|
One Hundred Views Of Mount Fuji
is a series of three illustrated books by Japanese ukiyo-e artist Hokusai. It is considered one of Japan's most exceptional illustrated books ('' e-hon''), and alongside the ''Hokusai Manga'', the most influential in the West. The first two volumes were published in 1834 and 1835, shortly after completion of his seminal '' Thirty-six Views of Mount Fuji'', with a third released in the late 1840s. The books contain over a hundred views of Mount Fuji in various styles and settings; Hokusai shows the peak in pure landscapes, with flora and fauna, in religious and mythological scenes and with different atmospheric effects, but above all, he focuses on ordinary people at work. The first two volumes are celebrated for their very high standards of woodblock printing, with "extremely fine cutting" and "exquisite gradation" ('' bokashi'') of the grey blocks; they have been called a "masterpiece of monochrome printing". Publication The first two volumes have embossed pink covers and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hokusai
, known simply as Hokusai, was a Japanese ukiyo-e artist of the Edo period, active as a painter and printmaker. He is best known for the woodblock printing in Japan, woodblock print series ''Thirty-Six Views of Mount Fuji'', which includes the iconic print ''The Great Wave off Kanagawa''. Hokusai was instrumental in developing ''ukiyo-e'' from a style of portraiture largely focused on courtesans and actors into a much broader style of art that focused on landscapes, plants, and animals. Hokusai created the monumental ''Thirty-Six Views of Mount Fuji'' as a response to a domestic travel boom in Japan and as part of a personal interest in Mount Fuji. It was this series, specifically, ''The Great Wave off Kanagawa'' and ''Fine Wind, Clear Morning'', that secured his fame both in Japan and overseas. Hokusai was best known for his woodblock ukiyo-e prints, but he worked in a variety of mediums including painting and book illustration. Starting as a young child, he continued workin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Works By Hokusai
Works may refer to: People * Caddy Works (1896–1982), American college sports coach * Samuel Works (c. 1781–1868), New York politician Albums * '' ''Works'' (Pink Floyd album)'', a Pink Floyd album from 1983 * ''Works'', a Gary Burton album from 1972 * ''Works'', a Status Quo album from 1983 * ''Works'', a John Abercrombie album from 1991 * ''Works'', a Pat Metheny album from 1994 * ''Works'', an Alan Parson Project album from 2002 * ''Works Volume 1'', a 1977 Emerson, Lake & Palmer album * ''Works Volume 2'', a 1977 Emerson, Lake & Palmer album * '' The Works'', a 1984 Queen album Other uses * Microsoft Works, a collection of office productivity programs created by Microsoft * IBM Works, an office suite for the IBM OS/2 operating system * Mount Works, Victoria Land, Antarctica See also * The Works (other) * Work (other) Work may refer to: * Work (human activity), intentional activity people perform to support themselves, others, or the community ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jack Hillier (art Historian)
Jack Ronald Hillier (29 August 1912 – 5 January 1995) was a British scholar of Japanese art. Hillier was born on 29 August 1912 in Fulham, England to Charles Hillier and his wife Minnie (née Davies).''Who's Who in the World'', 1976, Marquis Who's Who, p. 352 His father was a postman; one of five siblings, Hillier had a "happy, if slightly impoverished, childhood." His only early "tenuous connection with art was that his father, during his rounds, delivered the mail of Edward Burne Jones, the noted late Victorian artist, who lived in Kensington." He left Fulham Secondary School at 15 and worked for an insurance company until 1967. During World War II he served in the Royal Air Force. Although he applied to be a pilot, "regrettably, the detailed work that he carried out during the day, combined with his wood engraving, had slightly impaired his eyesight, and his application, therefore, was not accepted".Essays on Japanese Art presented to Jack Hillier, ed. Matthi Forrer, R. G. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colophon (publishing)
In publishing, a colophon () is a brief statement containing information about the publication of a book such as an "imprint" (the place of publication, the publisher, and the date of publication). A colophon may include the device (logo) of a printer or publisher. Colophons are traditionally printed at the ends of books (see History below for the origin of the word), but sometimes the same information appears elsewhere (when it may still be referred to as colophon) and many modern (post-1800) books bear this information on the title page or on the verso of the title-leaf, which is sometimes called a "biblio-page" or (when bearing copyright data) the " copyright-page". History The term ''colophon'' derives from the Late Latin ''colophōn'', from the Greek κολοφών (meaning "summit" or "finishing touch"). The term colophon was used in 1729 as the bibliographic explication at the end of the book by the English printer Samuel Palmer in his ''The General History of Printing, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagoya
is the largest city in the Chūbu region, the fourth-most populous city and third most populous urban area in Japan, with a population of 2.3million in 2020. Located on the Pacific coast in central Honshu, it is the capital and the most populous city of Aichi Prefecture, and is one of Japan's major ports along with those of Tokyo, Osaka, Kobe, Yokohama, and Chiba. It is the principal city of the Chūkyō metropolitan area, which is the third-most populous metropolitan area in Japan with a population of 10.11million in 2020. In 1610, the warlord Tokugawa Ieyasu, a retainer of Oda Nobunaga, moved the capital of Owari Province from Kiyosu to Nagoya. This period saw the renovation of Nagoya Castle. The arrival of the 20th century brought a convergence of economic factors that fueled rapid growth in Nagoya, during the Meiji Restoration, and became a major industrial hub for Japan. The traditional manufactures of timepieces, bicycles, and sewing machines were followed by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egawa Tomekichi
Egawa Tomekichi (fl. ) was a master carver of Japanese woodblock prints in Edo period Japan. He is known for his exceptional work on Hokusai's illustrated books (''e-hon'') such as the ''Hokusai Manga'' and his ''100 Views of Mount Fuji'' which is considered a masterpiece of the artform. Hokusai had studied carving as an apprentice and as an exceptional draughtsman, he relied on the woodblock carver to accurately replicate the quality of his line when it came to printing. In an 1835 letter sent to various publishers, he complained about the standard of cutting in earlier editions of his ''Manga'', ''Musha-e zukushi'', and other books, and urged repeatedly that they employ Egawa Tomechiki of Asakusa in future. Egawa is credited in the twelfth volume of the ''Manga'' published in 1834, and Hokusai praised his work on his recently issued ''100 Views of Mount Fuji is a series of three illustrated books by Japanese ukiyo-e artist Hokusai. It is considered one of Japan's most exce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nishimuraya Yohachi
Nishimuraya Yohachi (dates unknown) was one of the leading publishers of woodblock prints in late 18th Japan. He founded the Nishimuraya Yohachi publishing house, also known as Nishiyo (西与), which operated in Nihonbashi's Bakurochō Nichōme under the shop name Eijudō. The firm's exact dates are unclear, but many art historians date its activity to between . According to Andreas Marks, Nishimuraya is "one of the most important publishers in the history of prints and may be the publisher with the biggest output over time," attributing his success to "engaging the best artists and providing a broad range of prints to satisfy the public's interest." One of the press' most significant products was Hokusai's famous '' Thirty-six Views of Mount Fuji'', which appeared between and the first two volumes of his exquisite ''100 Views of Mount Fuji'' ehon in 1834 and 1835. Nishimuraya Yohachi also published prints by Eishi, Kuniyasu, Toyokuni I and Kunisada. Nishimuraya is immortalized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bokashi (printing)
''Bokashi'' (Japanese: ぼかし) is a technique used in Japanese woodblock printmaking. It achieves a variation in lightness and darkness (value) of a single color or multiple colors by hand applying a gradation of ink to a moistened wooden printing block, rather than inking the block uniformly. This hand-application had to be repeated for each sheet of paper that was printed. The best-known examples of bokashi are in the 19th-century ''ukiyo-e'' works of Hokusai and Hiroshige, in which the fading of Prussian blue dyes in skies and water create an illusion of depth. In later works by Hiroshige, for example the series ''One Hundred Famous Views of Edo'', most prints originally featured bokashi such as red-to-yellow-to-blue color sunrises. Techniques Gradations can be created on the blocks themselves using the ' technique, or brushed on by hand using '. They can also be done freehand directly onto a print, without using a printing block. ''Fukibokashi'' ' requires gradations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-hon
is the Japanese term for picture books. It may be applied in the general sense, or may refer specifically to a type of woodblock printed illustrated volume published in the Edo period (1603–1867). The first were religious items with images by Buddhist painters. Those from the Muromachi period are typically known as . In the early modern period (1600–1868) illustrated books exploded in popularity. They covered a diverse range of subjects with experimentation in production techniques. production was a significant part of the Japanese publishing industry (particularly) during the 19th century; most Japanese woodblock print artists of the period produced designs (often in large quantities), as commercial work. Toward the end of the 19th century, chapter-books were eclipsed in popularity by the new "Western" concept of literary magazines. These were larger books which contained more, and a wider range of material per-issue, but usually fewer pictures (measured on a text-to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moku Hanga
Woodblock printing in Japan (, ''mokuhanga'') is a technique best known for its use in the ''ukiyo-e'' artistic genre of single sheets, but it was also used for printing books in the same period. Widely adopted in Japan during the Edo period (1603–1868) and similar to woodcut in Western printmaking in some regards, the mokuhanga technique differs in that it uses water-based inks—as opposed to western woodcut, which typically uses oil-based inks. The Japanese water-based inks provide a wide range of vivid colors, glazes, and transparency. History Early, to 13th century In 764 the Empress Kōken commissioned one million small wooden pagodas, each containing a small woodblock scroll printed with a Buddhist text (''Hyakumantō Darani''). These were distributed to temples around the country as thanks for the suppression of the Emi Rebellion of 764. These are the earliest examples of woodblock printing known, or documented, from Japan. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
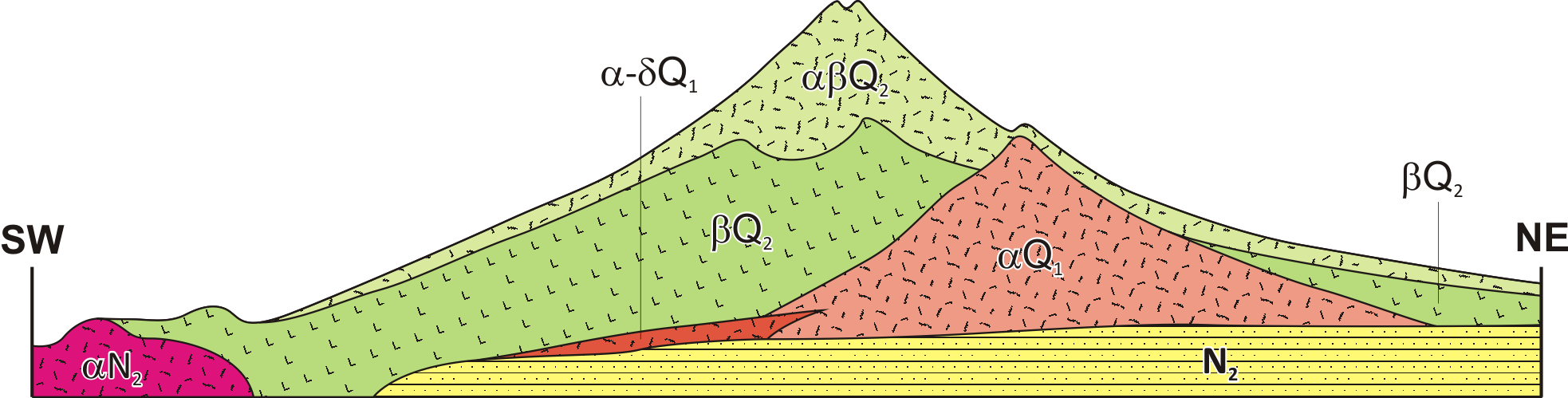
Mount Fuji
, or Fugaku, located on the island of Honshū, is the highest mountain in Japan, with a summit elevation of . It is the second-highest volcano located on an island in Asia (after Mount Kerinci on the island of Sumatra), and seventh-highest peak of an island on Earth. Mount Fuji is an active stratovolcano that last erupted from 1707 to 1708. The mountain is located about southwest of Tokyo and is visible from there on clear days. Mount Fuji's exceptionally symmetrical cone, which is covered in snow for about five months of the year, is commonly used as a cultural icon of Japan and it is frequently depicted in art and photography, as well as visited by sightseers and climbers. Mount Fuji is one of Japan's along with Mount Tate and Mount Haku. It is a Special Place of Scenic Beauty and one of Japan's Historic Sites. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |