|
PM (newspaper)
''PM'' was a liberal-leaning daily newspaper published in New York City by Ralph Ingersoll from June 1940 to June 1948 and financed by Chicago millionaire Marshall Field III. The paper borrowed many elements from weekly news magazines, such as many large photos and at first was bound with staples. In an attempt to be free of pressure from business interests, it did not accept advertising. These departures from the norms of newspaper publishing created excitement in the industry. Some 11,000 people applied for the 150 jobs available when the publication first hired staff. Publication history The origin of the name is unknown, although Ingersoll recalled that it probably referred to the fact that the paper appeared '' post meridiem'' (in the afternoon); ''The New Yorker'' reported that the name had been suggested by Lillian Hellman. (There is no historical evidence for the suggestion that the name was an abbreviation of ''Picture Magazine''.) The first year of the paper was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph Ingersoll (PM Publisher)
Ralph McAllister Ingersoll (December 8, 1900 in New Haven, Connecticut – March 8, 1985 in Miami Beach, Florida) was an American writer, editor, and publisher. He is best known as founder and publisher of '' PM'', a short-lived 1940s New York City left-wing daily newspaper that was financed by Chicago millionaire Marshall Field III. Biography Ingersoll went to Hotchkiss School, graduated from Yale University's Sheffield Scientific School and became a mining engineer in California, Arizona and Mexico. In 1923 he went to New York with the intention of becoming a writer. He worked as a reporter for the ''New York American'' from 1923 to 1925, and then joined ''The New Yorker'' where he was managing editor from 1925 to 1930. He had been hired by the ''New Yorker'' founder and editor Harold Ross a few months after the magazine commenced publication; Ross inadvertently spilled an inkwell on Ingersoll's new light suit (various sources claim it was either white or pale gray) during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Kronenberger
Louis Kronenberger (December 9, 1904April 30, 1980) was an American literary critic (longest with ''Time'', (1938-1961), novelist, and biographer who wrote extensively on drama and the 18th century. Background Kronenberger was born in Cincinnati, Ohio, to Louis Kronenberger Sr., a merchant, and Mabel Newwitter. From 1921 to 1924 Kronenberger attended (but did not graduate from) the University of Cincinnati (1921–24). Career Writer In 1924, Kronenberger began his career at the ''New York Times''. In 1926, he became an editor at Boni & Liveright. In 1933, he became an editor for Alfred A. Knopf. In 1938, he became drama critic for ''Time'', where he continued to 1961. In 1940, William Saroyan listed Kronenberger among the associate editors at ''Time'' in the play, ''Love's Old Sweet Song''. Starting in 1942, he worked under Whittaker Chambers, who became editor for the "Back of the Book" (1942-1944). During this period ''Time'' was, according to Chambers, "consistently a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
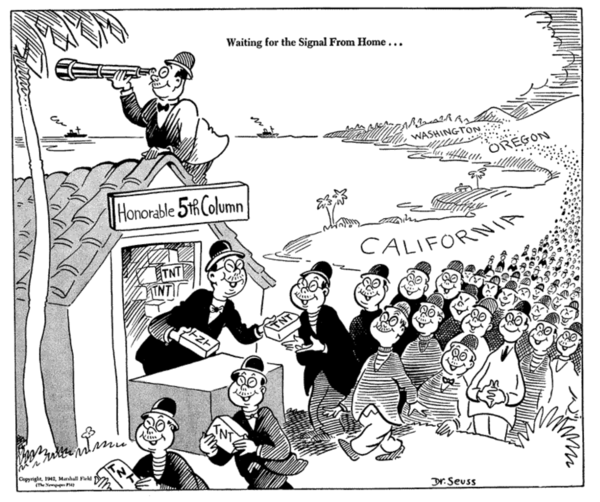
Jack Sparling
John Edmond Sparling (June 21, 1916 – February 15, 1997), was a Canadian comics artist. Biography Born in Winnipeg, Manitoba, Sparling moved to the United States as a child. He received his early arts training at the Arts and Crafts Club in New Orleans and later attended the Corcoran School of Art. He worked briefly as a gag cartoonist for the ''New Orleans Item-Tribune''. In 1941, Sparling, along with writer William Laas, created the United Feature Syndicate comic strip ''Hap Hopper, Washington Correspondent'', for which real-life newspaper columnists Drew Pearson and Robert S. Allen were listed as editors.''Hap Hopper'' at Don Markstein's Toonopedia. from the original on March 8, 2015. One source lists it as having launche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coulton Waugh
Frederick Coulton Waugh (; 10 March 1896 – 23 May 1973) was a cartoonist, painter, teacher and author, best known for his illustration work on the comic strip ''Dickie Dare'' and his book ''The Comics'' (1947), the first major study of the field. His father was the marine artist Frederick Judd Waugh, and his grandfather was the Philadelphia portrait painter Samuel Waugh.Laurel Guadazno. "", 31 August 2000. ''Provincetown Banner''. of thoriginal page on 10 February 2008. Retrieved on 2008-02-10. . Archived from th original on 10 Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jack Coggins
Jack Banham Coggins (July 10, 1911 – January 30, 2006) was an artist, author, and illustrator. He is known in the United States for his oil paintings, which focused predominantly on marine subjects. He is also known for his books on space travel, which were both authored and illustrated by Coggins. Besides his own works, Coggins also provided illustrations for advertisements and magazine covers and articles. During World War II, he served as an artist and correspondent for '' YANK'' magazine, capturing and conveying wartime scenes from the front lines. Over the course of his career, Coggins produced more than 1,000 paintings and taught art classes for 45 years. He retired in May 2001 and died at his home in Pennsylvania in January 2006. Biography Early life Coggins was born in London, England on July 10, 1911, the only child of Ethel May (née Dobby) and Sydney George Coggins. Sydney Coggins was Regimental Corporal Major of the First Regiment of Life Guards, the part of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ad Reinhardt
Adolph Dietrich Friedrich Reinhardt (December 24, 1913 – August 30, 1967) was an abstract painter active in New York for more than three decades. He was a member of the American Abstract Artists (AAA) and part of the movement centered on the Betty Parsons Gallery that became known as abstract expressionism. He was also a member of The Club, the meeting place for the New York School abstract expressionist artists during the 1940s and 1950s. He wrote and lectured extensively on art and was a major influence on conceptual art, minimal art and monochrome painting. Most famous for his "black" or "ultimate" paintings, he claimed to be painting the "last paintings" that anyone can paint. He believed in a philosophy of art he called ''Art-as-Art'' and used his writing and satirical cartoons to advocate for abstract art and against what he described as "the disreputable practices of artists-as-artists". Background Reinhardt was born in Buffalo, New York, and lived with his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnaby (comics)
''Barnaby'' is a comic strip which began April 20, 1942, in the newspaper '' PM'' and was later syndicated in 64 American newspapers (for a combined circulation of more than 5,500,000). Created by Crockett Johnson, who is best known today for his children's book ''Harold and the Purple Crayon'', the strip featured a cherubic-looking five-year-old and his far-from-cherubic fairy godfather, Jackeen J. O'Malley, a short, cigar-smoking man with four tiny wings. With a distinctive appearance because of its use of typography, the strip had numerous reprints and was adapted into a 1940s stage production. The usually caustic Dorothy Parker had nothing but praise: "I think, and I'm trying to talk calmly, that Barnaby and his friends and oppressors are the most important additions to American Arts and Letters in Lord knows how many years."Nel, PhilipNel, Philip. ''Harold, Barnaby, and Dave: A Biography of Crockett Johnson''K-state.edu Characters and story One night after having been read ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comic Strip
A comic strip is a sequence of drawings, often cartoons, arranged in interrelated panels to display brief humor or form a narrative, often serialized, with text in balloons and captions. Traditionally, throughout the 20th and into the 21st century, these have been published in newspapers and magazines, with daily horizontal strips printed in black-and-white in newspapers, while Sunday papers offered longer sequences in special color comics sections. With the advent of the internet, online comic strips began to appear as webcomics. Strips are written and drawn by a comics artist, known as a cartoonist. As the word "comic" implies, strips are frequently humorous. Examples of these gag-a-day strips are '' Blondie'', '' Bringing Up Father'', '' Marmaduke'', and ''Pearls Before Swine''. In the late 1920s, comic strips expanded from their mirthful origins to feature adventure stories, as seen in '' Popeye'', '' Captain Easy'', '' Buck Rogers'', '' Tarzan'', and '' Terry and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crockett Johnson
Crockett Johnson (October 20, 1906 – July 11, 1975) was the pen name of the American cartoonist and children's book illustrator David Johnson Leisk. He is best known for the comic strip '' Barnaby'' (1942–1952) and the ''Harold'' series of books, beginning with '' Harold and the Purple Crayon''. From 1965 until his death Johnson created over a hundred paintings relating to mathematics and mathematical physics. Eighty of these are found in the collections of the National Museum of American History. Biography Born in New York City, Johnson grew up in Corona, Queens, New York, attended PS 16 and Newtown High School. He studied art at Cooper Union in 1924, and at New York University in 1925."Harold, Barnaby, and Dave: A Biography of Crockett Johnson" Philip Nel. He exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elizabeth Hawes
Elizabeth Hawes (December 16, 1903 – September 6, 1971) was an American clothing designer, outspoken critic of the fashion industry, and champion of ready to wear and people's right to have the clothes they desired, rather than the clothes dictated to be fashionable, an idea encapsulated in her book ''Fashion Is Spinach'', published in 1938. She was among the first Americans to establish their reputations outside of Paris ''haute couture''. In addition to her work in the fashion industry as a sketcher, copyist, stylist, and journalist, and designer, she was an author, union organizer, champion of gender equality, and political activist. Early life Elizabeth Hawes was born in Ridgewood, New Jersey, the second child of four. Her father was an assistant manager for the Southern Pacific Company, and her mother worked on the Board of Education and was actively involved in local politics, especially the rights of the local African-American community. She had graduated from Vassar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Racing
Horse racing is an equestrian performance sport, typically involving two or more horses ridden by jockeys (or sometimes driven without riders) over a set distance for competition. It is one of the most ancient of all sports, as its basic premise – to identify which of two or more horses is the fastest over a set course or distance – has been mostly unchanged since at least classical antiquity. Horse races vary widely in format, and many countries have developed their own particular traditions around the sport. Variations include restricting races to particular breeds, running over obstacles, running over different distances, running on different track surfaces, and running in different gaits. In some races, horses are assigned different weights to carry to reflect differences in ability, a process known as handicapping. While horses are sometimes raced purely for sport, a major part of horse racing's interest and economic importance is in the gambling associated w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

