|
Orstomisis
''Orstomisis'' is a genus of deep-sea bamboo coral in the family Keratoisididae. It is monotypic with a single species, ''Orstomisis crosnieri''. It is distributed across the Pacific, with populations near Polynesia, Micronesia, and as far north as Atka Island. References Isididae Octocorallia genera {{Octocorallia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isididae
Bamboo coral, family Isididae, is a family of mostly deep-sea coral of the phylum Cnidaria. It is a commonly recognized inhabitant of the deep sea, due to the clearly articulated skeletons of the species. Deep water coral species such as this are especially affected by the practice of bottom trawling. These organisms may be an important environmental indicator in the study of long term climate change, as some specimens of bamboo coral have been discovered that are 4,000 years old. Description Relatively little is known about bamboo coral. The skeletons of bamboo coral are made up of calcium carbonate in the form of tree-like branches alternating with joint-like nodes or axes composed of gorgonin protein. The alternation of the bony structures with the smaller gorgonin parts give the bamboo coral a finger-like appearance similar to that of the bamboo plant on land. Bamboo coral was reported in 2005 to have been found on a dozen seamounts in the Pacific Ocean between Santa Bar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratoisididae
Bamboo coral, family Isididae, is a family of mostly deep-sea coral of the phylum Cnidaria. It is a commonly recognized inhabitant of the deep sea, due to the clearly articulated skeletons of the species. Deep water coral species such as this are especially affected by the practice of bottom trawling. These organisms may be an important environmental indicator in the study of long term climate change, as some specimens of bamboo coral have been discovered that are 4,000 years old. Description Relatively little is known about bamboo coral. The skeletons of bamboo coral are made up of calcium carbonate in the form of tree-like branches alternating with joint-like nodes or axes composed of gorgonin protein. The alternation of the bony structures with the smaller gorgonin parts give the bamboo coral a finger-like appearance similar to that of the bamboo plant on land. Bamboo coral was reported in 2005 to have been found on a dozen seamounts in the Pacific Ocean between Sant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
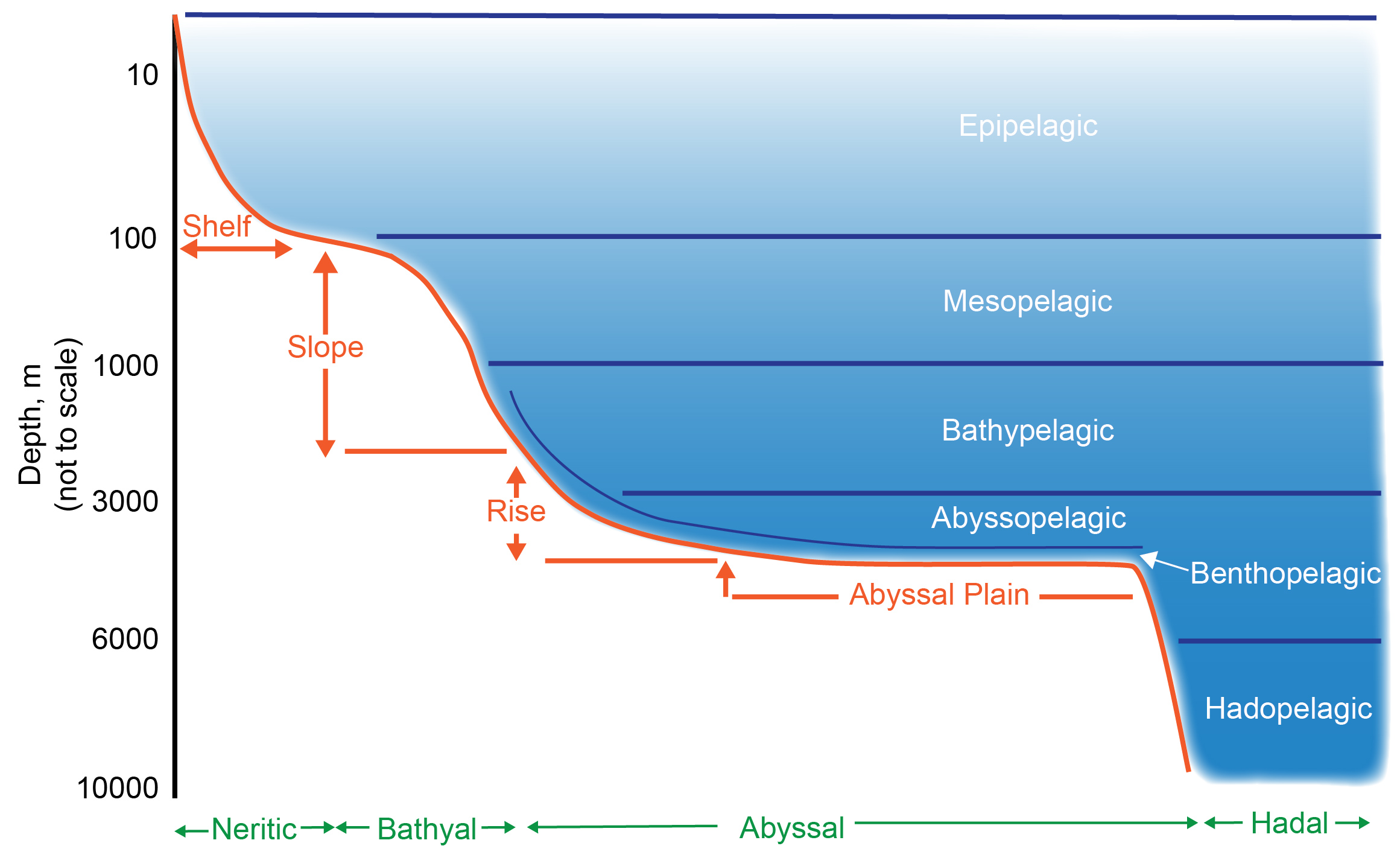
Deep Sea
The deep sea is broadly defined as the ocean depth where light begins to fade, at an approximate depth of 200 metres (656 feet) or the point of transition from continental shelves to continental slopes. Conditions within the deep sea are a combination of low temperatures, darkness and high pressure The deep sea is considered the least explored Earth biome, with the extreme conditions making the environment difficult to access and explore. Organisms living within the deep sea have a variety of adaptations to survive in these conditions. Organisms can survive in the deep sea through a number of feeding methods including scavenging, predation and filtration, with a number of organisms surviving by feeding on marine snow. Marine snow is organic material that has fallen from upper waters into the deep sea. In 1960, the bathyscaphe ''Trieste'' descended to the bottom of the Mariana Trench near Guam, at , the deepest known spot in any ocean. If Mount Everest () were submerged there, it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
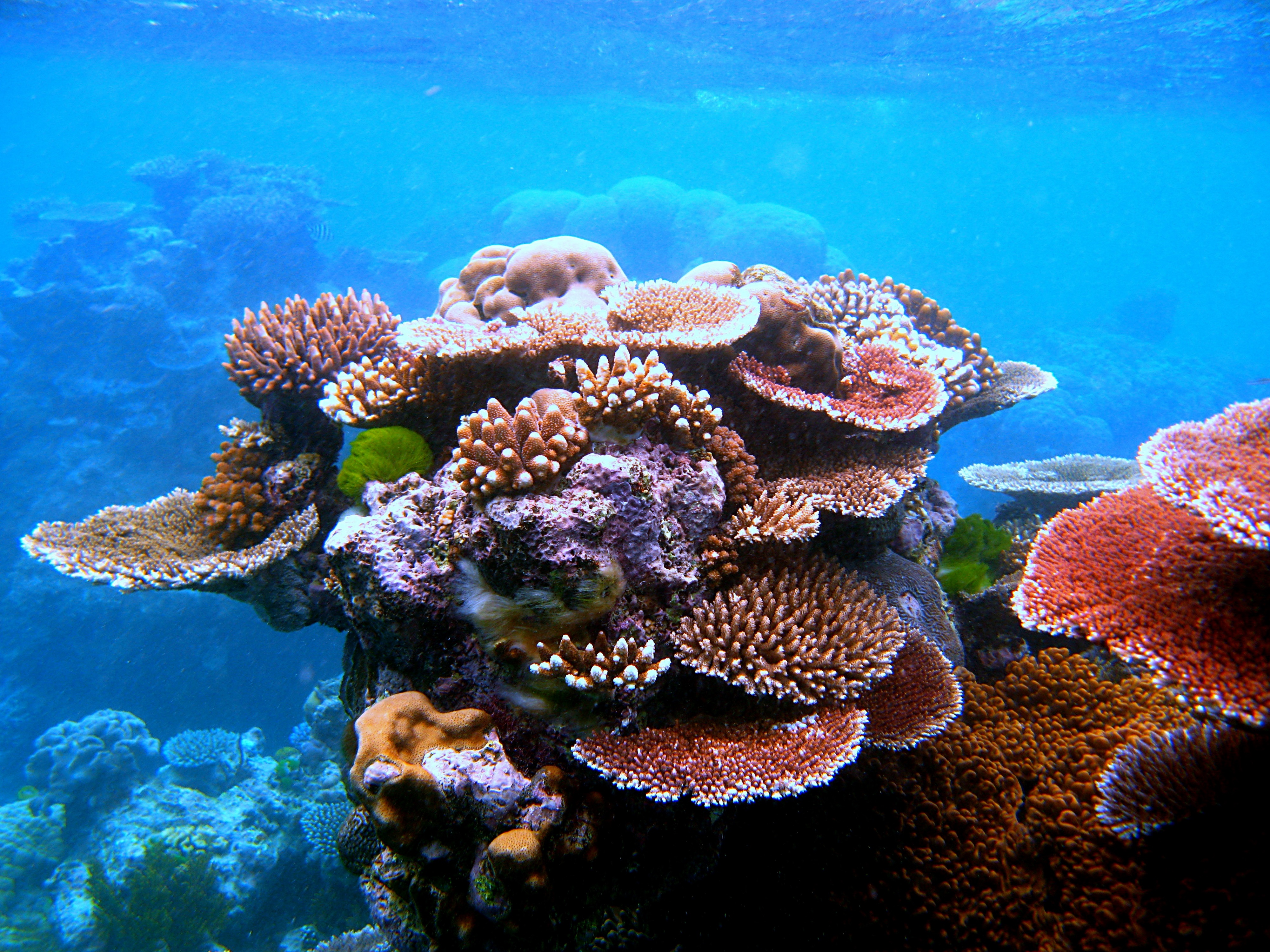
Coral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and secrete calcium carbonate to form a hard skeleton. A coral "group" is a colony of very many genetically identical polyps. Each polyp is a sac-like animal typically only a few millimeters in diameter and a few centimeters in height. A set of tentacles surround a central mouth opening. Each polyp excretes an exoskeleton near the base. Over many generations, the colony thus creates a skeleton characteristic of the species which can measure up to several meters in size. Individual colonies grow by asexual reproduction of polyps. Corals also breed sexually by spawning: polyps of the same species release gametes simultaneously overnight, often around a full moon. Fertilized eggs form planulae, a mobile early form of the coral polyp which, when m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. In contrast, an oligotypic taxon contains more than one but only a very few subordinate taxa. Examples Just as the term ''monotypic'' is used to describe a taxon including only one subdivision, the contained taxon can also be referred to as monotypic within the higher-level taxon, e.g. a genus monotypic within a family. Some examples of monotypic groups are: Plants * In the order Amborellales, there is only one family, Amborellaceae and there is only one genus, '' Amborella'', and in this genus there is only one species, namely ''Amborella trichopoda. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the |
Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in common, including language relatedness, cultural practices, and traditional beliefs. In centuries past, they had a strong shared tradition of sailing and using stars to navigate at night. The largest country in Polynesia is New Zealand. The term was first used in 1756 by the French writer Charles de Brosses, who originally applied it to all the islands of the Pacific. In 1831, Jules Dumont d'Urville proposed a narrower definition during a lecture at the Geographical Society of Paris. By tradition, the islands located in the southern Pacific have also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micronesia
Micronesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, consisting of about 2,000 small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions: the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, and Melanesia to the south—as well as with the wider community of Austronesian peoples. The region has a tropical marine climate and is part of the Oceanian realm. It includes four main archipelagos—the Caroline Islands, the Gilbert Islands, the Mariana Islands, and the Marshall Islands—as well as numerous islands that are not part of any archipelago. Political control of areas within Micronesia varies depending on the island, and is distributed among six sovereign nations. Some of the Caroline Islands are part of the Republic of Palau and some are part of the Federated States of Micronesia (often shortened to "FSM" or "Micronesia"—not to be confused with the identical name for the overall region). The Gilbert Islands (along with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atka Island
Atka Island ( ale, Atx̂ax̂, russian: Атка остров) is the largest island in the Andreanof Islands of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. The island is east of Adak Island. It is long and wide with a land area of , making it the 22nd largest island in the United States. The northeast of Atka Island contains the Korovin volcano which reaches a peak of . Oglodak Island is located off Cape Kigun, Atka's westernmost point. The city of Atka, Alaska is on the east side of the island. The 2000 census population of the island was 95 persons, almost all in the city of Atka.Atka Island: Blocks 1085 thru 1100 and Block 1103, Census Tract 1, Aleutians West Census Area, Alaska United States Census Bureau On December 5, 2008, |

.jpg)

.jpg)
