|
Opora (mythology)
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Opora ( grc, Ὀπώρα, Opṓra, autumn, fruit) is a minor goddess connected to fruit, the harvest, especially wine harvest, and the season of autumn. She is a fairly obscure goddess, although she features in a little-known myth centered around her romance with the stellar god Sirius, the Dog Star. A close equivalent in Roman mythology is found in the fertility goddess Pomona. Etymology The ancient Greek noun Opora referred to the part of the year between the rising of the stars Sirius and Arcturus, that is the end of July, all August and part of September at the end of summer; later it was used for late summer and autumn. In extension of its use for fruit-time it could refer to fruit itself, and figuratively to summer-bloom. The word apparently derives from the base of meaning "late, after" and meaning "hour, time". Robert Beekes suggests the Proto-Indo-European roots ''*h1opi'' meaning 'at, on' and ''*h1os-r/n-'' meaning 'harve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirius (mythology)
In Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology, Sirius . is the god and personification of the star Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky, also known as the Dog Star, the most prominent star in the constellation Canis Major (the Greater Dog). In ancient texts, Sirius is portrayed as the scorching bringer of the summer heatwaves, who intensifies the Sun's own heat. Etymology The ancient Greek word and proper noun has been connected to the verb (''seíō''), meaning to 'sparkle, to gleam' and has thus an Indo-European etymology; Furnée on the other hand compared it to the word (''tírios''), the Cretan word for summer, which, if correct, would mean that the word is pre-Greek instead. From this name an ancient phrase was derived, ' (literally "sirian passion", meaning burning passion). Description Sirius's divine parentage is not made entirely clear in ancient texts; in the ''Theogony'' the poet Hesiod names Eos (the dawn goddess) and her husband Astraeus (a star god) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eirene (goddess)
Eirene (; grc-gre, Εἰρήνη, ''Ëirene'', , "Peace"), more commonly known in English as Peace, was one of the Horae, the personification of peace. She was depicted in art as a beautiful young woman carrying a cornucopia, sceptre, and a torch or rhyton. She is said sometimes to be the daughter of Zeus and Themis and sister of Dike and Eunomia. Her Roman equivalent was Pax. Eirene was particularly well regarded by the citizens of Athens. After a naval victory over Sparta in 375 BC, the Athenians established a cult for Peace, erecting altars to her. They held an annual state sacrifice to her after 371 BC to commemorate the Common Peace of that year and set up a votive statue in her honour in the Agora of Athens. The statue was executed in bronze by Cephisodotus the Elder, likely the father or uncle of the famous sculptor Praxiteles. It was acclaimed by the Athenians, who depicted it on vases and coins. Although the statue is now lost, it was copied in marble by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scholia
Scholia (singular scholium or scholion, from grc, σχόλιον, "comment, interpretation") are grammatical, critical, or explanatory comments – original or copied from prior commentaries – which are inserted in the margin of the manuscript of ancient authors, as glosses. One who writes scholia is a scholiast. The earliest attested use of the word dates to the 1st century BC. History Ancient scholia are important sources of information about many aspects of the ancient world, especially ancient literary history. The earliest scholia, usually anonymous, date to the 5th or 4th century BC (such as the ''scholia minora'' to the ''Iliad''). The practice of compiling scholia continued to late Byzantine times, outstanding examples being Archbishop Eustathius' massive commentaries to Homer in the 12th century and the ''scholia recentiora'' of Thomas Magister, Demetrius Triclinius and Manuel Moschopoulos in the 14th. Scholia were altered by successive copyists an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexis (poet)
Alexis ( grc-gre, Ἄλεξις; c. 375 – c. 275 BC) was a Greek comic poet of the Middle Comedy period. He was born at Thurii (in present-day Calabria, Italy) in Magna Graecia and taken early to Athens, where he became a citizen, being enrolled in the deme ''Oion'' () and the tribe Leontides. It is thought he lived to the age of 106 and died on the stage while being crowned. According to the ''Suda'', a 10th-century encyclopedia, Alexis was the paternal uncle of the dramatist Menander and wrote 245 comedies, of which only fragments now survive, including some 130 preserved titles. Life He appears to have been rather addicted to the pleasures of the table, according to Athenaeus. He had a son named Stephanus (Στέφανος) who was also a comic poet. He won his first Lenaean victory in the 350s BC, most likely, where he was sixth after Eubulus, and fourth after Antiphanes. While being a Middle Comic poet, Alexis was contemporary with several leading figures of New Comedy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amphis
Amphis (Greek: Ἄμφις) was an Athenian comic poet of uncertain origin from approximately the 4th century BC. Pollux seems to refer to Amphis as a Middle Comedy poet, and Amphis' own repeated references to the philosopher PlatoAmphis (frr. 6; 13) place him in the early to mid-4th century BC. His name is not Athenian, and he was probably from the island of Andros (thus Kirchner). Surviving titles and fragments 49 fragments of his comedies survive, along with the following 28 titles. *''Athamas'' *''Acco'' *''Aleiptria'' (The Female Oiler, or Masseuse) *''Alcmaeon'' *''Ampleourgos'' (The Vine-Dresser) *''Amphicrates'' *''Balaneion'' (The Bath-House) *''Gynaikokratia'' (Women in Power) *''Gynaikomania'' (Crazy About Women) *''Daktylios'' (The Ring) *''Dexidemides'' *''Dithyrambos'' (The Dithyramb) *''Hepta Epi Thebais'' (Seven Against Thebes) *''Erithoi'' (Day-Labourers) *''Ialemos'' (The Oaf, or the Dirge) *''Kallisto'' (Callisto) *''Koniates'' (The Plasterer) *''Kouris'' (The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athenian
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates and is the capital of the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, with its recorded history spanning over 3,400 years and its earliest human presence beginning somewhere between the 11th and 7th millennia BC. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state. It was a centre for the arts, learning and philosophy, and the home of Plato's Academy and Aristotle's Lyceum. It is widely referred to as the cradle of Western civilization and the birthplace of democracy, largely because of its cultural and political influence on the European continent—particularly Ancient Rome. In modern times, Athens is a large cosmopolitan metropolis and central to economic, financial, industrial, maritime, political and cultural life in Greec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
