|
Oracle RAC
In database computing, Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC) — an option for the Oracle Database software produced by Oracle Corporation and introduced in 2001 with Oracle9i — provides software for clustering and high availability in Oracle database environments. Oracle Corporation includes RAC with the Enterprise Edition, provided the nodes are clustered using Oracle Clusterware. Functionality Oracle RAC allows multiple computers to run Oracle RDBMS software simultaneously while accessing a single database, thus providing clustering. In a non-RAC Oracle database, a single instance accesses a single database. The ''database'' consists of a collection of data files, control files, and redo logs located on disk. The ''instance'' comprises the collection of Oracle-related memory and background processes that run on a computer system. In an Oracle RAC environment, 2 or more instances concurrently access a single database. This allows an application or user to connect to ei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases spans formal techniques and practical considerations, including data modeling, efficient data representation and storage, query languages, security and privacy of sensitive data, and distributed computing issues, including supporting concurrent access and fault tolerance. A database management system (DBMS) is the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS software additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an appli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Database Cache
Database caching is a process included in the design of computer applications which generate web pages on-demand (dynamically) by accessing backend databases. When these applications are deployed on multi-tier environments that involve browser-based clients, web application servers and backend databases, middle-tier database caching is used to achieve high scalability and performance. In a three tier architecture, the application software tier and data storage tier can be in different hosts. Throughput of an application can be limited by the network speed. This limitation can be minimized by having the database at the application tier. Because commercial database software makes extensive use of system resources, it is not always practical to have the application and the database at the same host. In this case, a more light-weight database application can be used to cache data from the commercial database management system. Benefits Database caching improves scalability by di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Performance
A performance is an act of staging or presenting a play, concert, or other form of entertainment. It is also defined as the action or process of carrying out or accomplishing an action, task, or function. Management science In the work place, job performance is the hypothesized conception or requirements of a role. There are two types of job performances: contextual and task. Task performance is dependent on cognitive ability, while contextual performance is dependent on personality. Task performance relates to behavioral roles that are recognized in job descriptions and remuneration systems. They are directly related to organizational performance, whereas contextual performances are value-based and add additional behavioral roles that are not recognized in job descriptions and covered by compensation; these are extra roles that are indirectly related to organizational performance. Citizenship performance, like contextual performance, relates to a set of individual activity/co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Online Transaction Processing
In online transaction processing (OLTP), information systems typically facilitate and manage transaction-oriented applications. This is contrasted with online analytical processing. The term "transaction" can have two different meanings, both of which might apply: in the realm of computers or database transactions it denotes an atomic change of state, whereas in the realm of business or finance, the term typically denotes an exchange of economic entities (as used by, e.g., Transaction Processing Performance Council or commercial transactions.) OLTP may use transactions of the first type to record transactions of the second. OLTP has also been used to refer to processing in which the system responds immediately to user requests. An automated teller machine (ATM) for a bank is an example of a commercial transaction processing application. Online transaction processing applications have high throughput and are insert- or update-intensive in database management. These applications are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SAP AG
Sap is a fluid transported in xylem cells (vessel elements or tracheids) or phloem sieve tube elements of a plant. These cells transport water and nutrients throughout the plant. Sap is distinct from latex, resin, or cell sap; it is a separate substance, separately produced, and with different components and functions. Insect honeydew is called sap, particularly when it falls from trees, but is only the remains of eaten sap and other plant parts. Types of sap Saps may be broadly divided into two types: xylem sap and phloem sap. Xylem sap Xylem sap (pronounced ) consists primarily of a watery solution of hormones, mineral elements and other nutrients. Transport of sap in xylem is characterized by movement from the roots toward the leaves. Over the past century, there has been some controversy regarding the mechanism of xylem sap transport; today, most plant scientists agree that the cohesion-tension theory best explains this process, but multiforce theories that hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resource Mastering
