|
OnePlus 8T
The OnePlus 8T is an Android-based smartphone designed and marketed by OnePlus. It is the sixteenth phone released by OnePlus, and was announced on 14 October 2020, and released on 16 October 2020. A variant of this phone is sold by T-Mobile US as the OnePlus 8T+. Specifications Design The OnePlus 8T is similar to the OnePlus 8 externally, with an anodized aluminum frame and Gorilla Glass 5 panels. The display has a circular cutout for the front-facing camera. However, it is differentiated by its display glass, which is flat rather than curved. The back panel has a different camera module with a raised rectangular lens, split into two columns. The first contains three of the cameras, while the second contains the depth sensor, color temperature sensor and dual-LED flash. It is available in two finishes, Aquamarine Green (glossy) and Lunar Silver (matte). Hardware The OnePlus 8T is powered by the Snapdragon 865 5G processor with the Adreno 650 GPU, accompanied by 128 or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
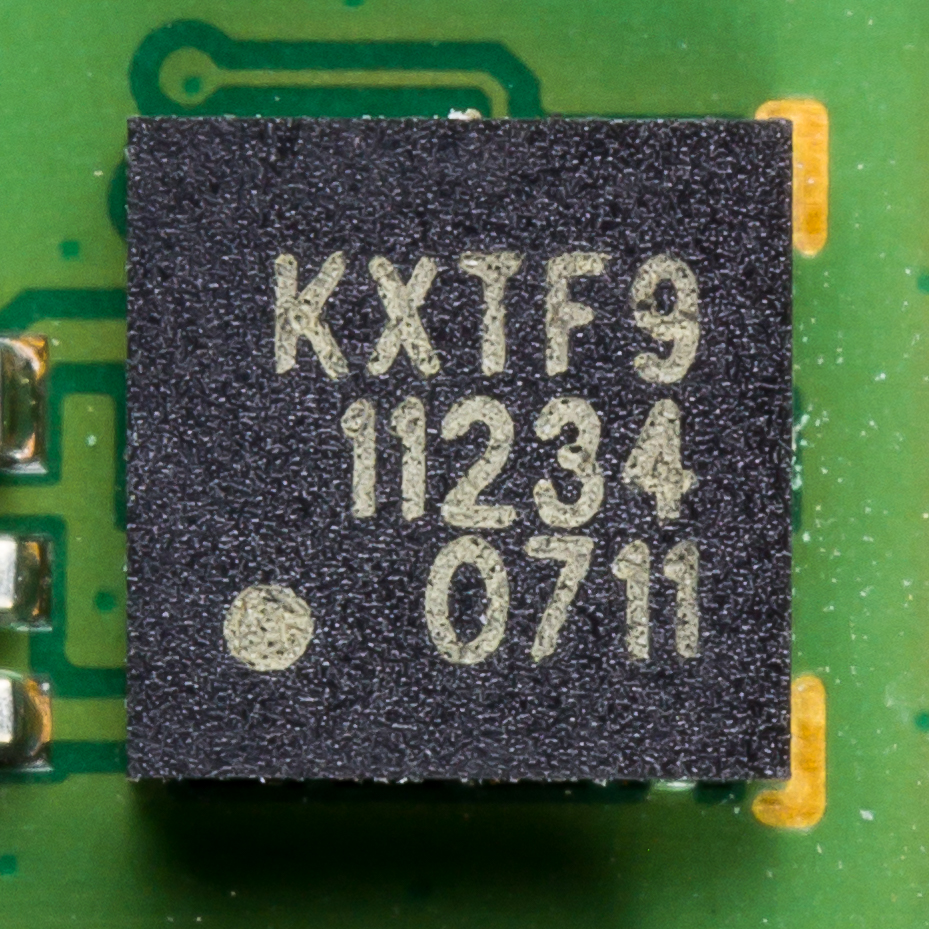
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration in a fixed coordinate system. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an acceleration due to Earth's gravity, straight upwards (by definition) of g ≈ 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, accelerometers in free fall (falling toward the center of the Earth at a rate of about 9.81 m/s2) will measure zero. Accelerometers have many uses in industry and science. Highly sensitive accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems for aircraft and missiles. Vibration in rotating machines is monitored by accelerometers. They are used in tablet computers and digital cameras so that images on screens are always displayed upright. In unmanned aerial vehicles, accelerometers help to stabilise flight. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
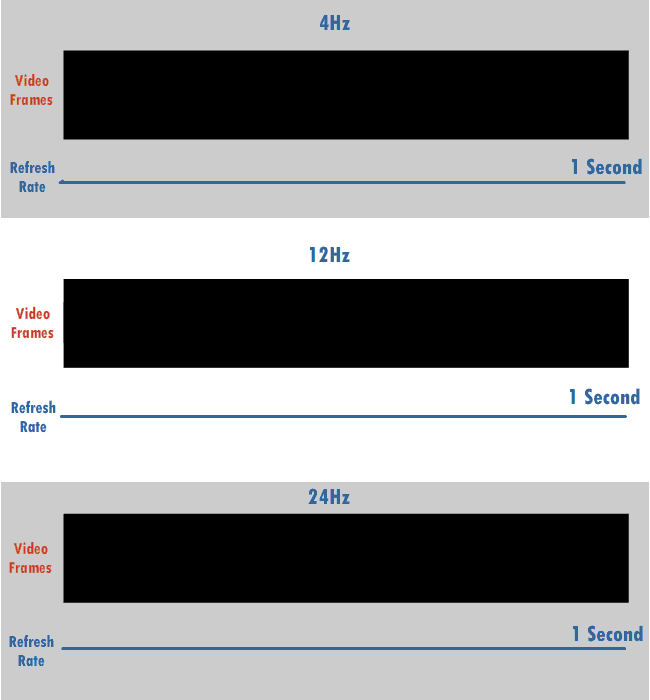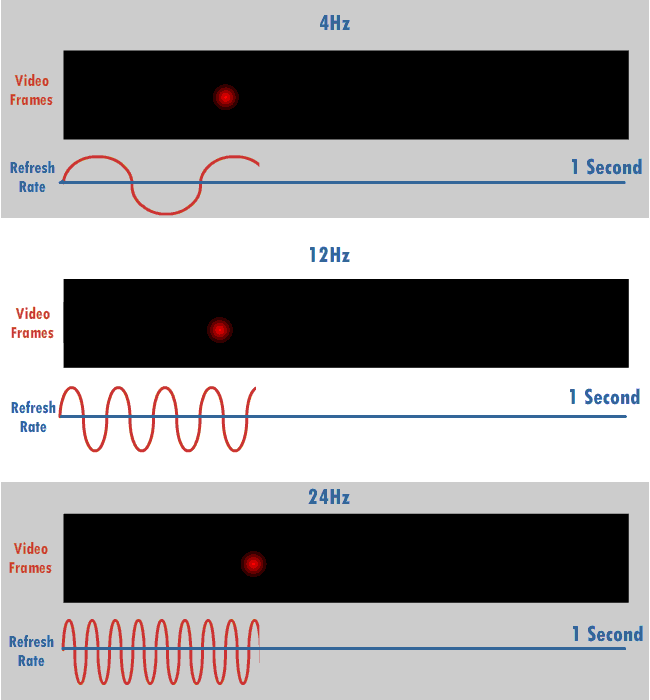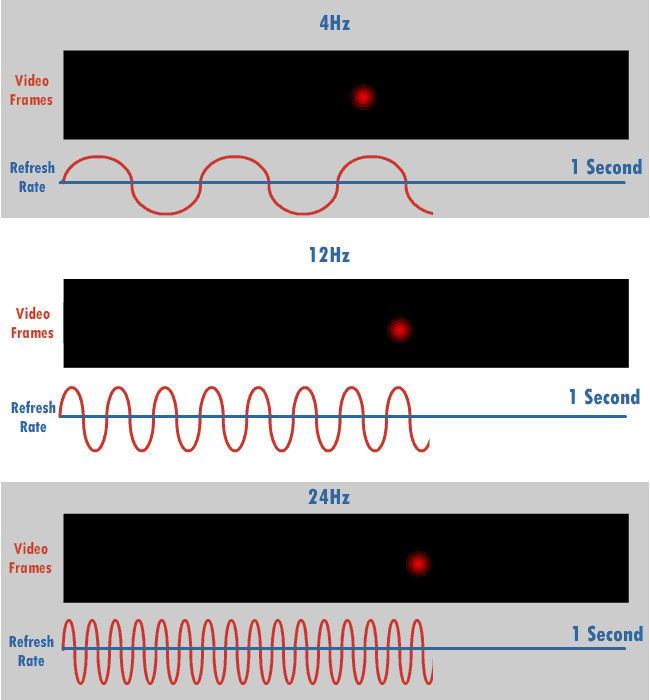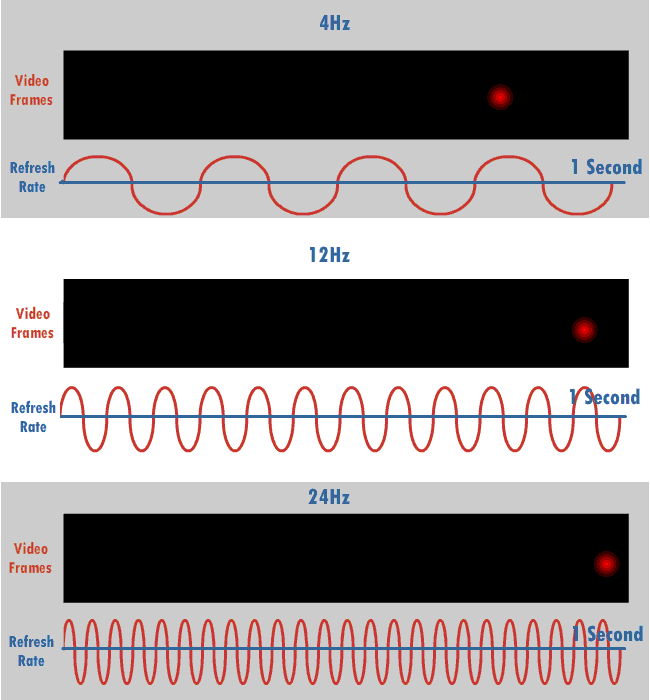
Refresh Rate
The refresh rate (or "vertical refresh rate", "vertical scan rate", terminology originating with the cathode ray tubes) is the number of times per second that a raster-based display device displays a new image. This is independent from frame rate, which describes how many images are stored or generated every second by the device driving the display. On cathode ray tube (CRT) displays, higher refresh rates produce less flickering, thereby reducing eye strain. In other technologies such as liquid-crystal displays, the refresh rate affects only how often the image can potentially be updated. Non-raster displays may not have a characteristic refresh rate. Vector displays, for instance, do not trace the entire screen, only the actual lines comprising the displayed image, so refresh speed may differ by the size and complexity of the image data. For computer programs or telemetry, the term is sometimes applied to how frequently a datum is updated with a new external value from anothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one hertz is the reciprocal of one second. It is named after Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (1857–1894), the first person to provide conclusive proof of the existence of electromagnetic waves. Hertz are commonly expressed in multiples: kilohertz (kHz), megahertz (MHz), gigahertz (GHz), terahertz (THz). Some of the unit's most common uses are in the description of periodic waveforms and musical tones, particularly those used in radio- and audio-related applications. It is also used to describe the clock speeds at which computers and other electronics are driven. The units are sometimes also used as a representation of the energy of a photon, via the Planck relation ''E'' = ''hν'', where ''E'' is the photon's energy, ''ν'' is its freq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Display Aspect Ratio
The aspect ratio of a display device is the proportional relationship between the width and the height of the display. It is expressed as two numbers separated by a colon (''x'':''y''), where ''x'' corresponds to the width and ''y'' to the height. Common aspect ratios for displays, past and present, include 5:4, 4:3, 16:10 and 16:9. Computer displays As of 2016, most computer monitors use widescreen displays with an aspect ratio of 16:9, although some portable PCs use narrower aspect ratios like 3:2 and 16:10 while some high-end desktop monitors have adopted ultrawide displays. The following table summarises the different aspect ratios that have been used in computer displays: † The resolution doesn't match the aspect ratio exactly, but is commonly marketed or described as such. History 4:3, 5:4 and 16:10 Until about 2003, most computer monitors used an aspect ratio of 4:3, and in some cases 5:4. For cathode ray tubes (CRT)s 4:3 was most common even in resolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pixel Density
Pixels per inch (ppi) and pixels per centimetre (ppcm or pixels/cm) are measurements of the pixel density of an electronic image device, such as a computer monitor or television display, or image digitizing device such as a camera or image scanner. Horizontal and vertical density are usually the same, as most devices have square pixels, but differ on devices that have non-square pixels. Note that pixel density is not the same as where the former describes the amount of detail on a physical surface or device, the latter describes the amount of pixel information regardless of its scale. Considered in another way, a pixel has no inherent size or unit (a pixel is actually a sample), but when it is printed, displayed, or scanned, then the pixel has both a physical size (dimension) and a pixel density (ppi). Basic principles Since most digital hardware devices use dots or pixels, the size of the media (in inches) and the number of pixels (or dots) are directly related by the 'pixels per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AMOLED
AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode, ) is a type of OLED display device technology. OLED describes a specific type of thin-film-display technology in which organic compounds form the electroluminescence, electroluminescent material, and active matrix refers to the technology behind the addressing of pixels. Since 2007, AMOLED technology has been used in mobile phones, media players, TVs and digital cameras, and it has continued to make progress toward low-power, low-cost, high resolution and large size (for example, 88-inch and 8K resolution) applications. Design An AMOLED display consists of an active matrix of OLED pixels generating light (luminescence) upon electrical activation that have been deposited or integrated onto a thin-film transistor (TFT) array, which functions as a series of switches to control the current flowing to each individual pixel. Typically, this continuous current flow is controlled by at least two TFTs at each pixel (to trigger the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
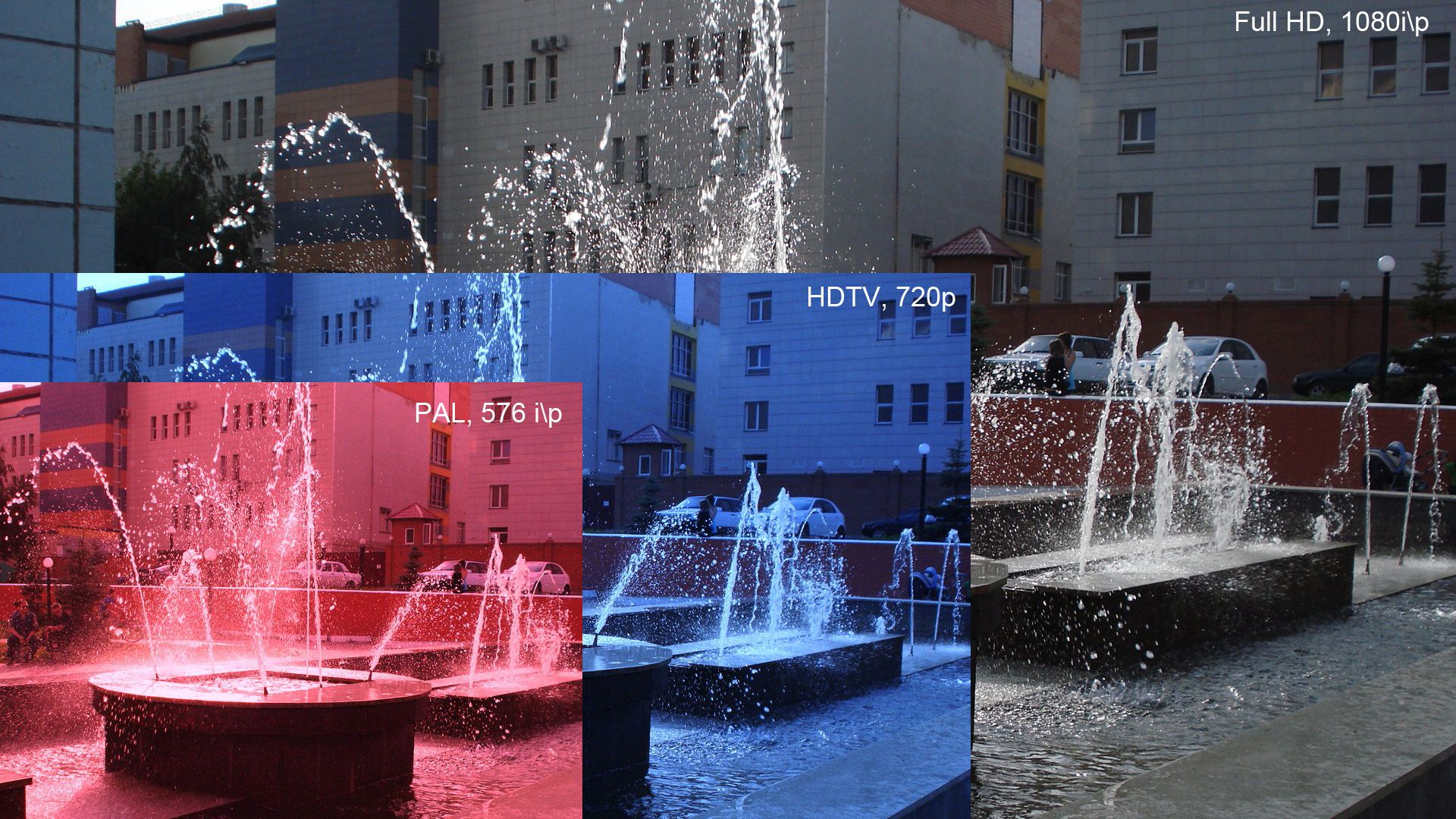
1080p
1080p (1920×1080 progressively displayed pixels; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709) is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the ''p'' stands for progressive scan, ''i.e.'' non-interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixels. It is often marketed as Full HD or FHD, to contrast 1080p with 720p resolution screens. Although 1080p is sometimes informally referred to as 2K, these terms reflect two distinct technical standards, with differences including resolution and aspect ratio. 1080p video signals are supported by ATSC standards in the United States and DVB standards in Europe. Applications of the 1080p standard include television broadcasts, Blu-ray Discs, smartphones, Internet content such as YouTube videos and Netflix TV shows and movies, consumer-grade televisions and projector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
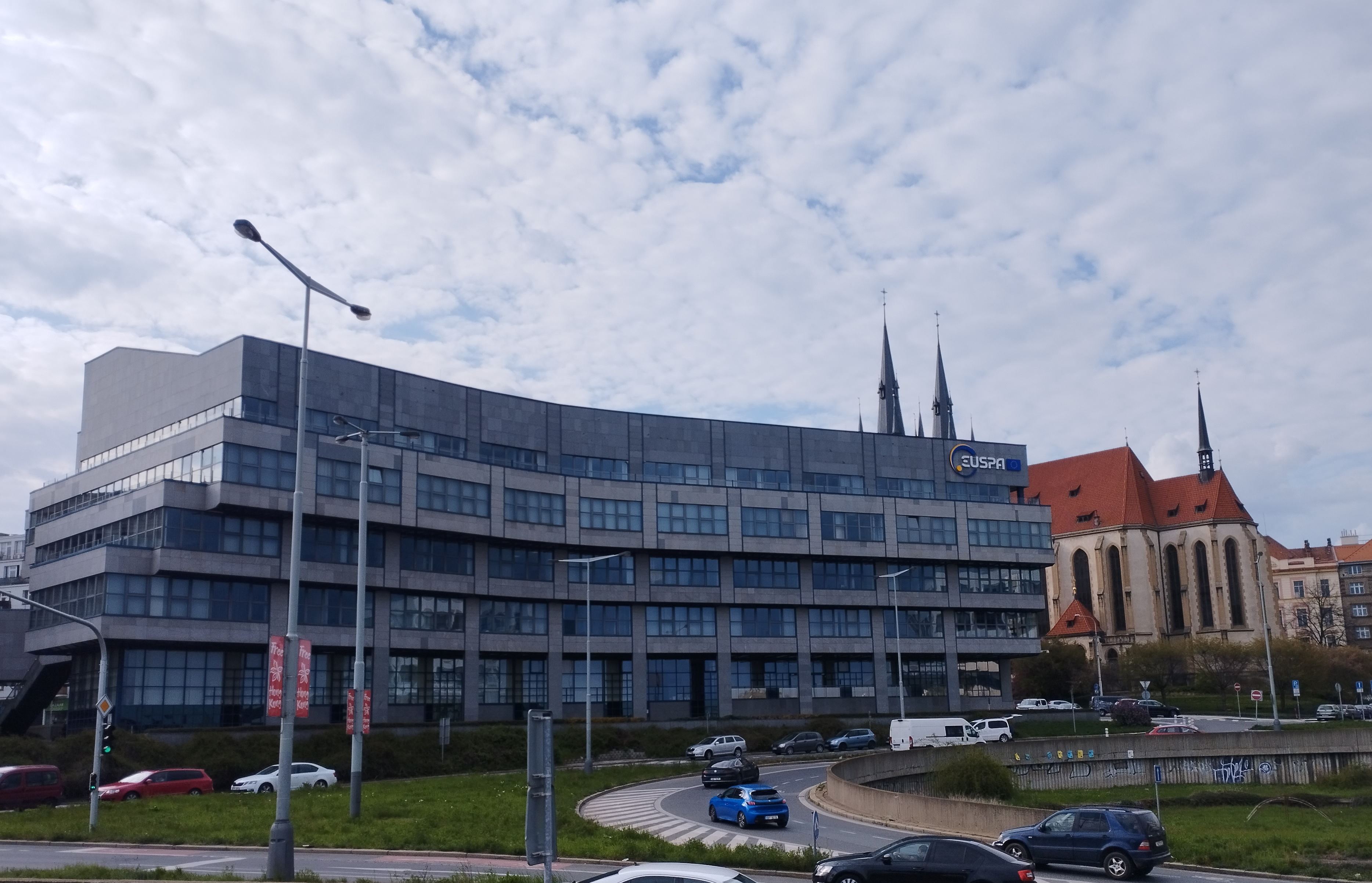
Galileo (satellite Navigation)
Galileo is a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) that went live in 2016, created by the European Union through the European Space Agency (ESA), operated by the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA), headquartered in Prague, Czech Republic, with two ground operations centres in Fucino, Italy, and Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany. The €10 billion project is named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei. One of the aims of Galileo is to provide an independent high-precision positioning system so European political and military authorities do not have to rely on the US GPS, or the Russian GLONASS systems, which could be disabled or degraded by their operators at any time. The use of basic (lower-precision) Galileo services is free and open to everyone. A fully encrypted higher-precision service is available for free to government-authorized users. Galileo is intended to provide horizontal and vertical position measurements within 1 m precision. Galileo is al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BeiDou Navigation Satellite System
The BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS; ) is a Chinese satellite navigation system. It consists of two separate satellite constellations. The first BeiDou system, officially called the BeiDou Satellite Navigation Experimental System and also known as BeiDou-1, consisted of three satellites which, beginning in 2000, offered limited coverage and navigation services, mainly for users in China and neighboring regions. BeiDou-1 was decommissioned at the end of 2012. The second generation of the system, officially called the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) and also known as COMPASS or BeiDou-2, became operational in China in December 2011 with a partial constellation of 10 satellites in orbit. Since December 2012, it has been offering services to customers in the Asia-Pacific region. In 2015, China launched the third generation BeiDou system (BeiDou-3) for global coverage. The first BDS-3 satellite was launched on 30 March 2015. On 27 December 2018, BeiDou Navigation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GLONASS
GLONASS (russian: ГЛОНАСС, label=none, ; rus, links=no, Глобальная навигационная спутниковая система, r=Global'naya Navigatsionnaya Sputnikovaya Sistema, t=Global Navigation Satellite System) is a Russian satellite navigation system operating as part of a radionavigation-satellite service. It provides an alternative to Global Positioning System (GPS) and is the second navigational system in operation with global coverage and of comparable precision. Satellite navigation devices supporting both GPS and GLONASS have more satellites available, meaning positions can be fixed more quickly and accurately, especially in built-up areas where buildings may obscure the view to some satellites. GLONASS supplementation of GPS systems also improves positioning in high latitudes (north or south). Development of GLONASS began in the Soviet Union in 1976. Beginning on 12 October 1982, numerous rocket launches added satellites to the system, unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Navigation
A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geo-spatial positioning. It allows satellite navigation devices to determine their location (longitude, latitude, and altitude/elevation) to high precision (within a few centimetres to metres) using time signals transmitted along a line of sight by radio from satellites. The system can be used for providing position, navigation or for tracking the position of something fitted with a receiver (satellite tracking). The signals also allow the electronic receiver to calculate the current local time to a high precision, which allows time synchronisation. These uses are collectively known as Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT). One set of critical vulnerabilities in satellite communications are the signals that govern positioning, navigation and timing (PNT). Failure to properly secure these transmissions could not only disrupt satellite networks but wreak havoc on a host of dependent s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |