|
Orvin Paz
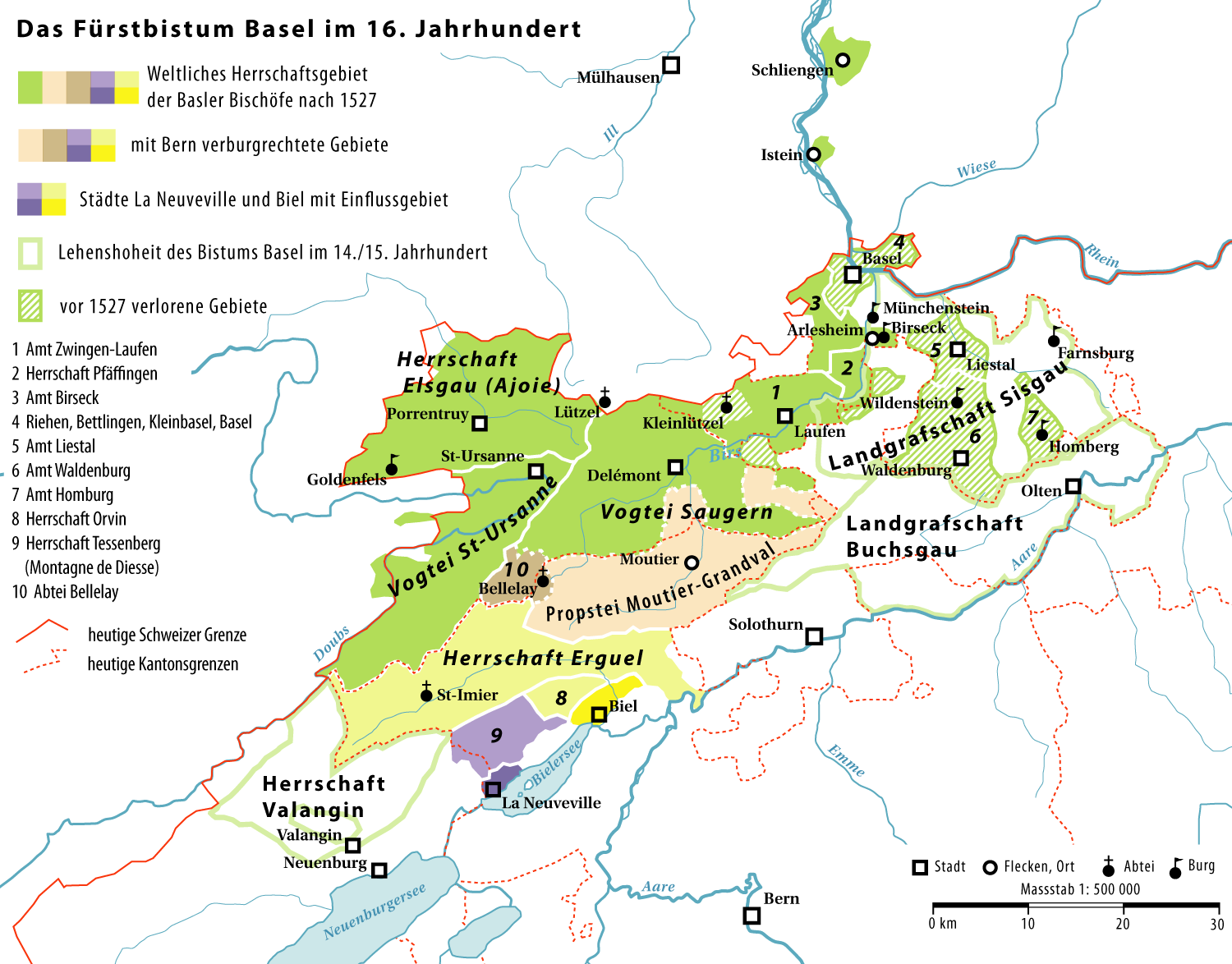
Orvin is a municipality in the Jura bernois administrative district in the canton of Bern in Switzerland. It is located in the French-speaking Bernese Jura (''Jura Bernois''). Above it, there is a small year round resort, called les " Prés-d'Orvin". History Orvin is first mentioned in 866 as ''Ulvinc''. In 999 King Rudolph III of Burgundy gave Moutier-Grandval Abbey and its lands, including Orvin, to the Prince-Bishop of Basel. The village remained under the Bishop's direct control until 1295, when the Lords of Orvin received the village as a fief. They held the village until the end of the 14th century, after which it passed to the d'Orsans family and then the Lords of Rondchâtel. After the Rondchâtel line died out, the village returned to the Bishop's control who placed it under the ecclesiastical vogt of Biel. The first town charter of 1352 was expanded and revised in 1643 and confirmed by the Bishop in 1668. It remained in effect until the end of the Ancien R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jura Bernois (administrative District)
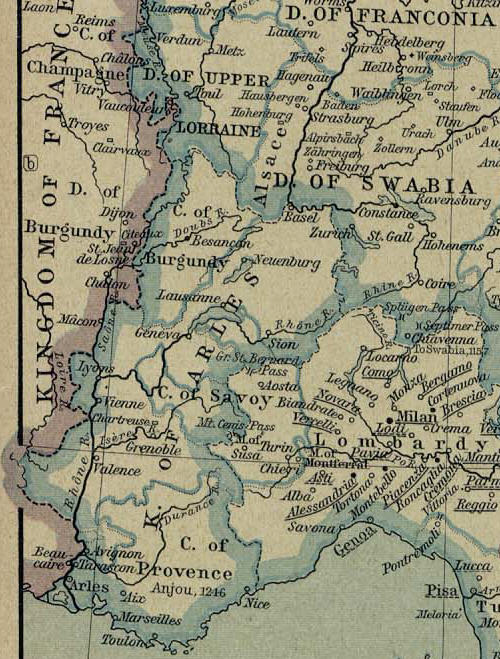
Bernese Jura (french: Jura bernois, ) is the name for the French-speaking area of the Swiss canton of Bern, and from 2010 one of ten administrative divisions of the canton. Comprising the three French-speaking districts in the northern part of the canton, it contains 40 municipalities with an area of and a population () of . More than 90% of the population of the three districts speak French. The Bernese Jura of today comprises only three out of a total of seven districts which were known as the Bernese Jura during the period of 1815–1979. Of the remaining four, three seceded as the canton of Jura in 1979, while the fourth, the Laufen district, joined the canton of Basel-Landschaft in 1994. Additionally, Moutier, a municipality, voted to secede from Bern in a referendum in 2021 and join Jura, with the changeover expected to be implemented by 2026. History Most of the territory of the Bernese Jura was passed from the County of Burgundy to the Bishopric of Basel in AD 9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudolph III Of Burgundy
Rudolph III (french: Rodolphe, german: Rudolf; – 6 September 1032), called the Idle or the Pious, was the king of Burgundy from 993 until his death. He was the last ruler of an independent Kingdom of Burgundy, and the last male member of the Burgundian group of the Elder House of Welf. Family Rudolph was the son and heir of King Conrad I of Burgundy (925–993). His mother Matilda (943–980), a member of the Frankish Carolingian dynasty, was the daughter of King Louis IV of France. Rudolph himself had three sisters: Gerberga, who married Duke Herman II of Swabia about 988, Bertha, married to Count Odo I of Blois and secondly to King Robert II of France in 996, and Gisela, who married the Ottonian duke Henry II of Bavaria and became the mother of Emperor Henry II. Reign Rudolph succeeded to the Burgundian throne upon his father's death on 19 October 993 and was crowned king in Lausanne. His reign was marked with turbulence when he made attempts to confiscate several Burgun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campaigns Of 1797 In The French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars continued from 1796, with France fighting the First Coalition. On 14 February, British admiral Jervis met and defeated a Spanish fleet off Portugal at the Battle of Cape St. Vincent. This prevented the Spanish fleet from rendezvousing with the French, removing a threat of invasion to Britain. However, the British fleet was weakened over the rest of the year by the Spithead and Nore mutinies, which kept many ships in port through the summer. On 22 February, a French invasion force consisting of 1,400 troops from the ''Légion Noire'' (The Black Legion) under the command of Irish American Colonel William Tate landed near Fishguard (Wales). They were met by a quickly assembled group of around 500 British reservists, militia and sailors under the command of John Campbell, 1st Baron Cawdor. After brief clashes with the local civilian population and Lord Cawdor's forces on 23 February, Tate was forced into an unconditional surrender by 24 February. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in particular to papal authority, arising from what were perceived to be errors, abuses, and discrepancies by the Catholic Church. The Reformation was the start of Protestantism and the split of the Western Church into Protestantism and what is now the Roman Catholic Church. It is also considered to be one of the events that signified the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the early modern period in Europe.Davies ''Europe'' pp. 291–293 Prior to Martin Luther, there were many earlier reform movements. Although the Reformation is usually considered to have started with the publication of the '' Ninety-five Theses'' by Martin Luther in 1517, he was not excommunicated by Pope Leo X until January 1521. The Diet of Worms of May 1521 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque Architecture
Baroque architecture is a highly decorative and theatrical style which appeared in Italy in the early 17th century and gradually spread across Europe. It was originally introduced by the Catholic Church, particularly by the Jesuits, as a means to combat the Reformation and the Protestant church with a new architecture that inspired surprise and awe. It reached its peak in the High Baroque (1625–1675), when it was used in churches and palaces in Italy, Spain, Portugal, France, Bavaria and Austria. In the Late Baroque period (1675–1750), it reached as far as Russia and the Spanish and Portuguese colonies in Latin America. About 1730, an even more elaborately decorative variant called Rococo appeared and flourished in Central Europe. Baroque architects took the basic elements of Renaissance architecture, including domes and colonnades, and made them higher, grander, more decorated, and more dramatic. The interior effects were often achieved with the use of ''quadratura'', or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Architecture
Gothic architecture (or pointed architecture) is an architectural style that was prevalent in Europe from the late 12th to the 16th century, during the High and Late Middle Ages, surviving into the 17th and 18th centuries in some areas. It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was succeeded by Renaissance architecture. It originated in the Île-de-France and Picardy regions of northern France. The style at the time was sometimes known as ''opus Francigenum'' (lit. French work); the term ''Gothic'' was first applied contemptuously during the later Renaissance, by those ambitious to revive the architecture of classical antiquity. The defining design element of Gothic architecture is the pointed or ogival arch. The use of the pointed arch in turn led to the development of the pointed rib vault and flying buttresses, combined with elaborate tracery and stained glass windows. At the Abbey of Saint-Denis, near Paris, the choir was reconstructed between 1140 and 1144, draw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Lausanne
The Bishop of Lausanne (French: ''Évêque de Lausanne'') was a Prince-Bishop of the Holy Roman Empire (since 1011) and the Ordinary of the diocese of Lausanne, Switzerland (Latin: ''Dioecesis Lausannensis''). Bern secularized the bishopric in 1536. The bishop fled into exile, first in Evian, and then in Burgundy. Today, the Catholic diocese of Fribourg, Lausanne, and Geneva has its seat in Fribourg. :For the ecclesiastical history, see Lausanne and Geneva bishopric(s) List of bishops Bishop of Avenches * Bubulcus (517-535) * Grammatius (535-549) Bishop of Lausanne 574-1536 * Saint Marius (574-594) * Arricus 639-654 * Prothasius 652 * Chilmegiselus 670 * Udalricus 690 * Fredarius 814-825 *David 827-850 * Hartmannus 852-878 *Hieronimus 878-892 * Boso 892-927 * Libo 927-932 * Bero 932-947 * Magnerius 947-968 * Eginolfus 968-985 *Henri of Bourgogne 985-1018 *Hugues of Bourgogne 1018-1037 * Henri II of Lenzbourg 1039-1051/56 * Burchard of Oltingen 1056-1089 *Lambert of Grand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erguel
Erguël is an medieval seigniory of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Basel, and under protectorate of Biel/Bienne, under military jurisdiction from 1335, in the now called valley of St.-Imier, in the now Bernese Jura, Switzerland. The Sire of the area used to live in the Château d'Erguel. History In 1264, the Bishop of Basel appointed Otto of Erguel as the vogt over the Saint-Imier valley fief. Otto raised the valley to become a seigniory and parish of the Diocese of Basel, named Erguel. accessed 29 January 2011 Asteroid Asteroid ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feudal Levies
Conscription (also called the draft in the United States) is the state-mandated enlistment of people in a national service, mainly a military service. Conscription dates back to antiquity and it continues in some countries to the present day under various names. The modern system of near-universal national conscription for young men dates to the French Revolution in the 1790s, where it became the basis of a very large and powerful military. Most European nations later copied the system in peacetime, so that men at a certain age would serve 1–8 years on active duty and then transfer to the reserve force. Conscription is controversial for a range of reasons, including conscientious objection to military engagements on religious or philosophical grounds; political objection, for example to service for a disliked government or unpopular war; sexism, in that historically men have been subject to the draft in the most cases; and ideological objection, for example, to a perceived vio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Modern Switzerland
The early modern history of the Old Swiss Confederacy (''Eidgenossenschaft'', also known as the "Swiss Republic" or ''Republica Helvetiorum'') and its constituent Thirteen Cantons encompasses the time of the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) until the French invasion of 1798. The early modern period was characterized by an increasingly aristocratic and oligarchic ruling class as well as frequent economic or religious revolts. This period came to be referred to as the ''Ancien Régime'' retrospectively, in post-Napoleonic Switzerland. The loosely organized Confederation remained generally disorganized and crippled by the religious divisions created by the Swiss Reformation. During this period the Confederation gained formal independence from the Holy Roman Empire with support from France, and had very close relations with France. The early modern period also saw the growth of French-Swiss literature, and notable authors of the Age of Enlightenment such as the mathematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Town Charter
A city charter or town charter (generically, municipal charter) is a legal document (''charter'') establishing a municipality such as a city or town. The concept developed in Europe during the Middle Ages. Traditionally the granting of a charter gave a settlement and its inhabitants the right to town privileges under the feudal system. Townspeople who lived in chartered towns were burghers, as opposed to serfs who lived in villages. Towns were often " free", in the sense that they were directly protected by the king or emperor, and were not part of a feudal fief. Today the process for granting is determined by the type of government of the state in question. In monarchies, charters are still often a royal charter given by the Crown or the authorities acting on behalf of the Crown. In federations, the granting of charters may be within the jurisdiction of the lower level of government such as a province. Canada In Canada charters are granted by provincial authorities. Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vogt
During the Middle Ages, an (sometimes given as modern English: advocate; German: ; French: ) was an office-holder who was legally delegated to perform some of the secular responsibilities of a major feudal lord, or for an institution such as an abbey. Many such positions developed, especially in the Holy Roman Empire. Typically, these evolved to include responsibility for aspects of the daily management of agricultural lands, villages and cities. In some regions, advocates were governors of large provinces, sometimes distinguished by terms such as (in German). While the term was eventually used to refer to many types of governorship and advocacy, one of the earliest and most important types of was the church advocate (). These were originally lay lords, who not only helped defend religious institutions in the secular world, but were also responsible for exercising lordly responsibilities within the church's lands, such as the handling of legal cases which might require the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

.jpg)


