|
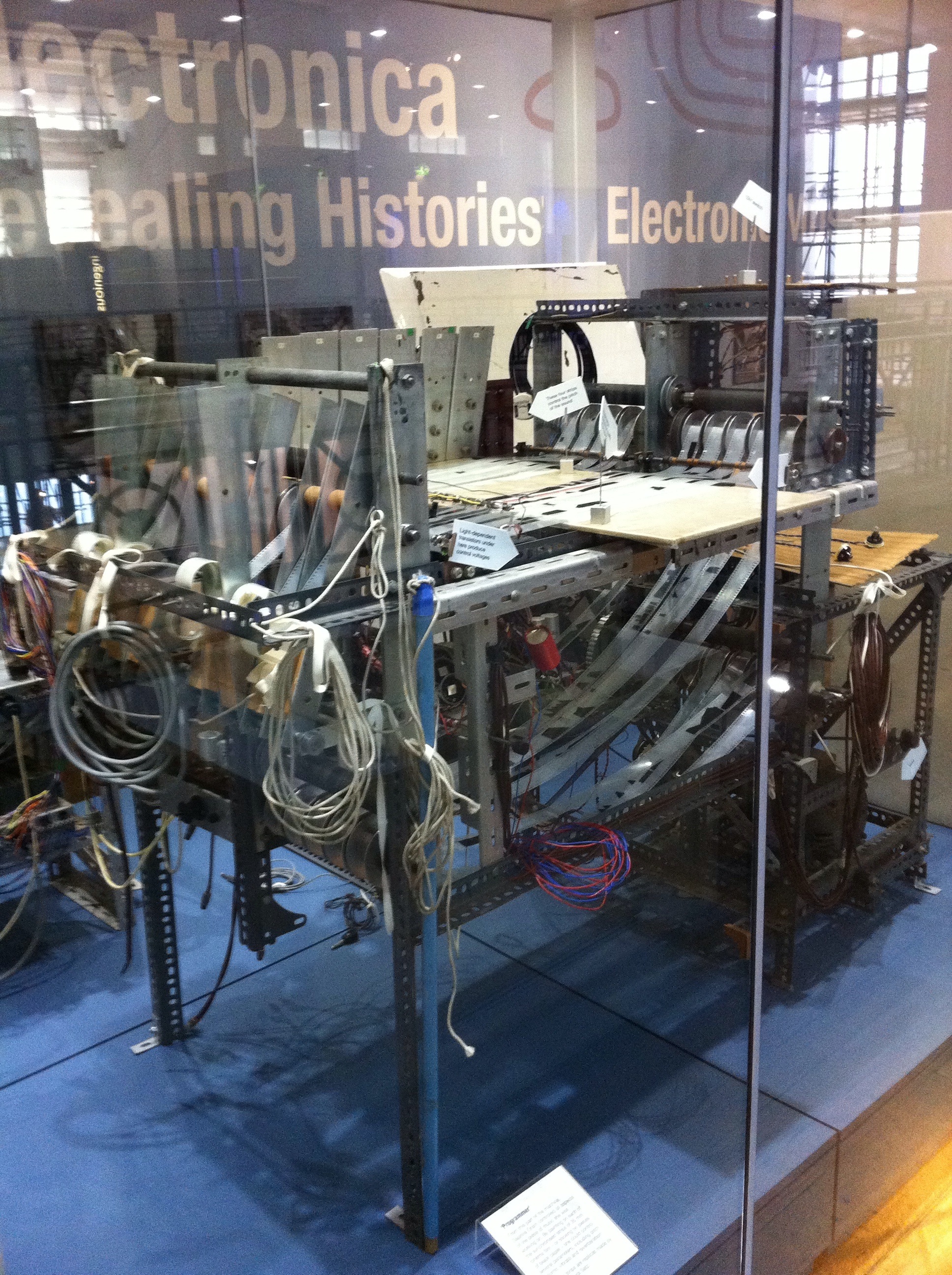
Oramics
__NOTOC__ Oramics is a drawn sound technique designed in 1957 by musician Daphne Oram. The machine was further developed in 1962 after receiving a grant from the Gulbenkian Foundation. The technique involves drawing on 35mm film strips to control the sound produced. Oramics was also the name used by Oram to refer to her studio and business interests generally. Oram's composition machine consisted of a large rectangular metal frame, providing a table-like surface traversed by ten synchronised strips of clear, sprocketed 35mm film. The musician drew shapes on the film to create a mask, which modulated the light received by photocells. Although the output from the machine was monophonic, the sounds could be added to multitrack tapes to provide more texture and create polyphony. The original machine was exhibited at the Science Museum in London between 2011 and 2015. Related techniques The Oramics machine, which creates music from graphic elements uses similar principles to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphne Oram
Daphne Blake Oram (31 December 1925 – 5 January 2003) was a British composer and electronic musician. She was one of the first British composers to produce electronic sound, and was an early practitioner of musique concrète in the UK. As a co-founder of the BBC Radiophonic Workshop, she was central to the development of British electronic music. Her uncredited scoring work on the 1961 film '' The Innocents'' helped to pioneer the electronic soundtrack. Oram was the creator of the Oramics technique for creating electronic sounds using drawn sound. Besides being a musical innovator, she was the first woman to independently direct and set up a personal electronic music studio, and the first woman to design and construct an electronic musical instrument. In her book ''An Individual Note of Music, Sound and Electronics'' (1971) she explored philosophical themes related to the physics of sound. Early life and education Oram was born to James and Ida Oram on 31 December 1925 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oramics Machine - Details 2-2
__NOTOC__ Oramics is a drawn sound technique designed in 1957 by musician Daphne Oram. The machine was further developed in 1962 after receiving a grant from the Gulbenkian Foundation. The technique involves drawing on 35mm film strips to control the sound produced. Oramics was also the name used by Oram to refer to her studio and business interests generally. Oram's composition machine consisted of a large rectangular metal frame, providing a table-like surface traversed by ten synchronised strips of clear, sprocketed 35mm film. The musician drew shapes on the film to create a mask, which modulated the light received by photocells. Although the output from the machine was monophonic, the sounds could be added to multitrack tapes to provide more texture and create polyphony. The original machine was exhibited at the Science Museum in London between 2011 and 2015. Related techniques The Oramics machine, which creates music from graphic elements uses similar principles to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oramics
__NOTOC__ Oramics is a drawn sound technique designed in 1957 by musician Daphne Oram. The machine was further developed in 1962 after receiving a grant from the Gulbenkian Foundation. The technique involves drawing on 35mm film strips to control the sound produced. Oramics was also the name used by Oram to refer to her studio and business interests generally. Oram's composition machine consisted of a large rectangular metal frame, providing a table-like surface traversed by ten synchronised strips of clear, sprocketed 35mm film. The musician drew shapes on the film to create a mask, which modulated the light received by photocells. Although the output from the machine was monophonic, the sounds could be added to multitrack tapes to provide more texture and create polyphony. The original machine was exhibited at the Science Museum in London between 2011 and 2015. Related techniques The Oramics machine, which creates music from graphic elements uses similar principles to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oramics - Two Waveform Slides Painted By Daphne Oram, 1965-80
__NOTOC__ Oramics is a drawn sound technique designed in 1957 by musician Daphne Oram. The machine was further developed in 1962 after receiving a grant from the Gulbenkian Foundation. The technique involves drawing on 35mm film strips to control the sound produced. Oramics was also the name used by Oram to refer to her studio and business interests generally. Oram's composition machine consisted of a large rectangular metal frame, providing a table-like surface traversed by ten synchronised strips of clear, sprocketed 35mm film. The musician drew shapes on the film to create a mask, which modulated the light received by photocells. Although the output from the machine was monophonic, the sounds could be added to multitrack tapes to provide more texture and create polyphony. The original machine was exhibited at the Science Museum in London between 2011 and 2015. Related techniques The Oramics machine, which creates music from graphic elements uses similar principles to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oramics Machine - Front Right-
__NOTOC__ Oramics is a drawn sound technique designed in 1957 by musician Daphne Oram. The machine was further developed in 1962 after receiving a grant from the Gulbenkian Foundation. The technique involves drawing on 35mm film strips to control the sound produced. Oramics was also the name used by Oram to refer to her studio and business interests generally. Oram's composition machine consisted of a large rectangular metal frame, providing a table-like surface traversed by ten synchronised strips of clear, sprocketed 35mm film. The musician drew shapes on the film to create a mask, which modulated the light received by photocells. Although the output from the machine was monophonic, the sounds could be added to multitrack tapes to provide more texture and create polyphony. The original machine was exhibited at the Science Museum (London), Science Museum in London between 2011 and 2015. Related techniques The Oramics machine, which creates music from graphic elements use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANS Synthesizer
The ANS synthesizer is a photoelectronic musical instrument created by Russian engineer Evgeny Murzin from 1937 to 1957. The technological basis of his invention was the method of graphical sound recording used in cinematography (developed in Russia concurrently with USA), which made it possible to obtain a visible image of a sound wave, as well as to realize the opposite goal— synthesizing a sound from an artificially drawn sound spectrogram. In this case the sine waves generated by the ANS are printed onto five glass discs using a process that Murzin (an optical engineer) had to develop himself. Each disc has 144 individual tracks printed onto it, for a total of 720 microtones (discrete pitches), spanning 10 octaves. This yields a resolution of 1/72 octave (16.67 cents). The modulated light from these wheels is then projected onto the back of the synthesizer's interface. These are arranged in a continuous swath vertically, with low frequencies at the bottom and high fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variophone
The Variophone was developed by Evgeny Sholpo in 1930 at Lenfilm Studio Productions, in Leningrad, the Soviet Union, during his experiments with graphical sound techniques, also known as ''ornamental'', ''drawn'', ''paper'', ''artificial'' or ''synthetic'' sound. In his research Sholpo was assisted by the composer Georgy Rimsky‐Korsakov. The Variophone was an optical synthesizer that utilized sound waves cut onto cardboard disks rotating synchronously with a moving 35mm movie film while being photographed onto it to produce a continuous soundtrack. Afterwards this filmstrip is played as a normal movie by means of a film projector. Being read by photocell, amplified and monitored by a loudspeaker, it functions as a musical recording process. Although with the first version of the Variophone, polyphonic soundtracks of up to 6 voices could be produced by shooting of several monophonic parts and combining them later, by the late 1930s and 1940s, some soundtracks contained up to twe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical Sound
Graphical sound or drawn sound (Fr. ''son dessiné'', Ger. ''graphische Tonerzeugung'',; It. ''suono disegnato'') is a sound recording created from images drawn directly onto film or paper that were then played back using a sound system. There are several different techniques depending on the technology employed, but all are a consequence of the sound-on-film technology and based on the creation of artificial optical polyphonic sound tracks on transparent film. History The first practical sound-on-film systems were created almost simultaneously in the USSR, USA and Germany. In Soviet Russia Pavel Tager initiated the first developments in 1926 in Moscow. In 1927, just over a few months later, Alexander Shorin started his research in Leningrad. The popular version of his “Shorinophone”, widely used for field and studio sound recording, was based on a mechanical reproduction of gramophone-like longitudinal grooves along the filmstrip. Another version of Shorin’s system – “ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drawn Sound
