|
Oscar Scherer State Park
Oscar Scherer State Park is a Florida State Park located between Sarasota and Venice, near Osprey. The address is 1843 South Tamiami Trail. There are more than 250,000 visitors a year. History The park's genesis was in 1955, when Elsa Scherer Burrows, owner of the South Creek Ranch, died. Her will left the ranch to the state to form a park. It was to be dedicated to the memory of her father, Oscar Scherer, who had, in 1872, developed a shoe leather dyeing process. A year later, the park was ready and opened to visitors. Thirty years after that, realtor and environmentalist Jon Thaxton started work to protect the neighboring Florida scrub jay territory. In 1992 this resulted in being added from the adjacent Palmer Ranch that had been among the holdings of Bertha Honoré Palmer, in large part due to the Nature Conservancy, public support, and the use of Preservation 2000 funds, expanding the park's size to . In September 2008, in recognition of National Public Lands Day, Lee W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarasota County, Florida
Sarasota County is a county located in Southwest Florida. At the 2020 US census, the population was 434,006. Its county seat is Sarasota and its largest city is North Port. Sarasota County is part of the North Port–Sarasota–Bradenton, FL metropolitan statistical area. History The area that is now known as Sarasota County has been inhabited by humans for some 10,000 years. Evidence of human remains as well as a burned out log at the Warm Mineral Springs, in North Port, were discovered that date to the early Archaic period. Although the name was associated with the area from the beginning of European contacts, the origin of the name "Sarasota" is unknown. Some believe a fanciful story created for a popular early twentieth-century pageant held in Sarasota, that it was named after the daughter of famous explorer Hernando de Soto's daughter Sara. An early map of the area from 1763 shows the word "Zarazote" across present day Sarasota. Following exploration, the area w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preservation 2000
Florida Forever is a land conservation program in Florida. In 1999, the Florida Legislature passed the Florida Forever Act which was signed into law by Florida governor Jeb Bush, which would lead to the creation of the Florida Forever program. Since the program was created in July 2001, the state of Florida has purchased more than 818,616 acres of land with a little over $3.1 billion (as of July 2020). Approximately 2.5 million acres have been purchased under the program and its predecessor, Preservation 2000 (P2000). Florida Department of Environmental Protection According to one 2011 poll
Poll, polled, or polling may refer to:
Figurative head counts
* Poll, a formal electi ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acrostichum
''Acrostichum'' is a fern genus in the Parkerioideae subfamily of the Pteridaceae. It was one of the original pteridophyte genera delineated by Linnaeus. It was originally drawn very broadly, including all ferns that had sori apparently "acrostichoid", or distributed in a uniform mass across the back of the frond, rather than organized in discrete sori. This led Linnaeus to include such species as ''Asplenium platyneuron'' in the genus, because the specimen he received had sori so crowded that it appeared acrostichoid. Since '' Acrostichum aureum'' is regarded as the type for the genus, it is now narrowly circumscribed only to the natural genus of three species, that are allied to the genus '' Ceratopteris''. They are collectively known as the leather ferns or leather swamp ferns, genus members commonly being found in swamps. The species of ''Acrostichum'' are massive ferns, with fronds up to 12 feet (3.5 meters) tall, that depend on a semi-aquatic existence. They do not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florida Mangroves
The Florida mangroves ecoregion, of the mangrove forest biome, comprise an ecosystem along the coasts of the Florida peninsula, and the Florida Keys. Four major species of mangrove populate the region: red mangrove, black mangrove, white mangrove, and the buttonwood. The mangroves live in the coastal zones in the more tropical southern parts of Florida; mangroves are particularly vulnerable to frosts. Mangroves are important habitat as both fish nursery and brackish water habitats for birds and other coastal species. Though climate change is expected to extend the mangrove range further north, sea level rise, extreme weather and other changes related to climate change may endanger existing mangrove populations. Other threats include development and other human disruption. Florida's mangrove species The Florida mangroves ecoregion includes three mangrove species: * ''Rhizophora mangle'' — red mangrove Red mangroves are characterized by a dendritic network of aerial prop roots e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
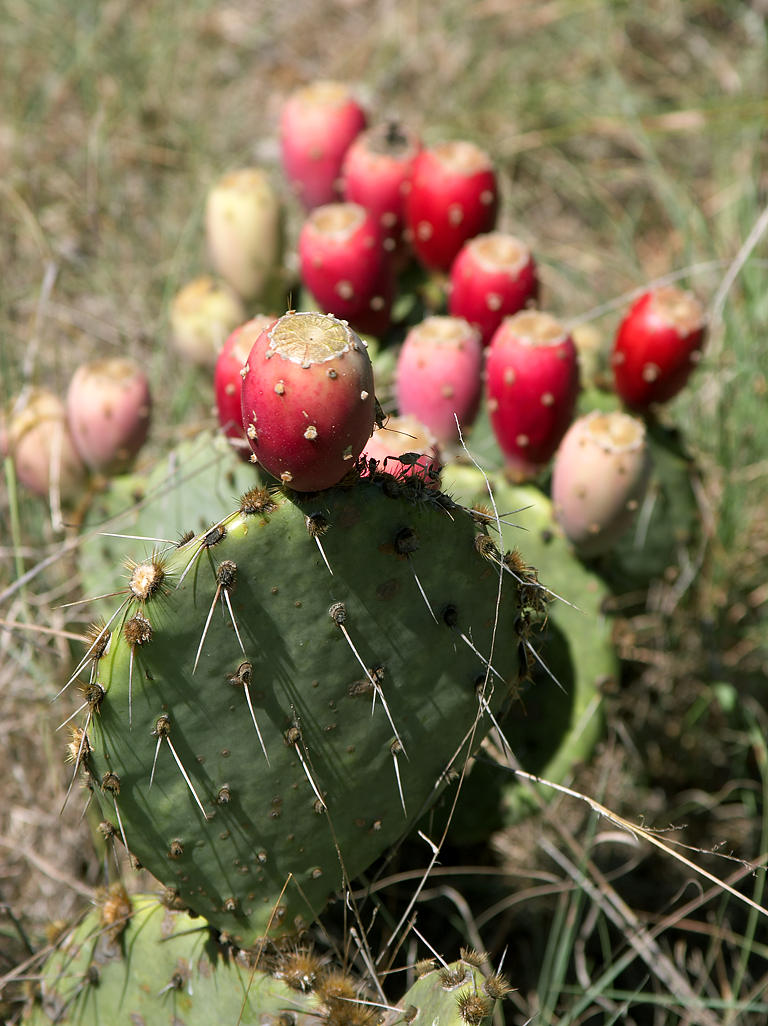
Opuntia
''Opuntia'', commonly called prickly pear or pear cactus, is a genus of flowering plants in the cactus family Cactaceae. Prickly pears are also known as ''tuna'' (fruit), ''sabra'', ''nopal'' (paddle, plural ''nopales'') from the Nahuatl word for the pads, or nostle, from the Nahuatl word for the fruit; or paddle cactus. The genus is named for the Ancient Greek city of Opus, where, according to Theophrastus, an edible plant grew and could be propagated by rooting its leaves. The most common culinary species is the Indian fig opuntia (''O. ficus-indica''). Description ''O. ficus-indica'' is a large, trunk-forming, segmented cactus that may grow to with a crown of over in diameter and a trunk diameter of . Cladodes (large pads) are green to blue-green, bearing few spines up to or may be spineless. Prickly pears typically grow with flat, rounded cladodes (also called platyclades) containing large, smooth, fixed spines and small, hairlike prickles called glochids that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myrica Cerifera
''Myrica cerifera'' is a small evergreen tree or large shrub native to North and Central America and the Caribbean. Its common names include southern wax myrtle, southern bayberry, candleberry, bayberry tree, and tallow shrub. It sees uses both in the garden and for candlemaking, as well as a medicinal plant. Description ''Myrica cerifera'' is a small tree or large shrub, reaching up to 14m tall. It is adaptable to many habitats, growing naturally in wetlands, near rivers and streams, sand dunes, fields, hillsides, pine barrens, and in both coniferous and mixed-broadleaf forests. ''M. cerifera'' can weather coastal storms, long droughts, and tropical high temperatures. In nature, it ranges from Central America, northward into the southeastern and south-central United States. Wax Myrtle can be successfully cultivated as far north as the New York City area and southern Ohio Valley. It also grows in Bermuda and the Caribbean. In terms of succession, ''M. cerifera'' is often one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zamia Integrifolia
''Zamia integrifolia'', also known as coontie palm is a small, tough, woody cycad native to the southeastern United States (in Florida and Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia), the Bahamas, Cuba, and the Cayman Islands. Description ''Zamia integrifolia'' produces reddish seed Conifer cone, cones with a distinct acuminate tip. The leaf, leaves are 20–100 cm long, with 5-30 pairs of leaflets (pinnae). Each leaflet is linear to lanceolate or oblong-obovate, 8–25 cm long and 0.5–2 cm broad, entire or with indistinct teeth at the tip. They are often revolute, with prickly petioles. It is similar in many respects to the closely related ''Zamia pumila'', but that species differs in the more obvious toothing on the leaflets. This is a low-growing plant, with a trunk that grows to 3–25 cm high, but is often subterranean. Over time, it forms a multi-branched cluster, with a large, tuberous root system, which is actually an extension of the above-ground stems. The le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabal Palmetto
''Sabal palmetto'' (, '' SAY-bəl''), also known as cabbage palm, cabbage palmetto, sabal palm, blue palmetto, Carolina palmetto, common palmetto, Garfield's tree, and swamp cabbage, is one of 15 species of palmetto palm. It is native to the Southern United States and the West Indies. Description ''Sabal palmetto'' grows up to tall. Starting at half to two-thirds the height, the tree develops into a rounded, costapalmate fan of numerous leaflets. A costapalmate leaf has a definite costa (midrib) unlike the typical palmate or fan leaf, but the leaflets are arranged radially like in a palmate leaf. All costapalmate leaves are about across, produced in large compound panicles up to in radius, extending out beyond the leaves. The fruit is a black drupe about long containing a single seed. It is extremely salt-tolerant and is often seen growing near both the Atlantic Ocean coast and the Gulf of Mexico coast. Sabal palmetto00.jpg, ''Sabal palmetto'' from Carl Friedrich Philipp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wild Grape
Wild grape may refer to: * ''Vitis'' species; specially Vitis vinifera, ''Vitis vinifera'' subsp. ''sylvestris'' (the wild ancestor of ''Vitis vinifera''), ''Vitis californica'' (California wild grape), ''Vitis girdiana'' (desert wild grape), and ''Vitis riparia'' * ''Ampelocissus acetosa'', also known as Djabaru * ''Ampelopsis glandulosa'', also known as porcelain berry * ''Cyphostemma juttae'', a slow-growing ornamental plant. ReferencesWild grape at Integrated Taxonomic Information System {{plant common name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diospyros Virginiana
''Diospyros virginiana'' is a persimmon species commonly called the American persimmon, common persimmon, eastern persimmon, simmon, possumwood, possum apples, or sugar plum. It ranges from southern Connecticut to Florida, and west to Texas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, Kansas, and Iowa. The tree grows wild but has been cultivated for its fruit and wood since prehistoric times by Native Americans. ''Diospyros virginiana'' grows to , in well-drained soil. The tree is typically dioecious, so one must have both male and female plants to obtain fruit. Most cultivars are parthenocarpic (setting seedless fruit without pollination). The fragrant flowers are pollinated by insects and wind. Fruiting typically begins when the tree is about 6 years old. The fruit is round or oval and usually orange-yellow, sometimes bluish, and from in diameter. Both the tree and the fruit are referred to as persimmons, with the latter appearing in desserts and cuisine in the U.S. South and Midwest. Commerc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
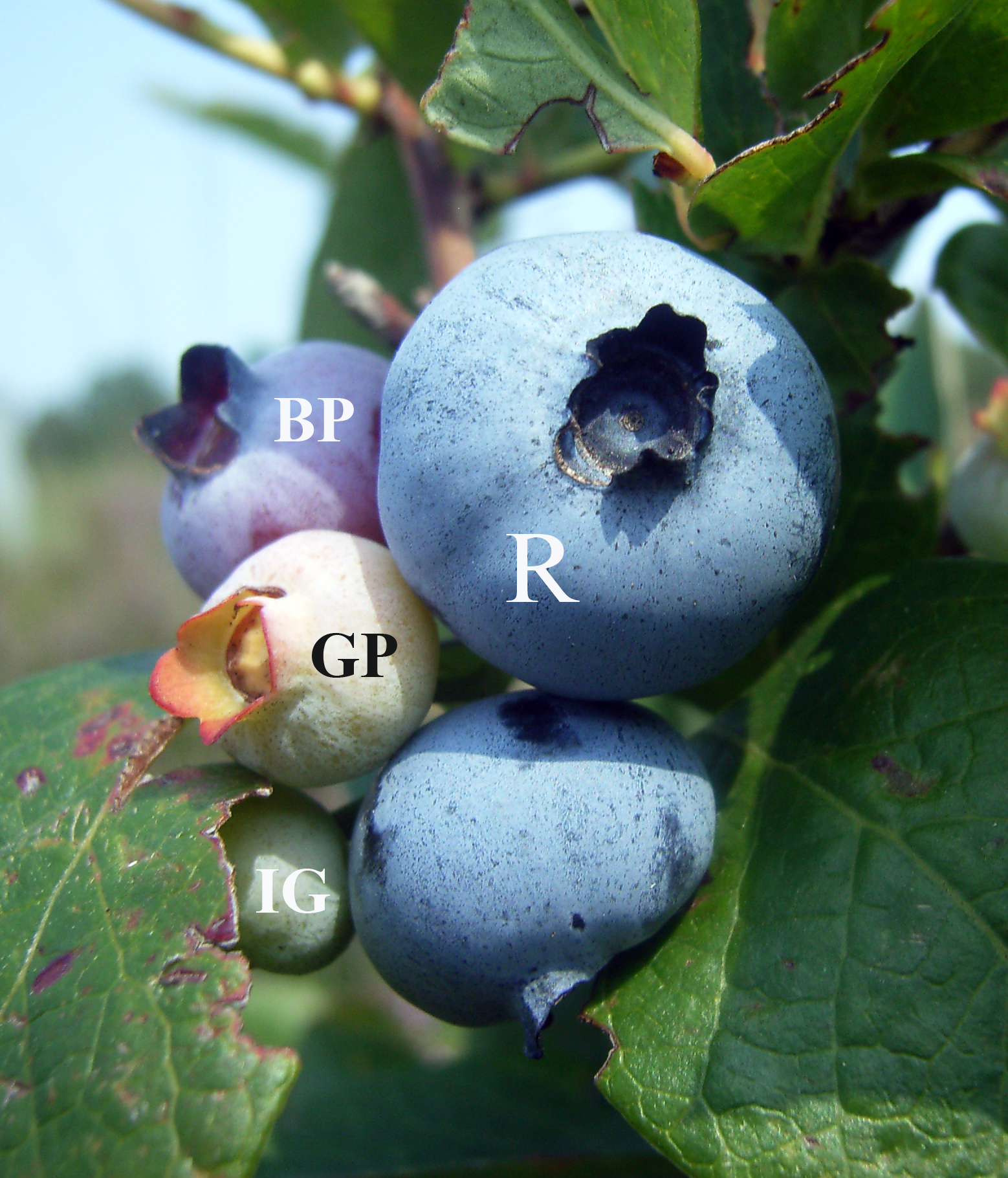
Blueberry
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' within the genus ''Vaccinium''. ''Vaccinium'' also includes cranberries, bilberries, huckleberries and Madeira blueberries. Commercial blueberries—both wild (lowbush) and cultivated (highbush)—are all native to North America. The highbush varieties were introduced into Europe during the 1930s. Blueberries are usually prostrate shrubs that can vary in size from to in height. In commercial production of blueberries, the species with small, pea-size berries growing on low-level bushes are known as "lowbush blueberries" (synonymous with "wild"), while the species with larger berries growing on taller, cultivated bushes are known as "highbush blueberries". Canada is the leading producer of lowbush blueberries, while the United States produces some 40% of the world supply of highbush blueberries. Origin and h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hammock (ecology)
Hammock is a term used in the southeastern United States for stands of trees, usually hardwood, that form an ecological island in a contrasting ecosystem. Hammocks grow on elevated areas, often just a few inches high, surrounded by wetlands that are too wet to support them. The term ''hammock'' is also applied to stands of hardwood trees growing on slopes between wetlands and drier uplands supporting a mixed or coniferous forest. Types of hammocks found in the United States include tropical hardwood hammocks, temperate hardwood hammocks, and maritime or coastal hammocks. Hammocks are also often classified as hydric (wet soil), mesic (moist soil) or xeric (dry soil). The types are not exclusive, but often grade into each other. Unlike many ecosystems of the coastal plain of the southeastern United States, hammocks are not tolerant of fire. Hammocks tend to occur in locations where fire is not common, or where there is some protection from fire in neighboring ecosystems. Hammocks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(7270558948).jpg)