Resource refers to all the materials available in our environment which are technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally sustainable and help us to satisfy our needs and wants. Resources can broadly be classified upon their availability — they are classified into renewable and non-renewable resources. They can also be classified as actual and potential on the basis of the level of development and use, on the basis of origin they can be classified as biotic and abiotic, and on the basis of their distribution, as ubiquitous and localised (private, community-owned, national and international resources). An item becomes a resource with time and developing technology. The benefits of resource utilization may include increased wealth, proper functioning of a system, or enhanced well-being. From a human perspective, a natural resource is anything obtained from the environment to satisfy human needs and wants.WanaGopa - Nyawakan From a broader biological or ecologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
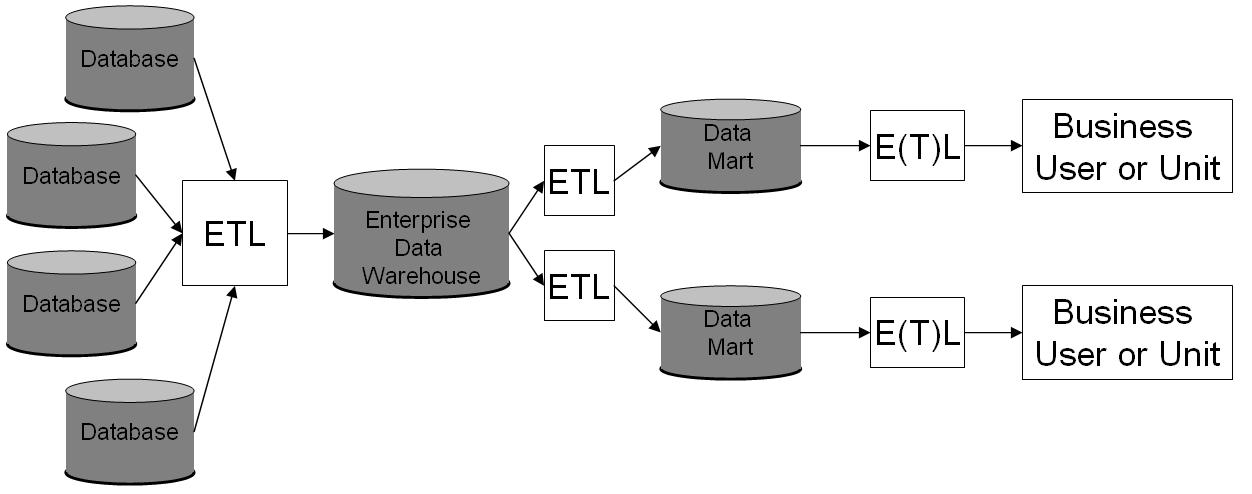
Data Warehousing
In computing, a data warehouse (DW or DWH), also known as an enterprise data warehouse (EDW), is a system used for reporting and data analysis and is considered a core component of business intelligence. DWs are central repositories of integrated data from one or more disparate sources. They store current and historical data in one single place that are used for creating analytical reports for workers throughout the enterprise. The data stored in the warehouse is uploaded from the operational systems (such as marketing or sales). The data may pass through an operational data store and may require data cleansing for additional operations to ensure data quality before it is used in the DW for reporting. Extract, transform, load (ETL) and extract, load, transform (ELT) are the two main approaches used to build a data warehouse system. ETL-based data warehousing The typical extract, transform, load (ETL)-based data warehouse uses staging, data integration, and access layers to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalability
Scalability is the property of a system to handle a growing amount of work by adding resources to the system. In an economic context, a scalable business model implies that a company can increase sales given increased resources. For example, a package delivery system is scalable because more packages can be delivered by adding more delivery vehicles. However, if all packages had to first pass through a single warehouse for sorting, the system would not be as scalable, because one warehouse can handle only a limited number of packages. In computing, scalability is a characteristic of computers, networks, algorithms, networking protocols, programs and applications. An example is a search engine, which must support increasing numbers of users, and the number of topics it indexes. Webscale is a computer architectural approach that brings the capabilities of large-scale cloud computing companies into enterprise data centers. In mathematics, scalability mostly refers to closure u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millisecond
A millisecond (from '' milli-'' and second; symbol: ms) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one thousandth (0.001 or 10−3 or 1/1000) of a second and to 1000 microseconds. A unit of 10 milliseconds may be called a centisecond, and one of 100 milliseconds a decisecond, but these names are rarely used. To help compare orders of magnitude of different times, this page lists times between 10−3 seconds and 100 seconds (1 millisecond and one second). ''See also'' times of other orders of magnitude. Examples The Apollo Guidance Computer used metric units internally, with centiseconds used for time calculation and measurement. *1 millisecond (1 ms) – cycle time for frequency 1 kHz; duration of light for typical photo flash strobe; time taken for sound wave to travel about 34 cm; repetition interval of GPS C/A PN code *1 millisecond - time taken for light to travel 204.19 km in a single mode fiber optic cable for a wavelength o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Block (data Storage)
In computing (specifically data transmission and data storage), a block, sometimes called a physical record, is a sequence of bytes or bits, usually containing some whole number of records, having a maximum length; a ''block size''. Data thus structured are said to be ''blocked''. The process of putting data into blocks is called ''blocking'', while ''deblocking'' is the process of extracting data from blocks. Blocked data is normally stored in a data buffer, and read or written a whole block at a time. Blocking reduces the overhead and speeds up the handling of the data stream. For some devices, such as magnetic tape and CKD disk devices, blocking reduces the amount of external storage required for the data. Blocking is almost universally employed when storing data to 9-track magnetic tape, NAND flash memory, and rotating media such as floppy disks, hard disks, and optical discs. Most file systems are based on a block device, which is a level of abstraction for the hardwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Cluster
Oracle Solaris Cluster (sometimes Sun Cluster or SunCluster) is a high-availability cluster software product for Solaris, originally created by Sun Microsystems, which was acquired by Oracle Corporation in 2010. It is used to improve the availability of software services such as databases, file sharing on a network, electronic commerce websites, or other applications. Sun Cluster operates by having redundant computers or nodes where one or more computers continue to provide service if another fails. Nodes may be located in the same data center or on different continents. Background Solaris Cluster provides services that remain available even when individual nodes or components of the cluster fail. Solaris Cluster provides two types of HA services: failover services and scalable services. To eliminate single points of failure, a Solaris Cluster configuration has redundant components, including multiple network connections and data storage which is multiply connected via a st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |