|
PAL-M (television)
PAL-M is the analogue TV system used in Brazil since 19 February 1972. At that time, Brazil was the first South American country to broadcast in colour. Colour TV broadcast began on 19 February 1972, when the TV networks Globo and Bandeirantes transmitted the Caxias do Sul Grape Festival. Transition from black and white to colour, however, was not complete until 1978. Two years later, in 1980, colour broadcast nationwide in Brazil was commonplace. It is unique among analogue TV systems in that it combines the 525-line 30 frames-per-second System M with the PAL colour encoding system (using very nearly the NTSC colour subcarrier frequency), unlike all other countries which pair PAL with 625-line systems and NTSC with 525-line systems. Origins NTSC being the "natural" choice for countries with monochrome standard M, the choice of a different colour system poses problems of incompatibility with available hardware and the need to develop new television sets and production hard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Spectrum
The radio spectrum is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum with frequencies from 0 Hz to 3,000 GHz (3 THz). Electromagnetic waves in this frequency range, called radio waves, are widely used in modern technology, particularly in telecommunication. To prevent interference between different users, the generation and transmission of radio waves is strictly regulated by national laws, coordinated by an international body, the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). Different parts of the radio spectrum are allocated by the ITU for different radio transmission technologies and applications; some 40 radiocommunication services are defined in the ITU's Radio Regulations (RR). In some cases, parts of the radio spectrum are sold or licensed to operators of private radio transmission services (for example, cellular telephone operators or broadcast television stations). Ranges of allocated frequencies are often referred to by their provisioned use (for example, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aiwa
is a consumer electronics brand owned and used by various companies in different regions of the world. American and other regions are owned by Chicago-based Aiwa Corporation. Towada Audio based in Tokyo owns the rights to the brand in Japan and other countries, and has been manufacturing Aiwa-branded products since 2017. In Mexico and other countries in Latin America, the rights are owned by Audio Mobile Americas, S.A. Aiwa was founded in 1951 and was once a globally well-regarded brand known for making quality audio products such as speakers, boomboxes and stereo systems. It was the market leader in several product categories. Aiwa created the first Japanese cassette tape recorder in 1964. The company was listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange from October 1961 until September 2003. The company became unprofitable in the late 1990s, and was fully bought by Sony in 2003. Aiwa was then rebranded as a new youth-focused division of Sony, but it was unsuccessful and the brand was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panasonic
formerly between 1935 and 2008 and the first incarnation of between 2008 and 2022, is a major Japanese multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate corporation, headquartered in Kadoma, Osaka, Kadoma, Osaka Prefecture, Osaka. It was founded by Kōnosuke Matsushita in 1918 as a lightbulb socket manufacturer. In addition to consumer electronics, of which it was the world's largest maker in the late 20th century, Panasonic offers a wide range of products and services, including Rechargeable battery, rechargeable batteries, automotive and avionic systems, industrial systems, as well as home renovation and construction. Panasonic has a primary listing on the Tokyo Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the Nikkei 225 and TOPIX, TOPIX 100 indices. It has a secondary listing on the Nagoya Stock Exchange. Corporate name From 1935 to October 1, 2008, the company's corporate name was "Matsushita Electric Industrial Co." (MEI). On January 10, 2008, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Videocassette Recorder
A videocassette recorder (VCR) or video recorder is an electromechanical device that records analog audio and analog video from broadcast television or other source on a removable, magnetic tape videocassette Videotape is magnetic tape used for storing video and usually sound in addition. Information stored can be in the form of either an analog or digital signal. Videotape is used in both video tape recorders (VTRs) and, more commonly, videocasset ..., and can play back the recording. Use of a VCR to record a television program to play back at a more convenient time is commonly referred to as ''timeshifting''. VCRs can also play back prerecorded tapes. In the 1980s and 1990s, prerecorded videotapes were widely available for purchase and rental, and blank tapes were sold to make recordings. VCRs declined in popularity during the early 2000s and in July 2016, Funai Electric, the last manufacturer of them ceased production. History Early machines and formats The h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog-to-digital Converter
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a digital signal. An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an analog input voltage or current to a digital number representing the magnitude of the voltage or current. Typically the digital output is a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. There are several ADC architectures. Due to the complexity and the need for precisely matched components, all but the most specialized ADCs are implemented as integrated circuits (ICs). These typically take the form of metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) mixed-signal integrated circuit chips that integrate both analog and digital circuits. A digital-to-analog converter (DAC) performs the reverse function; it converts a digital signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Illuminant
A standard illuminant is a theoretical source of visible light with a spectral power distribution that is published. Standard illuminants provide a basis for comparing images or colors recorded under different lighting. CIE illuminants The International Commission on Illumination (usually abbreviated CIE for its French name) is the body responsible for publishing all of the well-known standard illuminants. Each of these is known by a letter or by a letter-number combination. Illuminants A, B, and C were introduced in 1931, with the intention of respectively representing average incandescent light, direct sunlight, and average daylight. Illuminants D represent variations of daylight, illuminant E is the equal-energy illuminant, while illuminants F represent fluorescent lamps of various composition. There are instructions on how to experimentally produce light sources ("standard sources") corresponding to the older illuminants. For the relatively newer ones (such as series D), exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
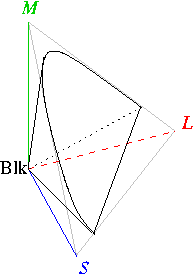
Color Model
A color model is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers, typically as three or four values or color components. When this model is associated with a precise description of how the components are to be interpreted (viewing conditions, etc.), taking account of visual perception, the resulting set of colors is called "color space." This article describes ways in which human color vision can be modeled, and discusses some of the models in common use. Tristimulus color space One can picture this space as a region in three-dimensional Euclidean space if one identifies the ''x'', ''y'', and ''z'' axes with the stimuli for the long-wavelength (''L''), medium-wavelength (''M''), and short-wavelength (''S'') light receptors. The origin, (''S'',''M'',''L'') = (0,0,0), corresponds to black. White has no definite position in this diagram; rather it is defined according to the color temperature or white balance as desired or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Correction
Gamma correction or gamma is a nonlinear operation used to encode and decode luminance or tristimulus values in video or still image systems. Gamma correction is, in the simplest cases, defined by the following power-law expression: : V_\text = A V_\text^\gamma, where the non-negative real input value V_\text is raised to the power \gamma and multiplied by the constant ''A'' to get the output value V_\text. In the common case of , inputs and outputs are typically in the range 0–1. A gamma value \gamma 1 is called a ''decoding gamma'', and the application of the expansive power-law nonlinearity is called gamma expansion. Explanation Gamma encoding of images is used to optimize the usage of bits when encoding an image, or bandwidth used to transport an image, by taking advantage of the non-linear manner in which humans perceive light and color. The human perception of brightness ( lightness), under common illumination conditions (neither pitch black nor blindingly bright), fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
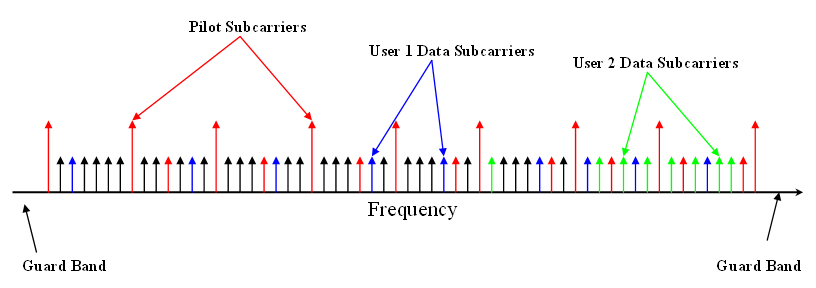
Subcarrier
A subcarrier is a sideband of a radio frequency carrier wave, which is modulated to send additional information. Examples include the provision of colour in a black and white television system or the provision of stereo in a monophonic radio broadcast. There is no physical difference between a carrier and a subcarrier; the "sub" implies that it has been derived from a carrier, which has been amplitude modulated by a steady signal and has a constant frequency relation to it. FM stereo Stereo broadcasting is made possible by using a subcarrier on FM radio stations, which takes the left channel and "subtracts" the right channel from it — essentially by hooking up the right-channel wires backward (reversing polarity) and then joining left and reversed-right. The result is modulated with suppressed carrier AM, more correctly called sum and difference modulation or SDM, at 38 kHz in the FM signal, which is joined at 2% modulation with the mono left+right audio (which ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Bandwidth
In broadcast television systems, VF bandwidth, video bandwidth or more formally video frequency bandwidth is the range of frequencies between 0 and the highest frequency used to transmit a live television image. The maximum frequency can be found by multiplying three figures; the number of frames (images) per second, number of lines Line most often refers to: * Line (geometry), object with zero thickness and curvature that stretches to infinity * Telephone line, a single-user circuit on a telephone communication system Line, lines, The Line, or LINE may also refer to: Arts ... per frame and maximum number of sine periods per line. In the table below number of frames per second, number of lines per frame and the video band width in different systems are shown.''Reference Data for Radio Engineers'', Howard W.Sams Co., Inc, , sec. 30, p. 33 References {{Analogue TV transmitter topics Television technology Video formats History of television ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandwidth (signal Processing)
Bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower frequencies in a continuous band of frequencies. It is typically measured in hertz, and depending on context, may specifically refer to ''passband bandwidth'' or ''baseband bandwidth''. Passband bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower cutoff frequencies of, for example, a band-pass filter, a communication channel, or a signal spectrum. Baseband bandwidth applies to a low-pass filter or baseband signal; the bandwidth is equal to its upper cutoff frequency. Bandwidth in hertz is a central concept in many fields, including electronics, information theory, digital communications, radio communications, signal processing, and spectroscopy and is one of the determinants of the capacity of a given communication channel. A key characteristic of bandwidth is that any band of a given width can carry the same amount of information, regardless of where that band is located in the frequency spectrum. For example, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)