microbiology, genetics, cell biology, and molecular biology, competence is the ability of a cell to alter its genetics by taking up extracellular ("naked") DNA from its environment in the process called transformation. Competence may be differentiated between ''natural competence'', a genetically specified ability of bacteria which is thought to occur under natural conditions as well as in the laboratory, and ''induced'' or ''artificial competence'', which arises when cells in laboratory cultures are treated to make them transiently permeable to DNA. Competence allows for rapid adaptation and DNA repair of the cell. This article primarily deals with natural competence in bacteria, although information about artificial competence is also provided. History Natural competence was discovered by Frederick Griffith in 1928, when he showed that a preparation of killed cells of a pathogenic bacterium contained something that could transform related non-pathogenic cells into the pathog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metazoans
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the echinoderms a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Subtilis
''Bacillus subtilis'', known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a Gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants, humans and marine sponges. As a member of the genus ''Bacillus'', ''B. subtilis'' is rod-shaped, and can form a tough, protective endospore, allowing it to tolerate extreme environmental conditions. ''B. subtilis'' has historically been classified as an obligate aerobe, though evidence exists that it is a facultative anaerobe. ''B. subtilis'' is considered the best studied Gram-positive bacterium and a model organism to study bacterial chromosome replication and cell differentiation. It is one of the bacterial champions in secreted enzyme production and used on an industrial scale by biotechnology companies. Description ''Bacillus subtilis'' is a Gram-positive bacterium, rod-shaped and catalase-positive. It was originally named ''Vibrio subtilis'' by Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg, and renamed ''B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)