|
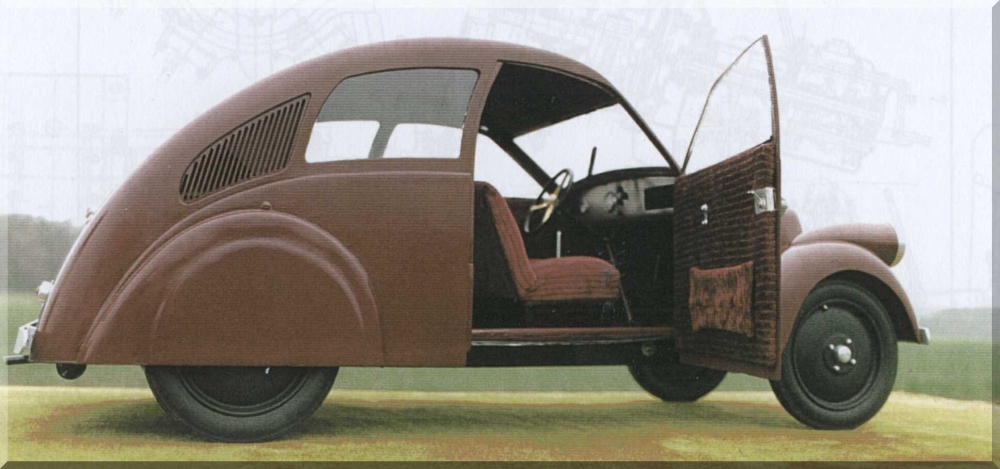
Opel Kadett B
The Opel Kadett B is a car that was launched by Opel at the Frankfurt Motor Show in late summer 1965. The Kadett B was larger all-round than the Kadett A: 5% longer both overall and in terms of the wheelbase, 7% wider and 9% heavier (unladen weight), albeit lower in basic standard "Limousine" (sedan/saloon) form. Production ended in July 1973, with the successor model introduced a month later following the summer shut-down, in August. Bodies: more choice Opel had built a reputation for providing stylish cars, and the simple well balanced proportions of the recently introduced Opel Rekord Series A had continued the tradition. The unapologetic slab-sided functionalism of the Kadett B disappointed some commentators. However, customers were not deterred, possibly because the simple car body enabled the car to provide an aggressively priced practical and modern car with far more interior space than the Volkswagen which hitherto had dominated the German small car market without seri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opel
Opel Automobile GmbH (), usually shortened to Opel, is a German automobile manufacturer which has been a subsidiary of Stellantis since 16 January 2021. It was owned by the American automaker General Motors from 1929 until 2017 and the PSA Group, a predecessor of Stellantis, from 2017 until 2021. Opel vehicles are sold in the United Kingdom as Vauxhall Motors, Vauxhall. Some Opel vehicles were badge engineering, badge-engineered in Australia under the Holden brand until 2020 and in North America and China under the Buick, Saturn Corporation, Saturn, and Cadillac brands. Opel traces its roots to a sewing machine manufacturer founded by Adam Opel in 1862 in Rüsselsheim am Main. The company began manufacturing bicycles in 1886 and produced its first automobile in 1899. With the Opel RAK program, the world's first rocket program, under the leadership of Fritz von Opel, the company played an important role in the history of aviation and spaceflight: Various land speed records were a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opel Kadett C
The Opel Kadett C is a small family car which was produced by the German automobile manufacturer Opel from 1973 to 1979. The Kadett C, which was the third generation of the Opel Kadett, was released in August 1973, Oswald 1945 - 90 (vol 3), pp. 236 & 239 and was Opel's version of the General Motors' "T-Car". It was the last small Opel to feature rear-wheel drive, and remained in production at Opel's Bochum plant until July 1979, by which time Opel had produced 1,701,076. Of these, 52% had been exported outside West Germany, Oswald 1945 - 90 (vol 3), p 237 most of them to markets in other parts of western Europe. In other world markets however, various badge engineered versions of the Kadett C remained in production as late as the mid 1990s under other GM brand names. Despite being out of mainstream production since 1979, in Europe the Kadett C retains something of a cult following (along with its Vauxhall Chevette sister) largely due to its popularity in the sport of drifting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opel Ascona
The Opel Ascona is a large family car (D-segment in Europe) that was produced by the German automaker Opel from 1970 to 1988. It was produced in three separate generations, beginning with rear-wheel-drive and ending up as a front-wheel drive J-car derivative. The Ascona took its name from the lakeside resort of that name in Ticino, Switzerland, and already in the 1950s a special edition of the Opel Rekord P1 was sold as an Opel Ascona in Switzerland, where the name was again used in 1968 for a locally adapted version of the Opel Kadett B into which the manufacturers had persuaded a 1.7-litre engine borrowed from the larger Rekord model of the time. The Opel Ascona A launched in 1970 and sold across Europe was, however, the first mainstream Opel model to carry the name. The Ascona was introduced in September 1970, lasting for 18 years and 3 generations and ended production in August 1988, to be replaced by the Opel Vectra A. In motorsport, Walter Röhrl won the 1982 World Rall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetraethyllead
Tetraethyllead (commonly styled tetraethyl lead), abbreviated TEL, is an organolead compound with the formula Pb( C2H5)4. It is a fuel additive, first being mixed with gasoline beginning in the 1920s as a patented octane rating booster that allowed engine compression to be raised substantially. This in turn increased vehicle performance and fuel economy. TEL was first synthesised by German chemist Carl Jacob Löwig in 1853. American chemical engineer Thomas Midgley Jr., who was working for General Motors, was the first to discover its effectiveness as an antiknock agent in 1921, after spending several years attempting to find an additive that was both highly effective and inexpensive. Concerns were later raised over the toxic effects of lead, especially on children. On cars not designed to operate on leaded gasoline, lead and lead oxides coat the catalyst in catalytic converters, rendering them ineffective, and can sometimes foul spark plugs. Starting in the 1970s, many cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
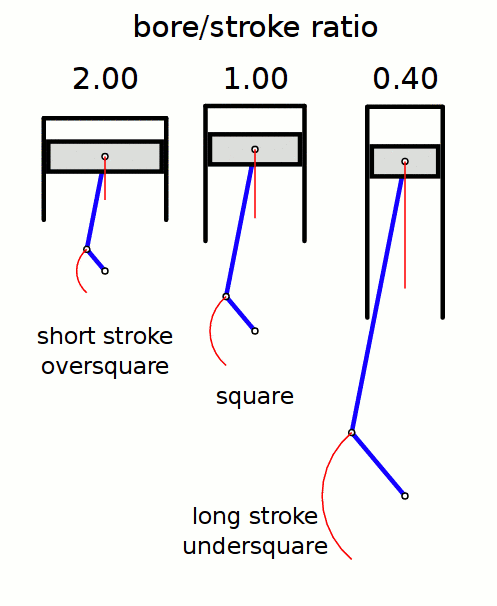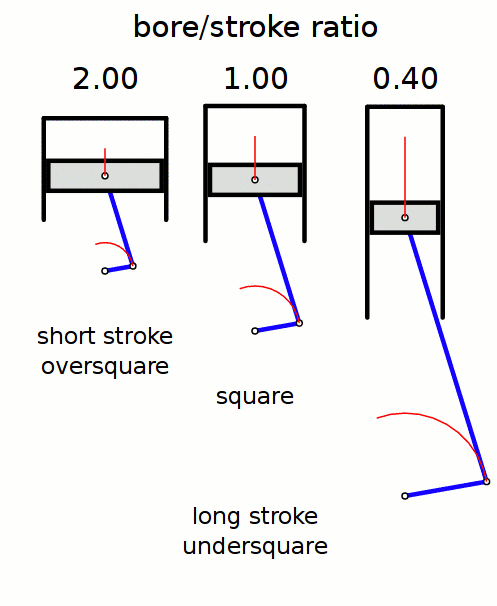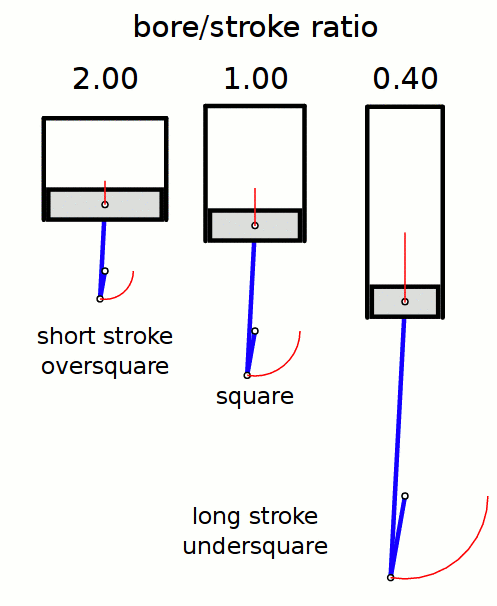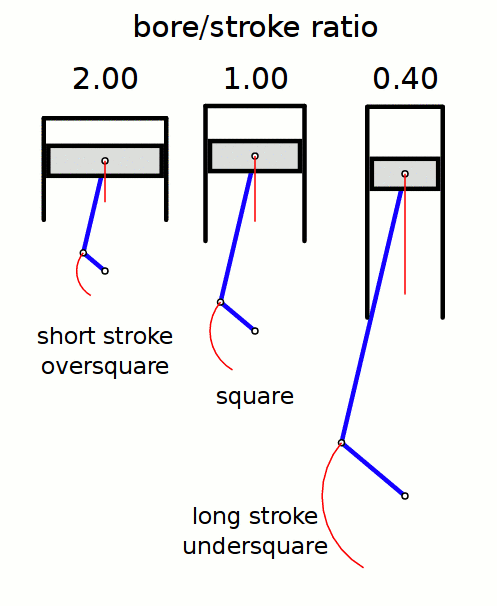
Stroke Ratio
In a reciprocating piston engine, the stroke ratio, defined by either bore/stroke ratio or stroke/bore ratio, is a term to describe the ratio between cylinder bore diameter and piston stroke length. This can be used for either an internal combustion engine, where the fuel is burned within the cylinders of the engine, or external combustion engine, such as a steam engine, where the combustion of the fuel takes place ''outside'' the working cylinders of the engine. A fairly comprehensive yet understandable study of stroke/bore effects was published in ''Horseless Age'', 1916. Conventions In a piston engine, there are two different ways of describing the ''stroke ratio'' of its cylinders, namely: ''bore/stroke'' ratio, and ''stroke/bore'' ratio. Bore/stroke ratio Bore/stroke is the more commonly used term, with usage in North America, Europe, United Kingdom, Asia, and Australia. The diameter of the cylinder bore is divided by the length of the piston stroke to give the rati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
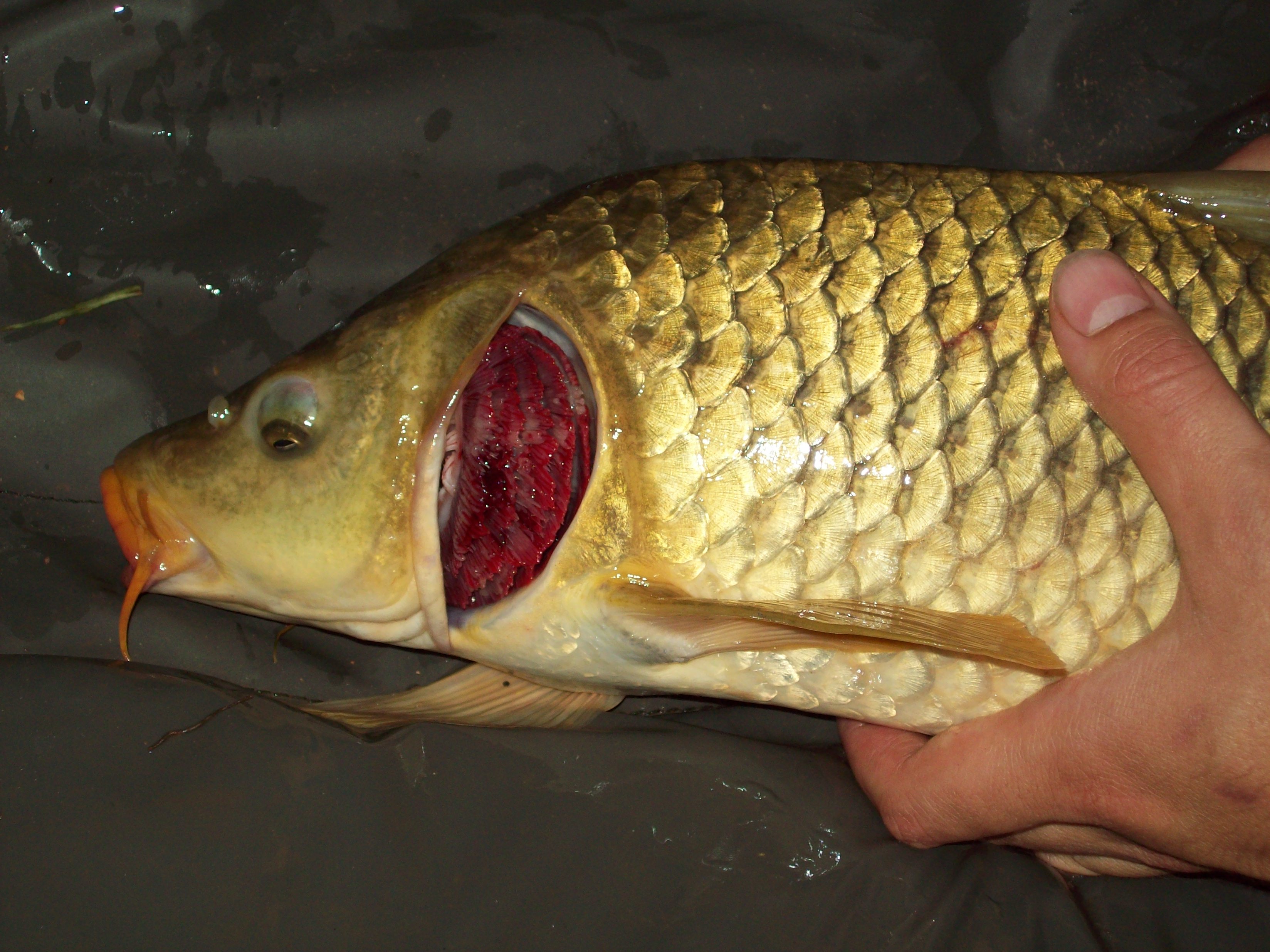
Gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are kept moist. The microscopic structure of a gill presents a large surface area to the external environment. Branchia (pl. branchiae) is the zoologists' name for gills (from Ancient Greek ). With the exception of some aquatic insects, the filaments and lamellae (folds) contain blood or coelomic fluid, from which gases are exchanged through the thin walls. The blood carries oxygen to other parts of the body. Carbon dioxide passes from the blood through the thin gill tissue into the water. Gills or gill-like organs, located in different parts of the body, are found in various groups of aquatic animals, including mollusks, crustaceans, insects, fish, and amphibians. Semiterrestrial marine animals such as crabs and mudskippers have gill cham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B-pillar
The pillars on a car with permanent roof body style (such as four-door sedans) are the vertical or nearly vertical supports of its window area or greenhouse—designated respectively as the ''A, B, C'' and (in larger cars such as 4-door station wagons and sport utility vehicles) ''D-pillar,'' moving from front to rear, in profile view. Nomenclature Car pillars are components that support the structure of an enclosed automobile body. This is similar to that of a house with pillars supporting the roof over the floor. Car pillars are designed to stand in near vertical or inclined positions to support the roof. The consistent alphabetical designation of a car's pillars provides a common reference for design discussion and critical communication. This is used by insurance companies to identify damaged components and rescue teams employ pillar nomenclature to facilitate communication when cutting wrecked vehicles, as when using the jaws of life. The A-pillars on each side of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-pillar
The pillars on a car with permanent roof body style (such as four-door sedans) are the vertical or nearly vertical supports of its window area or greenhouse—designated respectively as the ''A, B, C'' and (in larger cars such as 4-door station wagons and sport utility vehicles) ''D-pillar,'' moving from front to rear, in profile view. Nomenclature Car pillars are components that support the structure of an enclosed automobile body. This is similar to that of a house with pillars supporting the roof over the floor. Car pillars are designed to stand in near vertical or inclined positions to support the roof. The consistent alphabetical designation of a car's pillars provides a common reference for design discussion and critical communication. This is used by insurance companies to identify damaged components and rescue teams employ pillar nomenclature to facilitate communication when cutting wrecked vehicles, as when using the jaws of life. The A-pillars on each side of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deutsche Mark
The Deutsche Mark (; English: ''German mark''), abbreviated "DM" or "D-Mark" (), was the official currency of West Germany from 1948 until 1990 and later the unified Germany from 1990 until the adoption of the euro in 2002. In English, it was typically called the "Deutschmark" (). One Deutsche Mark was divided into 100 pfennigs. It was first issued under Allied occupation in 1948 to replace the Reichsmark and served as the Federal Republic of Germany's official currency from its founding the following year. On 31 December 1998, the Council of the European Union fixed the irrevocable exchange rate, effective 1 January 1999, for German mark to euros as DM 1.95583 = €1. In 1999, the Deutsche Mark was replaced by the euro; its coins and banknotes remained in circulation, defined in terms of euros, until the introduction of euro notes and coins on 1 January 2002. The Deutsche Mark ceased to be legal tender immediately upon the introduction of the euro—in contrast to the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volkswagen Type 1
The Volkswagen Beetle—officially the Volkswagen Type 1, informally in German (meaning "beetle"), in parts of the English-speaking world the Bug, and known by many other nicknames in other languages—is a two-door, rear-engine economy car, intended for five occupants (later, Beetles were restricted to four people in some countries), that was manufactured and marketed by German automaker Volkswagen (VW) from 1938 until 2003. The need for a ''people's car'' ( in German), its concept and its functional objectives were formulated by the leader of Nazi Germany, Adolf Hitler, who wanted a cheap, simple car to be mass-produced for his country's new road network (Reichsautobahn). Members of the National Socialist party, with an additional dues surcharge, were promised the first production, but the Spanish Civil War shifted most production resources to military vehicles to support the Nationalists under Francisco Franco. Lead engineer Ferdinand Porsche and his team took until 1938 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opel Rekord Series A
The Opel Rekord Series A is an executive car introduced in March 1963, by Opel as a replacement for the Opel Rekord P2. It was fractionally shorter but also wider than its predecessor with a wheelbase approximately 10 cm longer. The Rekord (Series A) combined a stylish modern body with a range of engines little changed since 1937. In August 1965 it was replaced by the Opel Rekord (Series B) which from the outside was surprisingly similar, but which under the bonnet/hood would introduce a new generation of four-cylinder engines that would power Rekords until 1986, when Rüsselsheim produced its last Opel Rekord. The car The Rekord A that appeared in March 1963 was a robust response to the success of the Ford Taunus 17M. The design of the new Rekord sedan came not from Germany but from the General Motors Technical Center in Warren, Michigan, and was inspired by the successful Chevrolet II. It was styled to look slimmer and more sporty than its predecessor, but undern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |