|
Orthorhombic
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, resulting in a rectangular prism with a rectangular base (''a'' by ''b'') and height (''c''), such that ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' are distinct. All three bases intersect at 90° angles, so the three lattice vectors remain mutually orthogonal. Bravais lattices There are four orthorhombic Bravais lattices: primitive orthorhombic, base-centered orthorhombic, body-centered orthorhombic, and face-centered orthorhombic. For the base-centered orthorhombic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of a right rhombic prism;See , row oC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β = 90° it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. Note that the length a of the prim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthorhombic
In crystallography, the orthorhombic crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Orthorhombic lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along two of its orthogonal pairs by two different factors, resulting in a rectangular prism with a rectangular base (''a'' by ''b'') and height (''c''), such that ''a'', ''b'', and ''c'' are distinct. All three bases intersect at 90° angles, so the three lattice vectors remain mutually orthogonal. Bravais lattices There are four orthorhombic Bravais lattices: primitive orthorhombic, base-centered orthorhombic, body-centered orthorhombic, and face-centered orthorhombic. For the base-centered orthorhombic lattice, the primitive cell has the shape of a right rhombic prism;See , row oC, column Primitive, where the cell parameters are given as a1 = a2, α = β = 90° it can be constructed because the two-dimensional centered rectangular base layer can also be described with primitive rhombic axes. Note that the length a of the prim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal System
In crystallography, a crystal system is a set of point groups (a group of geometric symmetries with at least one fixed point). A lattice system is a set of Bravais lattices. Space groups are classified into crystal systems according to their point groups, and into lattice systems according to their Bravais lattices. Crystal systems that have space groups assigned to a common lattice system are combined into a crystal family. The seven crystal systems are triclinic, monoclinic, orthorhombic, tetragonal, trigonal, hexagonal, and cubic. Informally, two crystals are in the same crystal system if they have similar symmetries (albeit there are many exceptions). Classifications Crystals can be classified in three ways: lattice systems, crystal systems and crystal families. The various classifications are often confused: in particular the trigonal crystal system is often confused with the rhombohedral lattice system, and the term "crystal system" is sometimes used to mean "lattic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcasite
The mineral marcasite, sometimes called “white iron pyrite”, is iron sulfide (FeS2) with orthorhombic crystal structure. It is physically and crystallographically distinct from pyrite, which is iron sulfide with cubic crystal structure. Both structures do have in common that they contain the disulfide S22− ion, having a short bonding distance between the sulfur atoms. The structures differ in how these di-anions are arranged around the Fe2+ cations. Marcasite is lighter and more brittle than pyrite. Specimens of marcasite often crumble and break up due to the unstable crystal structure. On fresh surfaces, it is pale yellow to almost white and has a bright metallic luster. It tarnishes to a yellowish or brownish color and gives a black streak. It is a brittle material that cannot be scratched with a knife. The thin, flat, tabular crystals, when joined in groups, are called “cockscombs”. In marcasite jewellery, pyrite used as a gemstone is called “marcasite” � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coxeter Notation
In geometry, Coxeter notation (also Coxeter symbol) is a system of classifying symmetry groups, describing the angles between fundamental reflections of a Coxeter group in a bracketed notation expressing the structure of a Coxeter-Dynkin diagram, with modifiers to indicate certain subgroups. The notation is named after H. S. M. Coxeter, and has been more comprehensively defined by Norman Johnson. Reflectional groups For Coxeter groups, defined by pure reflections, there is a direct correspondence between the bracket notation and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram. The numbers in the bracket notation represent the mirror reflection orders in the branches of the Coxeter diagram. It uses the same simplification, suppressing 2s between orthogonal mirrors. The Coxeter notation is simplified with exponents to represent the number of branches in a row for linear diagram. So the ''A''''n'' group is represented by ''n''−1 to imply ''n'' nodes connected by ''n−1'' order-3 branches. Examp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Groups
In mathematics, physics and chemistry, a space group is the symmetry group of an object in space, usually in three dimensions. The elements of a space group (its symmetry operations) are the rigid transformations of an object that leave it unchanged. In three dimensions, space groups are classified into 219 distinct types, or 230 types if chiral copies are considered distinct. Space groups are discrete cocompact groups of isometries of an oriented Euclidean space in any number of dimensions. In dimensions other than 3, they are sometimes called Bieberbach groups. In crystallography, space groups are also called the crystallographic or Fedorov groups, and represent a description of the symmetry of the crystal. A definitive source regarding 3-dimensional space groups is the ''International Tables for Crystallography'' . History Space groups in 2 dimensions are the 17 wallpaper groups which have been known for several centuries, though the proof that the list was complete was only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Group
In mathematics, physics and chemistry, a space group is the symmetry group of an object in space, usually in three dimensions. The elements of a space group (its symmetry operations) are the rigid transformations of an object that leave it unchanged. In three dimensions, space groups are classified into 219 distinct types, or 230 types if chiral copies are considered distinct. Space groups are discrete cocompact groups of isometries of an oriented Euclidean space in any number of dimensions. In dimensions other than 3, they are sometimes called Bieberbach groups. In crystallography, space groups are also called the crystallographic or Fedorov groups, and represent a description of the symmetry of the crystal. A definitive source regarding 3-dimensional space groups is the ''International Tables for Crystallography'' . History Space groups in 2 dimensions are the 17 wallpaper groups which have been known for several centuries, though the proof that the list was complete was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers quickly on the surface. For this reason, olivine has been proposed as a good candidate for accelerated weathering to sequester carbon dioxide from the Earth's oceans and atmosphere, as part of climate change mitigation. Olivine also has many other historical uses, such as the gemstone peridot (or chrysolite), as well as industrial applications like metalworking processes. The ratio of magnesium to iron varies between the two endmembers of the solid solution series: forsterite (Mg-endmember: ) and fayalite (Fe-endmember: ). Compositions of olivine are commonly expressed as molar percentages of forsterite (Fo) and fayalite (Fa) (''e.g.'', Fo70Fa30). Forsterite's melting temperature is unusually high at atmospheric pressure, almost , while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bertrandite
Bertrandite is a beryllium sorosilicate hydroxide mineral with composition: Be4Si2O7(OH)2. Bertrandite is a colorless to pale yellow orthorhombic mineral with a hardness of 6-7. It is commonly found in beryllium rich pegmatites and is in part an alteration of beryl. Bertrandite often occurs as a pseudomorphic replacement of beryl. Associated minerals include beryl, phenakite, herderite, tourmaline, muscovite, fluorite and quartz. It, with beryl, are ores of beryllium. It was discovered near Nantes, France in 1883 and named after French mineralogist, Emile Bertrand (1844–1909). One of the world's largest deposits of bertrandite is Spor Mountain, Thomas Range, Utah which is currently the source of most of the world's beryllium production. See also *List of minerals *List of minerals named after people This is a list of minerals named after people. The chemical composition follows name. A * Abelsonite: C31H32N4Ni – American physicist Philip Hauge Abelson (1913–2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pearson Symbol
The Pearson symbol, or Pearson notation, is used in crystallography as a means of describing a crystal structure, and was originated by W. B. Pearson. The symbol is made up of two letters followed by a number. For example: * Diamond structure, ''cF''8 * Rutile structure, ''tP''6 The two (italicised) letters specify the Bravais lattice. The lower-case letter specifies the crystal family, and the upper-case letter the centering type. The number at the end of the Pearson symbol gives the number of the atoms in the conventional unit cell.Nomenclature of Inorganic Chemistry IUPAC Recommendations 2005 IR-3.4.4, pp. 49–51; IR-11.5, pp. 241–242. |
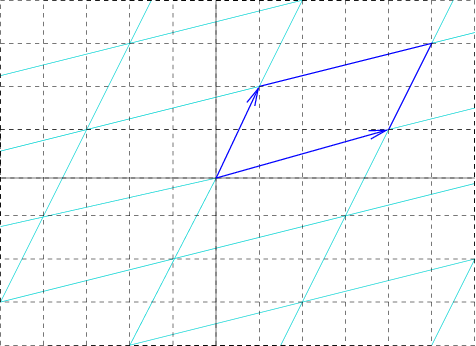
Unit Cell
In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a unit vector, for example) does not necessarily have unit size, or even a particular size at all. Rather, the primitive cell is the closest analogy to a unit vector, since it has a determined size for a given lattice and is the basic building block from which larger cells are constructed. The concept is used particularly in describing crystal structure in two and three dimensions, though it makes sense in all dimensions. A lattice can be characterized by the geometry of its unit cell, which is a section of the tiling (a parallelogram or parallelepiped) that generates the whole tiling using only translations. There are two special cases of the unit cell: the primitive cell and the conventional cell. The primitive cell is a unit cell corresponding to a single lattice point, it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
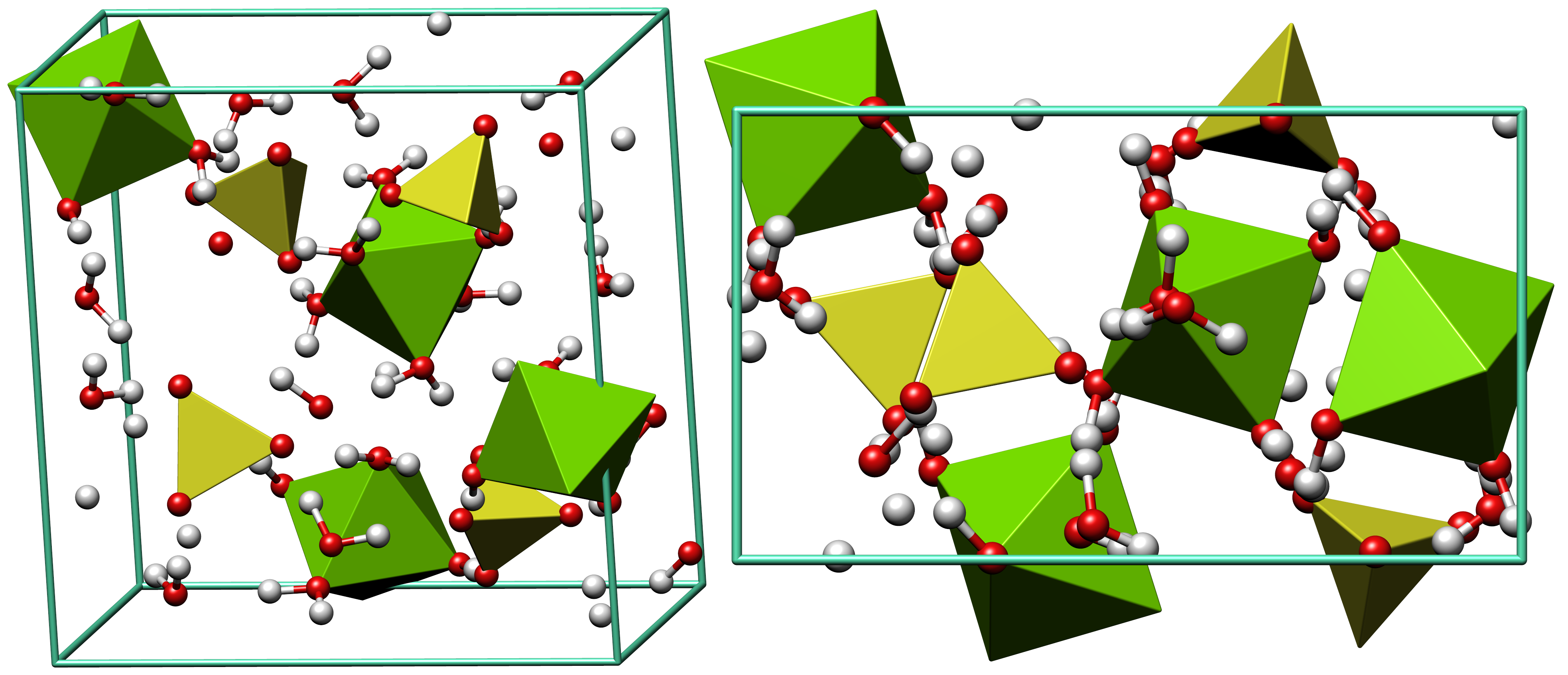
Epsomite
Epsomite, Epsom salt, or magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, is a hydrous magnesium sulfate mineral with formula MgSO4·7H2O. Epsomite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system as rarely found acicular or fibrous crystals, the normal form is as massive encrustations. It is colorless to white with tints of yellow, green and pink. The Mohs hardness is 2 to 2.5 and it has a low specific gravity of 1.67. It is readily soluble in water. It absorbs water from the air and converts to hexahydrate with the loss of one water molecule and a switch to monoclinic structure. Etymology It was first systematically described in 1806 for an occurrence near Epsom, Surrey, England, after which it was named. Discovery and occurrence Epsomite forms as encrustations or efflorescences on limestone cavern walls and mine timbers and walls, rarely as volcanic fumarole deposits, and as rare beds in evaporite layers such as those found in certain bodies of salt water. It occurs in association with melanterite, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primitive Cell
In geometry, biology, mineralogy and solid state physics, a unit cell is a repeating unit formed by the vectors spanning the points of a lattice. Despite its suggestive name, the unit cell (unlike a unit vector, for example) does not necessarily have unit size, or even a particular size at all. Rather, the primitive cell is the closest analogy to a unit vector, since it has a determined size for a given lattice and is the basic building block from which larger cells are constructed. The concept is used particularly in describing crystal structure in two and three dimensions, though it makes sense in all dimensions. A lattice can be characterized by the geometry of its unit cell, which is a section of the tiling (a parallelogram or parallelepiped) that generates the whole tiling using only translations. There are two special cases of the unit cell: the primitive cell and the conventional cell. The primitive cell is a unit cell corresponding to a single lattice point, it is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |