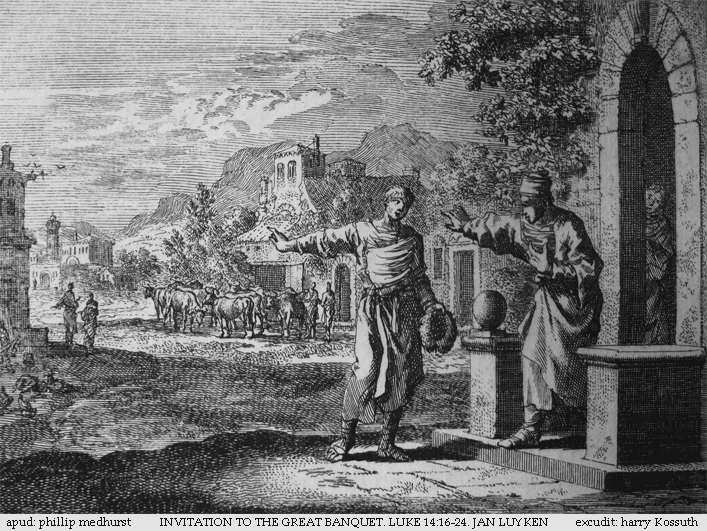|
Organ Sonatas (Bach)
The organ sonatas, BWV 525–530 by Johann Sebastian Bach are a collection of six sonatas in trio sonata form. Each of the sonatas has three movements, with three independent parts in the two manuals and obbligato pedal. The collection was put together in Leipzig in the late 1720s and contained reworkings of prior compositions by Bach from earlier cantatas, organ works and chamber music as well as some newly composed movements. The sixth sonata, BWV 530, is the only one for which all three movements were specially composed for the collection. When played on an organ, the second manual part is often played an octave lower on the keyboard with appropriate registration. Commentators have suggested that the collection might partly have been intended for private study to perfect organ technique, some pointing out that its compass allows it to be played on a pedal clavichord. The collection of sonatas is generally regarded as one of Bach's masterpieces for organ. The sonatas are also co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inventions And Sinfonias (Bach)
The Inventions and Sinfonias, BWV 772–801, also known as the Two- and Three-Part Inventions, are a collection of thirty short keyboard compositions by Johann Sebastian Bach (1685–1750): 15 '' inventions'', which are two-part contrapuntal pieces, and 15 '' sinfonias'', which are three-part contrapuntal pieces. They were originally written as "''Praeambula''" and "''Fantasiae''" in the Klavierbüchlein für Wilhelm Friedemann Bach, a ''Clavier-booklet'' for his eldest son, and later rewritten as musical exercises for his students. Bach titled the collection: Forthright instruction, wherewith lovers of the clavier, especially those desirous of learning, are shown in a clear way not only 1) to learn to play two voices clearly, but also after further progress 2) to deal correctly and well with three obbligato parts, moreover at the same time to obtain not only good ideas, but also to carry them out well, but most of all to achieve a '' cantabile'' style of playing, and thereby to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Die Himmel Erzählen Die Ehre Gottes, BWV 76
Johann Sebastian Bach composed the church cantata (), 76 in Leipzig for the second Sunday after Trinity of the liturgical year and first performed it on 6 June 1723. Bach composed the cantata at a decisive turning point in his career. Moving from posts in the service of churches and courts to the town of Leipzig on the first Sunday after Trinity, 30 May 1723, he began the project of composing a new cantata for every occasion of the liturgical year. He began his first annual cycle of cantatas ambitiously with , in an unusual layout of 14 movements in two symmetrical parts, to be performed before and after the sermon. , performed a week later, has the same structure. The unknown poet begins his text with a quotation from Psalm 19 and refers to both prescribed readings from the New Testament, the parable of the great banquet as the Gospel, and the First Epistle of John. Bach scored Part I with a trumpet as a symbol of God's Glory. In Part II, performed after the sermon and during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Café Zimmermann
The Café Zimmermann, or was the coffeehouse of Gottfried Zimmermann in Leipzig which formed the backdrop to the first performances of many of Bach's secular cantatas, e.g. the ''Coffee Cantata'' ('' Schweigt stille, plaudert nicht''), and instrumental works. In 1723, the year Bach moved to Leipzig, it was the largest and best-appointed Kaffeehaus of Leipzig and a centre for the middle classes and gentlemen. While women were forbidden from frequenting coffeehouses, they could attend public concerts at Zimmermann's. The coffeehouse was located at 14 Katharinenstrasse, then the most elegant street of Leipzig, connecting the Brühl to the market place. The name of the street had been taken from the old St. Catherine's Chapel which had been demolished in 1544. In Telemann's and Bach's day, only the name of the street remained. During the summer months, Zimmermann also ran an outdoor coffee garden in the outside the city walls, near the East Gate. The four-and-a-half-story Baroque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collegium Musicum
The Collegium Musicum was one of several types of musical societies that arose in German and German-Swiss cities and towns during the Reformation and thrived into the mid-18th century. Generally, while societies such as the (chorale) cultivated vocal music for church performance and the convivium musicum discussed musical philosophy over a banquet, the collegia musica performed both vocal and instrumental music for pleasure; they focused on instrumental music as it rose in stature during the Baroque era. Though closed amateur societies in concept, collegia frequently included professionals to fill out the music and admitted non-members to performances. Moreover, they often provided music for church, state, and academic occasions and gained the patronage of leading citizens. From the 1660s, their functions largely constituted the beginnings of public concert life in Germany. Leipzig Leipzig collegia musica, consisting mostly of university students, enjoyed a succession of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BWV 1044
The keyboard concertos, BWV 1052–1065, are concertos for harpsichord (or organ), strings and continuo by Johann Sebastian Bach. There are seven complete concertos for a single harpsichord (BWV 1052–1058), three concertos for two harpsichords (BWV 1060–1062), two concertos for three harpsichords (BWV 1063 and 1064), and one concerto for four harpsichords (BWV 1065). Two other concertos include solo harpsichord parts: the concerto BWV 1044, which has solo parts for harpsichord, violin and flute, and ''Brandenburg Concerto'' No. 5 in D major, with the same scoring. In addition, there is a nine-bar concerto fragment for harpsichord (BWV 1059) which adds an oboe to the strings and continuo. Most of Bach's harpsichord concertos (with the exception of the 5th ''Brandenburg Concerto'') are thought to be arrangements made from earlier concertos for melodic instruments probably written in Köthen. In many cases, only the harpsichord version has survived. They are among the first c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nekrolog Mizler Musikalische Bibliothek Bd 4 1754
Nekrolog (German for ''obituary'') may refer to: * Bach's Nekrolog Nekrolog is the name with which Johann Sebastian Bach's obituary, which appeared four years after the composer's death, is usually indicated. Publication The "Nekrolog" appeared in Lorenz Christoph Mizler's ''Musikalische Bibliothek'', a series of ..., the obituary of German composer Johann Sebastian Bach (1685-1750) * '' Nekrolog 43'', a 2007 album by Diary of Dreams {{dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dresden
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label=Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth largest by area (after Berlin, Hamburg and Cologne), and the third most populous city in the area of former East Germany, after Berlin and Leipzig. Dresden's urban area comprises the towns of Freital, Pirna, Radebeul, Meissen, Coswig, Radeberg and Heidenau and has around 790,000 inhabitants. The Dresden metropolitan area has approximately 1.34 million inhabitants. Dresden is the second largest city on the River Elbe after Hamburg. Most of the city's population lives in the Elbe Valley, but a large, albeit very sparsely populated area of the city east of the Elbe lies in the West Lusatian Hill Country and Uplands (the westernmost part of the Sudetes) and thus in Lusatia. Many boroughs west of the Elbe lie in the foreland of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sophienkirche
The Sophienkirche (Saint Sophia's Church) was a church in Dresden. It was located on the northeast corner of the Postplatz (post office square) in the old town before it was severely damaged in the Dresden bombing in 1945 and subsequently destroyed in 1962 by the party and government of the GDR. It was the only Gothic church in the city. History In 1250 The Order of Friars Minor, Franciscans, built a monastery and small church at the location of the future Sophienkirche — this was known as the Franziskanerkloster. Starting in 1331 the original structure was demolished and construction began of a larger church with two equally sized naves. Around 1400, at the southeast corner of the church, the Busmannkapelle was added, a private chapel for the patrician Busmann family to which the Dresden Mayor at the time, Lorenz Busmann, belonged and where he was later buried. The Franciscan monastery was abolished during the Reformation. Sophie of Brandenburg, Hofkirche The F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Caspar Vogler
Johann Caspar Vogler (23 May 1696 – 3 June 1763) was a German organist and composer taught by Johann Sebastian Bach. Biography He was born in Hausen, near Arnstadt; from 1706 he studied with Johann Sebastian Bach, who was organist there between 1703 and 1707. He also taught, in Rudolstadt, by P. H. Erlebach and Nicolaus Vetter. He moved to Weimar to study further with Bach from 1710 to 1715, during which time he copied Jacques Boyvin's two ''livres d'orgue''. He was appointed organist at Stadtilm in 1715, leaving in May 1721 to take up Bach's former post of organist to the Weimar court. He failed in two applications in 1729 for organ posts at the Nikolaikirche, Leipzig, and Sts Peter und Paul, Görlitz, which were filled by Bach pupils Johann Schneider and David Nicolai. The Leipzig judges remarked that he 'played too fast and confused the congregation'; this did not deter him from boasting of his 'swiftness of hand and feet' in the second application. He was selected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anna Magdalena Bach
Anna Magdalena Bach (née Wilcke or Wilcken) (22 September 1701 – 22 February 1760) was a professional singer and the second wife of Johann Sebastian Bach. Biography Anna Magdalena Wilcke was born at Zeitz, in the Electorate of Saxony. While little is known about her early musical education, the family was musical. Her father, Johann Caspar Wilcke (c. 1660–1733), was a trumpet player, who had a career at the courts of Zeitz and Weißenfels. Her mother, Margaretha Elisabeth Liebe, was the daughter of an organist. By 1721 Anna Magdalena was employed as a singer ( soprano) at the princely court of Anhalt-Cöthen. Johann Sebastian Bach had been working there as ''Capellmeister'', or director of music, since December 1717. It is possible that he first heard her sing at the ducal court in Weißenfels, where he is known to have performed as early as 1713, when his Hunting Cantata was premiered there. Anna and Johann married on 3 December 1721, seventeen months after the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |