|
Ortner's Syndrome
Ortner's syndrome is a rare cardiovocal syndrome and refers to recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy from cardiovascular disease. It was first described by Norbert Ortner (1865–1935), an Austrian physician, in 1897. Dysphagia caused by a similar mechanism is referred to as dysphagia aortica (also called Dysphagia megalatriensis), or, in the case of subclavian artery aberrancy, as dysphagia lusoria. Due to compression of the recurrent laryngeal nerve, it can cause the hoarseness of the voice, which can also be a sign of mitral stenosis. A second Ortner's syndrome, Ortner's syndrome II, refers to abdominal angina. Causes Due to its low frequency of occurrence, more common causes of hoarseness should be considered when suspecting left recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy (LRLN). When considering cardiovocal syndrome, the most common historical cause is a dilated left atrium due to mitral stenosis, but other causes, including pulmonary hypertension, thoracic aortic aneurysms, an enlarge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagus
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It comprises two nerves—the left and right vagus nerves—but they are typically referred to collectively as a single subsystem. The vagus is the longest nerve of the autonomic nervous system in the human body and comprises both sensory and motor fibers. The sensory fibers originate from neurons of the nodose ganglion, whereas the motor fibers come from neurons of the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus and the nucleus ambiguus. The vagus was also historically called the pneumogastric nerve. Structure Upon leaving the medulla oblongata between the olive and the inferior cerebellar peduncle, the vagus nerve extends through the jugular foramen, then passes into the carotid sheath between the internal carotid artery and the internal jugular vein down to the neck, chest, and abdomen, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
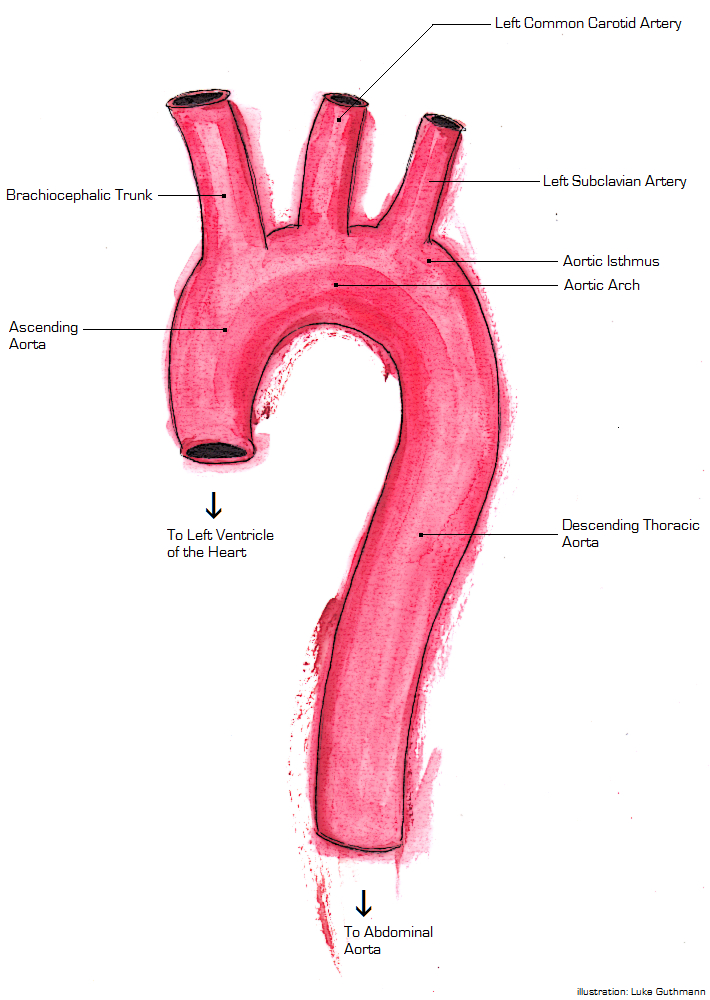
Aorta
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation. Structure Sections In anatomical sources, the aorta is usually divided into sections. One way of classifying a part of the aorta is by anatomical compartment, where the thoracic aorta (or thoracic portion of the aorta) runs from the heart to the diaphragm. The aorta then continues downward as the abdominal aorta (or abdominal portion of the aorta) from the diaphragm to the aortic bifurcation. Another system divides the aorta with respect to its course and the direction of blood flow. In this system, the aorta starts as the ascending aorta, travels superiorly from the heart, and then makes a hairpin turn known as the aortic arch. Following the aortic arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bleeding
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage – bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage – a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage – bleeding in the brain caused by the ruptur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paralysis
Paralysis (also known as plegia) is a loss of motor function in one or more muscles. Paralysis can also be accompanied by a loss of feeling (sensory loss) in the affected area if there is sensory damage. In the United States, roughly 1 in 50 people have been diagnosed with some form of permanent or transient paralysis. The word "paralysis" derives from the Greek παράλυσις, meaning "disabling of the nerves" from παρά (''para'') meaning "beside, by" and λύσις (''lysis'') meaning "making loose". A paralysis accompanied by involuntary tremors is usually called "palsy". Causes Paralysis is most often caused by damage in the nervous system, especially the spinal cord. Other major causes are stroke, trauma with nerve injury, poliomyelitis, cerebral palsy, peripheral neuropathy, Parkinson's disease, ALS, botulism, spina bifida, multiple sclerosis, and Guillain–Barré syndrome. Temporary paralysis occurs during REM sleep, and dysregulation of this system can lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical
Surgery ''cheirourgikē'' (composed of χείρ, "hand", and ἔργον, "work"), via la, chirurgiae, meaning "hand work". is a medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a person to investigate or treat a pathological condition such as a disease or injury, to help improve bodily function, appearance, or to repair unwanted ruptured areas. The act of performing surgery may be called a surgical procedure, operation, or simply "surgery". In this context, the verb "operate" means to perform surgery. The adjective surgical means pertaining to surgery; e.g. surgical instruments or surgical nurse. The person or subject on which the surgery is performed can be a person or an animal. A surgeon is a person who practices surgery and a surgeon's assistant is a person who practices surgical assistance. A surgical team is made up of the surgeon, the surgeon's assistant, an anaesthetist, a circulating nurse and a surgical technologist. Surgery usually spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patent Ductus Arteriosus
''Patent ductus arteriosus'' (PDA) is a medical condition in which the ''ductus arteriosus'' fails to close after birth: this allows a portion of oxygenated blood from the left heart to flow back to the lungs by flowing from the aorta, which has a higher pressure, to the pulmonary artery. Symptoms are uncommon at birth and shortly thereafter, but later in the first year of life there is often the onset of an increased work of breathing and failure to gain weight at a normal rate. With time, an uncorrected PDA usually leads to pulmonary hypertension followed by right-sided heart failure. The ''ductus arteriosus'' is a fetal blood vessel that normally closes soon after birth. In a PDA, the vessel does not close, but remains ''patent'' (open), resulting in an abnormal transmission of blood from the aorta to the pulmonary artery. PDA is common in newborns with persistent respiratory problems such as hypoxia, and has a high occurrence in premature newborns. Premature newborns are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebstein's Anomaly
Ebstein's anomaly is a congenital heart defect in which the septal and posterior leaflets of the tricuspid valve are displaced towards the apex of the right ventricle of the heart. It is classified as a critical congenital heart defect accounting for less than 1% of all congenital heart defects presenting in around per 200,000 live births. Ebstein anomaly is the congenital heart lesion most commonly associated with supraventricular tachycardia. Signs and symptoms The annulus of the valve is still in the normal position. The valve leaflets, however, are to a varying degree, attached to the walls and septum of the right ventricle. A subsequent "atrialization" of a portion of the morphologic right ventricle (which is then contiguous with the right atrium) is seen. This causes the right atrium to be large and the anatomic right ventricle to be small in size. * S3 heart sound * S4 heart sound * Triple or quadruple gallop due to widely split S1 and S2 sounds plus a loud S3 and/or S4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aortopulmonary Window
Aortopulmonary window (APW) refers to a congenital heart defect similar in some ways to persistent truncus arteriosus. Persistent truncus arteriosus involves a single valve; aortopulmonary window is a septal defect A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular .... A large number of patients with a large APW usually die within 1 year of age. It is extremely rare to find cases of APW surviving till adult age and it is still rare to surgically treat such patients who are incidentally detected in adult age because such subsets of patients invariably have associated pulmonary vascular obstructive disease in advanced stage and thus there is therapeutic dilemma to surgically correct these patients. Although cases of uncorrected APW presenting in adulthood have been reported but literat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atrial Septal Defect
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria (upper chambers) of the heart. Some flow is a normal condition both pre-birth and immediately post-birth via the foramen ovale; however, when this does not naturally close after birth it is referred to as a patent (open) foramen ovale (PFO). It is common in patients with a congenital atrial septal aneurysm (ASA). After PFO closure the atria normally are separated by a dividing wall, the interatrial septum. If this septum is defective or absent, then oxygen-rich blood can flow directly from the left side of the heart to mix with the oxygen-poor blood in the right side of the heart; or the opposite, depending on whether the left or right atrium has the higher blood pressure. In the absence of other heart defects, the left atrium has the higher pressure. This can lead to lower-than-normal oxygen levels in the arterial blood that supplies the brain, organs, and tissues. However, an ASD m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birth Defect
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may be visi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Numlabels
The heart is a muscular organ found in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest, called the mediastinum. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly, the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart, blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aortic Dissection Class
The aorta ( ) is the main and largest artery in the human body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and extending down to the abdomen, where it splits into two smaller arteries (the common iliac arteries). The aorta distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation. Structure Sections In anatomical sources, the aorta is usually divided into sections. One way of classifying a part of the aorta is by anatomical compartment, where the thoracic aorta (or thoracic portion of the aorta) runs from the heart to the diaphragm. The aorta then continues downward as the abdominal aorta (or abdominal portion of the aorta) from the diaphragm to the aortic bifurcation. Another system divides the aorta with respect to its course and the direction of blood flow. In this system, the aorta starts as the ascending aorta, travels superiorly from the heart, and then makes a hairpin turn known as the aortic arch. Following the aortic arch, the ao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)