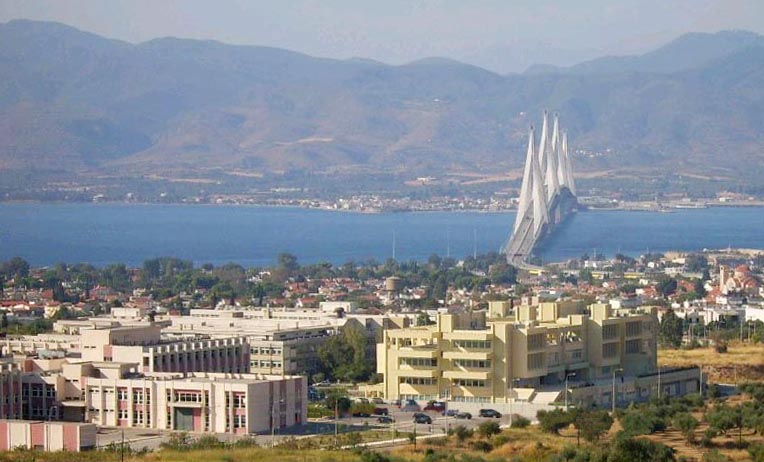
University Of Patras
The University of Patras (UPatras; el, Πανεπιστήμιο Πατρών, ''Panepistímio Patrón'') is a public university in Patras, Greece. It is the third-largest university in Greece with respect to the size of the student body, the staff, and the number of departments."''The EEC recommends that the Institution should develop and implement a pragmatic strategic planning process to set priorities for the university as a whole and for each School with an explicitly defined set of targets and timelines. The EEC evaluated and scored according to our estimate of where UPatras stands in relation to our understanding of an international norm of excellence. Although we are conscious of the severe constraints imposed by the Greek State, we have not used them as an excuse for not identifying areas of improvement. Please note that an EEC member gave a worthy of merit vote by taking into account with a heavier weight the negative influence of the external environment on UPatras's a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
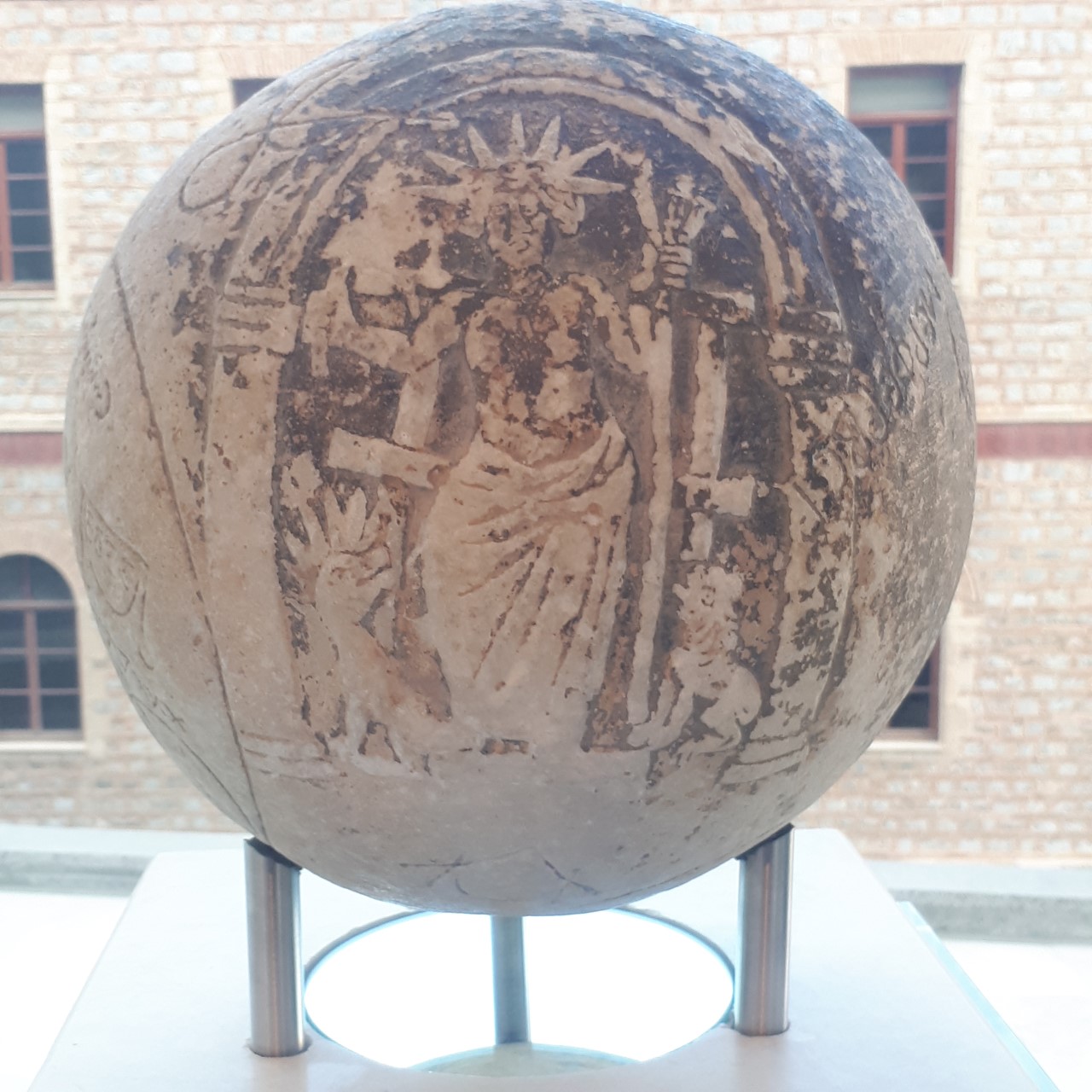
Helios
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Helios (; grc, , , Sun; Homeric Greek: ) is the deity, god and personification of the Sun (Solar deity). His name is also Latinized as Helius, and he is often given the epithets Hyperion ("the one above") and Phaethon ("the shining"). Helios is often depicted in art with a radiant crown and driving a horse-drawn chariot through the sky. He was a guardian of oaths and also the god of sight. Though Helios was a relatively minor deity in Classical Greece, his worship grew more prominent in late antiquity thanks to his identification with several major solar divinities of the Roman period, particularly Apollo and Sol (Roman mythology), Sol. The Roman Emperor Julian (emperor), Julian made Helios the central divinity of his short-lived revival of Religion in ancient Rome, traditional Roman religious practices in the 4th century AD. Helios figures prominently in several works of Greek mythology, poetry, and literature, in whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phaethon
Phaethon (; grc, Φαέθων, Phaéthōn, ), also spelled Phaëthon, was the son of the Oceanid Clymene and the sun-god Helios in Greek mythology. According to most authors, Phaethon is the son of Helios, and out of desire to have his parentage confirmed, travels to the sun-god's palace in the east. There he is recognised by his father, and asks him for the privilege to drive his chariot for a single day. Despite Helios' fervent warnings and attempts to talk him out of it, counting the numerous dangers he would face in his celestial journey and reminding Phaethon that only he can control the horses, the boy is not dissuaded and does not change his mind. He is then allowed to take the chariot's reins; his ride is disastrous, as he cannot keep a firm grip on the horses. As a result, he drives the chariot too close to the earth, burning it, and too far from it, freezing it. In the end, after many complaints, from the stars in the sky to the earth itself, Zeus strikes Phaethon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boreas (god)
In ancient Greek religion and myth, the Anemoi (Greek: , 'Winds') were wind gods who were each ascribed a cardinal direction from which their respective winds came (see Classical compass winds), and were each associated with various seasons and weather conditions. They were the progeny of the goddess of the dawn Eos and her husband Astraeus. Etymology The earliest attestation of the word in Greek and of the worship of the winds by the Greeks, are perhaps the Mycenaean Greek word-forms , , , , i.e. 'priestess of the winds'. These words, written in Linear B, are found on the KN Fp 1 and KN Fp 13 tablets. Mythology The Anemoi are minor gods and are subject to the god Aeolus. They were sometimes represented as gusts of wind, and at other times were personified as winged men. They were also sometimes depicted as horses kept in the stables of the storm god Aeolus, who provided Odysseus with the Anemoi in the ''Odyssey''. The Spartans were reported to sacrifice a horse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
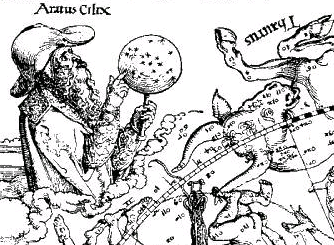
Aratus
Aratus (; grc-gre, Ἄρατος ὁ Σολεύς; c. 315 BC/310 BC240) was a Greek didactic poet. His major extant work is his hexameter poem ''Phenomena'' ( grc-gre, Φαινόμενα, ''Phainómena'', "Appearances"; la, Phaenomena), the first half of which is a verse setting of a lost work of the same name by Eudoxus of Cnidus. It describes the constellations and other celestial phenomena. The second half is called the ''Diosemeia'' (Διοσημεῖα "Forecasts"), and is chiefly about weather lore. Although Aratus was somewhat ignorant of Greek astronomy, his poem was very popular in the Greek and Roman world, as is proven by the large number of commentaries and Latin translations, some of which survive. Life There are several accounts of Aratus's life by anonymous Greek writers, and the Suda and Eudocia also mention him. From these it appears that he was a native of Soli in Cilicia, (although one authority says Tarsus). He is known to have studied with Menecrates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scholia
Scholia (singular scholium or scholion, from grc, σχόλιον, "comment, interpretation") are grammatical, critical, or explanatory comments – original or copied from prior commentaries – which are inserted in the margin of the manuscript of ancient authors, as glosses. One who writes scholia is a scholiast. The earliest attested use of the word dates to the 1st century BC. History Ancient scholia are important sources of information about many aspects of the ancient world, especially ancient literary history. The earliest scholia, usually anonymous, date to the 5th or 4th century BC (such as the ''scholia minora'' to the ''Iliad''). The practice of compiling scholia continued to late Byzantine times, outstanding examples being Archbishop Eustathius' massive commentaries to Homer in the 12th century and the ''scholia recentiora'' of Thomas Magister, Demetrius Triclinius and Manuel Moschopoulos in the 14th. Scholia were altered by successive copyists an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |