|
Orvet
Anguidae refers to a large and diverse family of lizards native to the Northern Hemisphere. Common characteristics of this group include a reduced supratemporal arch, striations on the medial faces of tooth crowns, osteoderms, and a lateral fold in the skin of most taxa. The group includes the slowworms, glass lizards, and alligator lizards, among others. The family is divided into two subfamilies (Anguinae and Gerrhonotinae), and contains about 87 species in 8 genera. Morphology and reproduction Anguids have hard osteoderms beneath their scales giving them an armored appearance. Many of the species have reduced or absent limbs, giving them a snake-like appearance, while others are fully limbed. Body type varies among species, with sizes ranging from 10 cm to 1.5 m. The group includes oviparous and viviparous species, both of which can be observed in a single genus at times. Feeding and habitat These lizards are known carnivorous or insectivorous foragers, feed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anguis Fragilis
The slow worm (''Anguis fragilis'') is a reptile native to western Eurasia. It is also called a deaf adder, a slowworm, a blindworm, or regionally, a long-cripple and hazelworm. These legless lizards are also sometimes called common slowworms. The "blind" in blindworm refers to the lizard's small eyes, similar to a blindsnake (although the slowworm's eyes are functional). Slow worms are semifossorial (burrowing) lizards, spending much of their time hiding underneath objects. The skin of slow worms is smooth with scales that do not overlap one another. Like many other lizards, they autotomize, meaning that they have the ability to shed their tails to escape predators. While the tail regrows, it does not reach its original length. In the UK, they are common in gardens and allotments, and can be encouraged to enter and help remove pest insects by placing black plastic or providing places to shelter such as piles of logs, corrugated iron sheets or under tiles. On warm days, one or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helodermoides Tuberculatus
''Helodermoides'' is an extinct genus of anguid lizards from the Oligocene of North America. The genus is monotypic, including only the species ''Helodermoides tuberculatus''. ''Helodermoides'' belongs to an extinct subfamily of anguids called Glyptosaurinae. In addition to many fragmentary bones, several complete skeletons of ''Helodermoides'' are known. Like other glyptosaurines, ''Helodermoides'' was covered in small scale-like bones called osteoderms. The osteoderms covering its skull are hexagonal, tightly interlocking, raised, and rounded. One fossil of ''Helodermoides'' preserves a fused mass of osteoderms at the tip of a shortened tail, thought to represent healing after the end of the tail fell off. The tail would not have been able to grow back because the osteoderms formed a thick bony cap preventing growth. The ability to lose a tail, called autotomy, is also present in living anguid Anguidae refers to a large and diverse family of lizards native to the Northern Hem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elgaria
''Elgaria'' is a genus of New World lizards in the family Anguidae. Their common name is western alligator lizards. Geographic range Species in the genus ''Elgaria'' are distributed in western North America, from Mexico to Canada. Species There are seven species: ''Nota bene'': A binomial authority In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bot ... in parentheses indicates that the species was originally described in a genus other than ''Elgaria''. References Further reading * Gray JE (1838). Catalogue of the Slender-tongued Saurians, with Descriptions of many new Genera and Species. ''Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist., First Series'' 1: 274–283, 388–394. (''Elgaria'', new genus, p. 390). *Gray JE (1845). ''Catalogue of the Specimens of Lizards in the Collection of the British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abronia (animal)
''Abronia'' is a genus of lizards in the family Anguidae. The genus is native to northern Central America, occurring mainly in Guatemala and Mexico. However, there are species that occur as far south as El Salvador and Honduras, for example, '' A. montercristoi''. ''Abronia'' species are almost exclusively arboreal. These lizards possess intriguing physical traits such as keeled body scales, patterns on each individual scale, and some, for example, '' A. lythrochila'', even have spikes on the back of the head. Traits vary from species to species. Species These species are recognized as being valid:''Abronia'' The Reptile Database. Consulted: 2012-04-06. *'' |
Barisia
''Barisia'' is a genus of lizards in the family Anguidae. The genus is endemic to Mexico. Species The following species are recognized as being valid."''Barisia'' ". The Reptile Database. www.reptile-database.org. http://reptile-database.reptarium.cz/advanced_search?genus=Barisia&submit=Search *'' Barisia ciliaris'' – Sierra alligator lizard, imbricate alligator lizard *'' Barisia herrerae'' – Herrera's alligator lizard *'' Barisia imbricata'' – imbricate alligator lizard, transvolcanic alligator lizard *'' Barisia jonesi'' – imbricate alligator lizard *''Barisia levicollis'' – Chihuahuan alligator lizard *'' Barisia planifrons'' – Oaxaca alligator lizard *'' Barisia rudicollis'' – rough-necked alligator lizard ''Nota bene'': A binomial authority In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudopus
''Pseudopus'' is a genus of anguid lizards that are native to Eurasia. One extant species remains, the sheltopusik, with four fossil species. They are the most robust members of subfamily Anguinae. The oldest fossils of the group date to the Early Miocene, but there are possible Oligocene records. Classification Genus ''Pseudopus'' *''Pseudopus apodus ''Pseudopus'' is a genus of anguid lizards that are native to Eurasia. One extant species remains, the sheltopusik, with four fossil species. They are the most robust members of subfamily Anguinae. The oldest fossils of the group date to the Earl ...'' – sheltopusik, Pallas's glass lizard, European legless lizard, European glass lizard *†''Pseudopus ahnikoviensis'' *†''Pseudopus laurillardi'' *†''Pseudopus pannonicus'' *†''Pseudopus rugosus'' References Anguids Lizards of Asia Lizards of Europe Lizard genera Reptile genera with one living species Taxa named by Blasius Merrem {{Lizard-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophisaurus
''Ophisaurus'' (from the Greek 'snake-lizard') is a genus of superficially snake-like lizards in the family Anguidae. Known as joint snakes, glass snakes, or glass lizards, they are so-named because their tails are easily broken; like many lizards, they have the ability to deter predation by dropping off part of the tail, which can break into several pieces, like glass. The tail remains mobile, distracting the predator, while the lizard becomes motionless, allowing eventual escape. This serious loss of body mass requires a considerable effort to replace, and can take years to do so. Despite this ability, the new tail is usually smaller than the original. Although most species have no legs, their head shapes, movable eyelids, and external ear openings identify them as lizards. A few species have very small, stub-like legs near their rear vents. These are vestigial organs, meaning they once served an evolved purpose but are no longer used. They reach lengths of up to , but about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopasia
''Dopasia'' is a genus of lizards in the family Anguidae. The genus contains seven species, which are native to Asia. They are most closely related to the North American ''Ophisaurus'', and are sometimes considered part of that genus. Species The following species are recognized as being valid. *'' Dopasia buettikoferi'' – Buettikofer's glass lizard *'' Dopasia gracilis'' – Burmese glass lizard, Asian glass lizard, Indian glass snake *'' Dopasia hainanensis'' – Hainan glass lizard *'' Dopasia harti'' – Hart's glass lizard *'' Dopasia ludovici'' – Ludovic's glass lizard *'' Dopasia sokolovi'' – Sokolov's glass lizard *'' Dopasia wegneri'' – Wegner's glass lizard ''Nota bene'': A binomial authority In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bot ... in parenth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
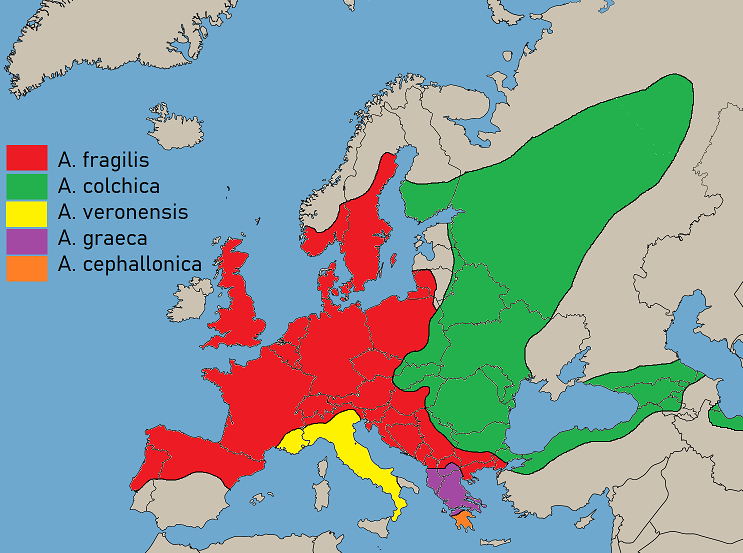
Anguis
SlowwormsThe "slow-" in slowworm is distinct from the English adjective ''slow'' ("not fast"); the word comes from Old English ''slāwyrm'', where ''slā-'' means "slowworm" and ''wyrm'' means "serpent, reptile". () (also called blindworms and hazelworms) are a small genus (''Anguis'') of snake-like legless lizards in the family Anguidae. The genus has several living species, including the common slowworm, the eastern slowworm, the Greek slowworm, the Peloponnese slowworm, and the Italian slowworm (''Anguis veronensis''). There are also known fossil species. Description Slowworms are typically grey-brown, with the females having a coppery sheen and two lateral black stripes, and the males displaying electric blue spots, particularly in the breeding season. They give birth to live young, which are about long at birth and generally have golden stripes. Slowworms are slow-moving and can be easily caught, which has given rise to the folk etymology that the "slow" in slowworm is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anguidae Phylogeny PDF
Anguidae refers to a large and diverse family of lizards native to the Northern Hemisphere. Common characteristics of this group include a reduced supratemporal arch, striations on the medial faces of tooth crowns, osteoderms, and a lateral fold in the skin of most taxa. The group includes the slowworms, glass lizards, and alligator lizards, among others. The family is divided into two subfamilies (Anguinae and Gerrhonotinae), and contains about 87 species in 8 genera. Morphology and reproduction Anguids have hard osteoderms beneath their scales giving them an armored appearance. Many of the species have reduced or absent limbs, giving them a snake-like appearance, while others are fully limbed. Body type varies among species, with sizes ranging from 10 cm to 1.5 m. The group includes oviparous and viviparous species, both of which can be observed in a single genus at times. Feeding and habitat These lizards are known carnivorous or insectivorous foragers, feeding p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campanian spans the time from 83.6 (± 0.2) to 72.1 (± 0.2) million years ago. It is preceded by the Santonian and it is followed by the Maastrichtian. The Campanian was an age when a worldwide sea level rise covered many coastal areas. The morphology of some of these areas has been preserved: it is an unconformity beneath a cover of marine sedimentary rocks. Etymology The Campanian was introduced in scientific literature by Henri Coquand in 1857. It is named after the French village of Champagne in the department of Charente-Maritime. The original type locality was a series of outcrop near the village of Aubeterre-sur-Dronne in the same region. Definition The base of the Campanian Stage is defined as a place in the stratigraphic column wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(3427292877).jpg)