Graphical sound or drawn sound (Fr. ''son dessiné'', Ger. ''graphische Tonerzeugung'',; It. ''suono disegnato'') is a sound recording created from images drawn directly onto film or paper that were then played back using a sound system. There are several different techniques depending on the technology employed, but all are a consequence of the sound-on-film technology and based on the creation of artificial optical polyphonic sound tracks on transparent film. History The first practical sound-on-film systems were created almost simultaneously in the USSR, USA and Germany. In Soviet Russia Pavel Tager initiated the first developments in 1926 in Moscow. In 1927, just over a few months later, Alexander Shorin started his research in Leningrad. The popular version of his “Shorinophone”, widely used for field and studio sound recording, was based on a mechanical reproduction of gramophone-like longitudinal grooves along the filmstrip. Another version of Shorin’s system – “ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Museum (London)
The Science Museum is a major museum on Exhibition Road in South Kensington, London. It was founded in 1857 and is one of the city's major tourist attractions, attracting 3.3 million visitors annually in 2019. Like other publicly funded national museums in the United Kingdom, the Science Museum does not charge visitors for admission, although visitors are requested to make a donation if they are able. Temporary exhibitions may incur an admission fee. It is one of the five museums in the Science Museum Group. Founding and history The museum was founded in 1857 under Bennet Woodcroft from the collection of the Royal Society of Arts and surplus items from the Great Exhibition as part of the South Kensington Museum, together with what is now the Victoria and Albert Museum. It included a collection of machinery which became the ''Museum of Patents'' in 1858, and the ''Patent Office Museum'' in 1863. This collection contained many of the most famous exhibits of what is now t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphony
Polyphony ( ) is a type of musical texture consisting of two or more simultaneous lines of independent melody, as opposed to a musical texture with just one voice, monophony, or a texture with one dominant melodic voice accompanied by chords, homophony. Within the context of the Western musical tradition, the term ''polyphony'' is usually used to refer to music of the late Middle Ages and Renaissance. Baroque forms such as fugue, which might be called polyphonic, are usually described instead as contrapuntal. Also, as opposed to the ''species'' terminology of counterpoint, polyphony was generally either "pitch-against-pitch" / "point-against-point" or "sustained-pitch" in one part with melismas of varying lengths in another. In all cases the conception was probably what Margaret Bent (1999) calls "dyadic counterpoint", with each part being written generally against one other part, with all parts modified if needed in the end. This point-against-point conception is opposed to " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norman McLaren
William Norman McLaren, LL. D. (11 April 1914 – 27 January 1987) was a Scottish Canadian animator, director and producer known for his work for the National Film Board of Canada (NFB).Rosenthal, Alan. ''The new documentary in action: a casebook in film making''. University of California Press, 1972. 267-8. Print. He was a pioneer in a number of areas of animation and filmmaking, including hand-drawn animation, drawn-on-film animation, visual music, abstract film, pixilation and graphical sound. McLaren was also an artist and printmaker, and explored his interest in dance in his films. His awards included an Academy Award for Best Documentary Short Subject in 1952 for ''Neighbours'', a Silver Bear for best short documentary at the 1956 Berlin International Film Festival for '' Rythmetic'' and a 1969 BAFTA Award for Best Animated Film for ''Pas de deux''. Early life Norman McLaren was born in Stirling, Scotland, on 11 April 1914. He had two older siblings, one brother, Jack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |