|
One-hot Encoding
In digital circuits and machine learning, a one-hot is a group of bits among which the legal combinations of values are only those with a single high (1) bit and all the others low (0). A similar implementation in which all bits are '1' except one '0' is sometimes called one-cold. In statistics, dummy variables represent a similar technique for representing categorical data. Applications Digital circuitry One-hot encoding is often used for indicating the state of a state machine. When using binary, a decoder is needed to determine the state. A one-hot state machine, however, does not need a decoder as the state machine is in the ''n''th state if, and only if, the ''n''th bit is high. A ring counter with 15 sequentially ordered states is an example of a state machine. A 'one-hot' implementation would have 15 flip-flops chained in series with the Q output of each flip-flop connected to the D input of the next and the D input of the first flip-flop connected to the Q output of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
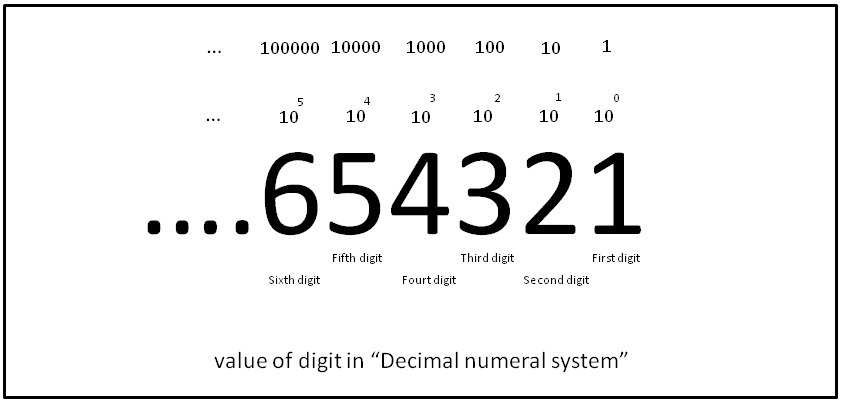
Decimal
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers (''decimal fractions'') of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. The way of denoting numbers in the decimal system is often referred to as ''decimal notation''. A decimal numeral (also often just ''decimal'' or, less correctly, ''decimal number''), refers generally to the notation of a number in the decimal numeral system. Decimals may sometimes be identified by a decimal separator (usually "." or "," as in or ). ''Decimal'' may also refer specifically to the digits after the decimal separator, such as in " is the approximation of to ''two decimals''". Zero-digits after a decimal separator serve the purpose of signifying the precision of a value. The numbers that may be represented in the decimal system are the decimal fractions. That is, fractions of the form , w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Address Decoder
In digital electronics, an address decoder is a binary decoder that has two or more inputs for address bits and one or more outputs for device selection signals. When the address for a particular device appears on the address inputs, the decoder asserts the selection output for that device. A dedicated, single-output address decoder may be incorporated into each device on an address bus, or a single address decoder may serve multiple devices. A single address decoder with n address input bits can serve up to 2n devices. Several members of the 7400 series of integrated circuit An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...s can be used as address decoders. For example, when used as an address decoder, the 74154 provides four address inputs and sixteen (i.e., 24) device selector o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ordinal Number
In set theory, an ordinal number, or ordinal, is a generalization of ordinal numerals (first, second, th, etc.) aimed to extend enumeration to infinite sets. A finite set can be enumerated by successively labeling each element with the least natural number that has not been previously used. To extend this process to various infinite sets, ordinal numbers are defined more generally using linearly ordered greek letter variables that include the natural numbers and have the property that every set of ordinals has a least or "smallest" element (this is needed for giving a meaning to "the least unused element"). This more general definition allows us to define an ordinal number \omega (omega) to be the least element that is greater than every natural number, along with ordinal numbers , , etc., which are even greater than . A linear order such that every non-empty subset has a least element is called a well-order. The axiom of choice implies that every set can be well-orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nominal Number
Nominal numbers are numerals used as labels to Unique identifier, identify items uniquely. Importantly, the actual values of the numbers which these numerals represent are less relevant, as they do not indicate quantity, rank, or any other measurement. Labelling referees Smith and Kumar as referees "1" and "2" is a use of nominal numbers. Any set of numbers (a subset of the natural numbers) will be consistent labels as long as a ''distinct'' number is uniquely used for each distinct term which needs to be labelled. Nonetheless, sequences of integers may naturally be used as the simplest way to begin labelling; for example, 1, 2, 3, and so on. Definition The term "nominal number" may be quite recent and of limited use. It appears to have originated in school textbooks derived from the statistical term "nominal data", defined as data indicating "...merely statements of qualitative category of membership." This usage comes from the sense of wikt:nominal, nominal as "name". Mathemat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Victoria, British Columbia
Victoria is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of British Columbia, on the southern tip of Vancouver Island off Canada's Pacific Ocean, Pacific coast. The city has a population of 91,867, and the Greater Victoria area has a population of 397,237. The city of Victoria is the seventh most densely populated city in Canada with . Victoria is the southernmost major city in Western Canada and is about southwest from British Columbia's largest city of Vancouver on the mainland. The city is about from Seattle by airplane, Harbour Air Seaplanes, seaplane, ferry, or the Clipper Navigation, Victoria Clipper passenger-only ferry, and from Port Angeles, Washington, Port Angeles, Washington (state), Washington, by ferry across the Strait of Juan de Fuca. Named for Queen Victoria, the city is one of the oldest in the Pacific Northwest, with British settlement beginning in 1843. The city has retained a large number of its historic buildings, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related to information retrieval, knowledge representation and computational linguistics, a subfield of linguistics. Major tasks in natural language processing are speech recognition, text classification, natural-language understanding, natural language understanding, and natural language generation. History Natural language processing has its roots in the 1950s. Already in 1950, Alan Turing published an article titled "Computing Machinery and Intelligence" which proposed what is now called the Turing test as a criterion of intelligence, though at the time that was not articulated as a problem separate from artificial intelligence. The proposed test includes a task that involves the automated interpretation and generation of natural language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Programmable Array Logic
Programmable Array Logic (PAL) is a family of programmable logic device semiconductors used to implement logic functions in digital circuits that was introduced by Monolithic Memories, Inc. (MMI) in March 1978. Introductory advertisement on PAL (Programmable Array Logic). MMI obtained a registered trademark on the term PAL for use in "Programmable Semiconductor Logic Circuits". The trademark is currently held by Lattice Semiconductor.Monolithic Memories, Inc (MMI) filed for a work mark on the term "PAL" for use in "Programmable Semiconductor Logic Circuits" on April 13, 1978. A registered trademark was granted on April 29, 1980, registration number 1134025. MMI's first use of the term PAL in commerce was on February 21, 1978. The trademark is currently held by Lattice Semiconductor Corporation of Hillsboro, Oregon. Source: United States Patent and Trademark Office online database. PAL devices consisted of a small PROM (programmable read-only memory) core and additional outp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Field-programmable Gate Array
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is a type of configurable integrated circuit that can be repeatedly programmed after manufacturing. FPGAs are a subset of logic devices referred to as programmable logic devices (PLDs). They consist of an array of programmable logic device, programmable logic block, logic blocks with a connecting grid, that can be configured "in the field" to interconnect with other logic blocks to perform various digital functions. FPGAs are often used in limited (low) quantity production of custom-made products, and in research and development, where the higher cost of individual FPGAs is not as important, and where creating and manufacturing a custom circuit would not be feasible. Other applications for FPGAs include the telecommunications, automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors, which benefit from their flexibility, high signal processing speed, and parallel processing abilities. A FPGA configuration is generally written using a hardware descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Flip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, flip-flops and latches are electronic circuit, circuits that have two stable states that can store state information – a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will output its state (often along with its logical complement too). It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are fundamental building blocks of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems. Flip-flops and latches are used as data storage elements to store a single ''bit'' (binary digit) of data; one of its two states represents a "one" and the other represents a "zero". Such data storage can be used for storage of ''state (computer science), state'', and such a circuit is described as sequential logic in electronics. When used in a finite-state machine, the output and next state depend not only on its current input, but also on its current stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
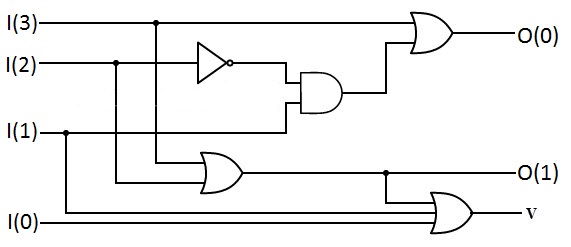
Priority Encoder
A priority encoder is a Electronic circuit, circuit or algorithm that compresses multiple Binary code, binary inputs into a smaller number of outputs, similar to a Encoder (digital), simple encoder. The output of a priority encoder is the binary representation of the Zero-based numbering, index of the Bit numbering, most significant activated line. In contrast to the simple encoder, if two or more inputs to the priority encoder are active at the same time, the input having the highest priority will take :wikt:precedence, precedence. It is an improvement on a simple encoder because it can handle all possible input combinations, but at the cost of extra logic. Applications of priority encoders include their use in Programmable interrupt controller, interrupt controllers (to allow some interrupt requests to have higher priority than others), decimal or binary encoding, and Analog-to-digital converter, analog-to-digital / Digital-to-analog converter, digital to-analog conversion. Imple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Flip-flop (electronics)
In electronics, flip-flops and latches are electronic circuit, circuits that have two stable states that can store state information – a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will output its state (often along with its logical complement too). It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are fundamental building blocks of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems. Flip-flops and latches are used as data storage elements to store a single ''bit'' (binary digit) of data; one of its two states represents a "one" and the other represents a "zero". Such data storage can be used for storage of ''state (computer science), state'', and such a circuit is described as sequential logic in electronics. When used in a finite-state machine, the output and next state depend not only on its current input, but also on its current stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Binary Number
A binary number is a number expressed in the Radix, base-2 numeral system or binary numeral system, a method for representing numbers that uses only two symbols for the natural numbers: typically "0" (zero) and "1" (one). A ''binary number'' may also refer to a rational number that has a finite representation in the binary numeral system, that is, the quotient of an integer by a power of two. The base-2 numeral system is a positional notation with a radix of 2. Each digit is referred to as a bit, or binary digit. Because of its straightforward implementation in digital electronic circuitry using logic gates, the binary system is used by almost all modern computer, computers and computer-based devices, as a preferred system of use, over various other human techniques of communication, because of the simplicity of the language and the noise immunity in physical implementation. History The modern binary number system was studied in Europe in the 16th and 17th centuries by Thoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |