|
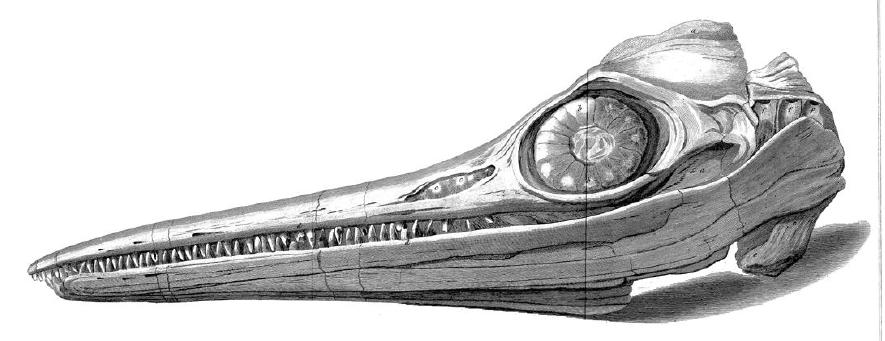
Omphalosaurus
''Omphalosaurus'' (from the Greek root "Button Lizard", for their button-like teeth) is an extinct genus of marine reptile from the Early Triassic to Middle Triassic, thought to be in the order of Ichthyosauria. Most of what is known about ''Omphalosaurus'' is based on multiple jaw fragments, ribs, and vertebrae. Specimens of ''Omphalosaurus'' have been described from the western United States, Poland, Austria and the island of Spitsbergen off the northern coast of Norway. Description ''Omphalosaurus'' is a moderately large and plump marine reptile, measuring long and weighing more than . It is best known for its highly specialized dentition compared to other ichthyosaurs. The teeth are button-like, with a dome shape when viewed laterally and almost circular crowns that have an irregular enamel surface akin to the texture of an orange peel. Individual teeth do not exceed 12mm in diameter and are arranged in tooth plates exclusively on the premaxilla, which sit at 90º from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
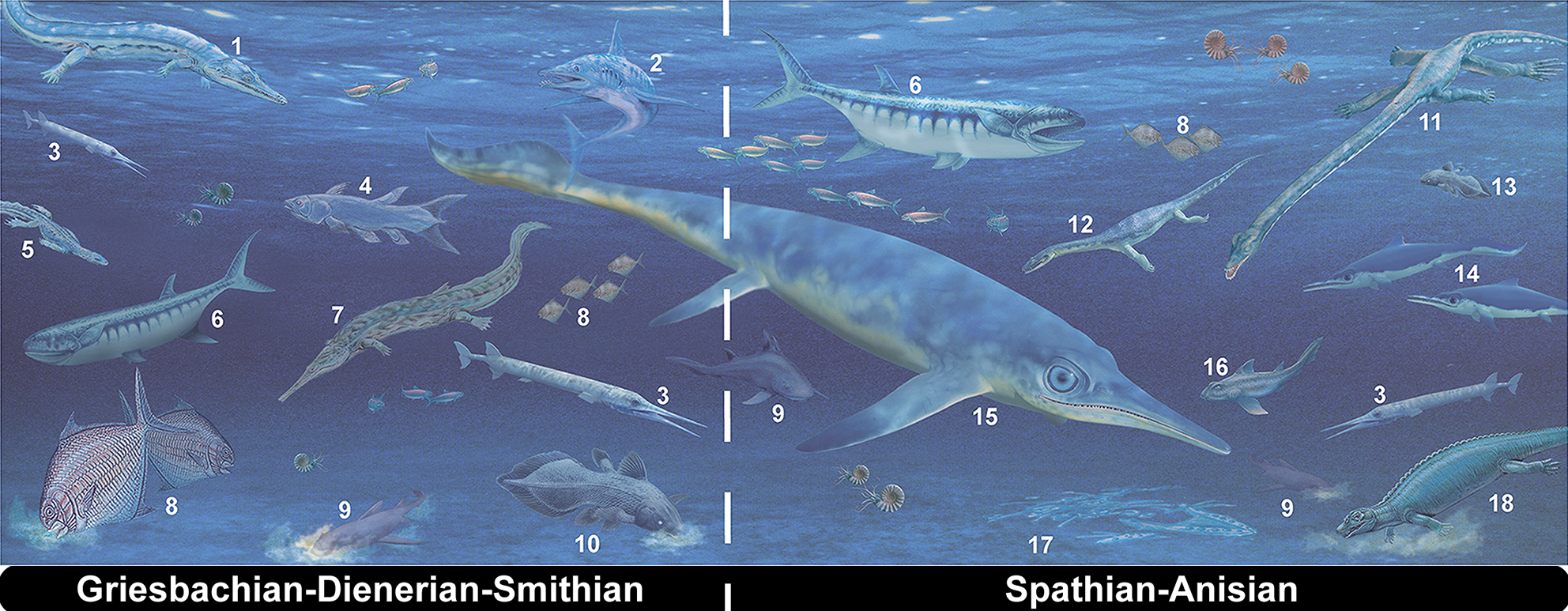
Ichthyosaur
Ichthyosaurs (Ancient Greek for "fish lizard" – and ) are large extinct marine reptiles. Ichthyosaurs belong to the order known as Ichthyosauria or Ichthyopterygia ('fish flippers' – a designation introduced by Sir Richard Owen in 1842, although the term is now used more for the parent clade of the Ichthyosauria). Ichthyosaurs thrived during much of the Mesozoic era; based on fossil evidence, they first appeared around 250 million years ago ( Ma) and at least one species survived until about 90 million years ago, into the Late Cretaceous. During the Early Triassic epoch, ichthyosaurs and other ichthyosauromorphs evolved from a group of unidentified land reptiles that returned to the sea, in a development similar to how the mammalian land-dwelling ancestors of modern-day dolphins and whales returned to the sea millions of years later, which they gradually came to resemble in a case of convergent evolution. Ichthyosaurs were particularly abundant in the Late Triassic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ichthyosauria
Ichthyosaurs (Ancient Greek for "fish lizard" – and ) are large extinct marine reptiles. Ichthyosaurs belong to the order known as Ichthyosauria or Ichthyopterygia ('fish flippers' – a designation introduced by Sir Richard Owen in 1842, although the term is now used more for the parent clade of the Ichthyosauria). Ichthyosaurs thrived during much of the Mesozoic era; based on fossil evidence, they first appeared around 250 million years ago ( Ma) and at least one species survived until about 90 million years ago, into the Late Cretaceous. During the Early Triassic epoch, ichthyosaurs and other ichthyosauromorphs evolved from a group of unidentified land reptiles that returned to the sea, in a development similar to how the mammalian land-dwelling ancestors of modern-day dolphins and whales returned to the sea millions of years later, which they gradually came to resemble in a case of convergent evolution. Ichthyosaurs were particularly abundant in the Late Triassic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
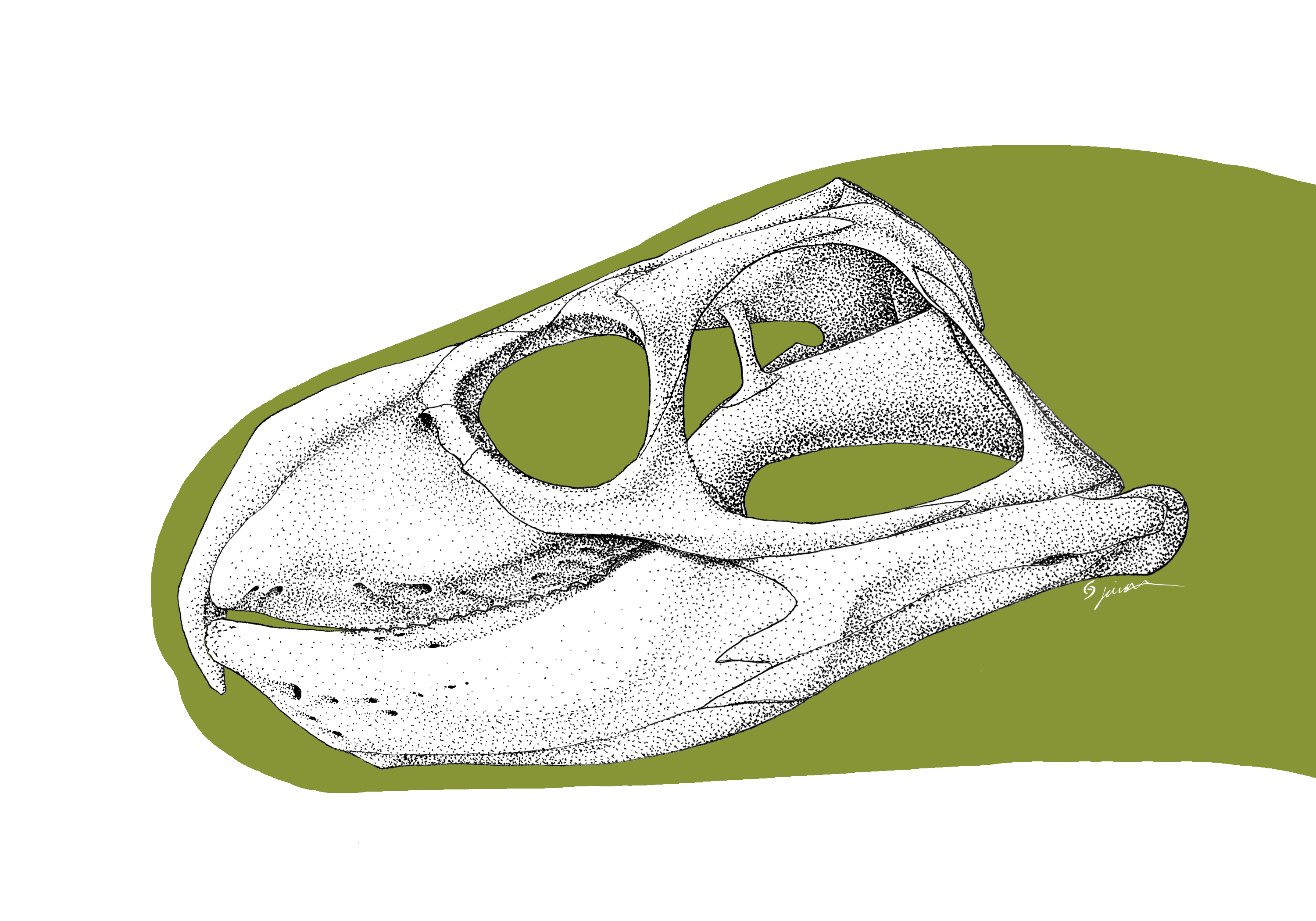
Pessopteryx
''Pessopteryx'' is an extinct genus of ichthyosaur from the Early Triassic (Olenekian) of Svalbard, Norway. The genus originally contained four species, ''P. nisseri'', ''P. arctica'', ''P. pinguis'', and ''P. minor'', which were named in 1910 by Carl Wiman. Wiman. C. (1910) Ichthyosaurs from the Triassic Spitzbergens Swedish Swedish or ' may refer to: Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically: * Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland ** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...]. ''Bulletin of the Geological Institution of the University of Upsala'' 10: 125–148. Only ''P. nisseri'' is still considered valid; ''P. arctica'' and ''P. pinguis'' are considered '' nomina dubia'' while ''P. minor'' was reassigned to the tenuous genus '' Isfjordosaurus''. '' Omphalosaurus nisseri'', '' Merriamosaurus hulkei'', and ''Rotundopteryx hulkei'' are all junior synonyms of ''P. nisseri''. Ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olenekian
In the geologic timescale, the Olenekian is an age in the Early Triassic epoch; in chronostratigraphy, it is a stage in the Lower Triassic series. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). The Olenekian is sometimes divided into the Smithian and the Spathian subages or substages. The Olenekian follows the Induan and is followed by the Anisian (Middle Triassic). The Olenekian saw the deposition of a large part of the Buntsandstein in Europe. The Olenekian is roughly coeval with the regional Yongningzhenian Stage used in China. Stratigraphic definitions The Olenekian Stage was introduced into scientific literature by Russian stratigraphers in 1956. The stage is named after Olenëk in Siberia. Before the subdivision in Olenekian and Induan became established, both stages formed the Scythian Stage, which has since disappeared from the official timescale. The base of the Olenekian is at the lowest occurrence of the ammonoids '' Hedenstroemia'' or '' Meekoceras graci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which is a unit in chronostratigraphy. The Early Triassic is the oldest epoch of the Mesozoic Era. It is preceded by the Lopingian Epoch (late Permian, Paleozoic Era) and followed by the Middle Triassic Epoch. The Early Triassic is divided into the Induan and Olenekian ages. The Induan is subdivided into the Griesbachian and Dienerian subages and the Olenekian is subdivided into the Smithian and Spathian subages. The Lower Triassic series is coeval with the Scythian Stage, which is today not included in the official timescales but can be found in older literature. In Europe, most of the Lower Triassic is composed of Buntsandstein, a lithostratigraphic unit of continental red beds. The Early Triassic and partly also the Middle Triassic span the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhynchosaurus
''Rhynchosaurus'' (''beaked lizard'') is a genus of rhynchosaur that lived during the Middle Triassic period. It lived in Europe. It was related to the archosaurs, but not within that group. The type species of ''Rhynchosaurus'' is ''R. articeps''. Michael Benton named two additional species, ''R. spenceri'' and ''R. brodiei'', but they were subsequently renamed ''Fodonyx'' and ''Langeronyx'' respectively.Martín D. Ezcurra, Felipe Montefeltro and Richard J. Butler (2016). "The Early Evolution of Rhynchosaurs". Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution 3: Article 142. doi:10.3389/fevo.2015.00142. Fossils of ''Rhynchosaurus'' have been found in the Tarporley Siltstone Formation (Mercia Mudstone Group) and possibly the Sherwood Sandstone Group of the United Kingdom.''Rhynchosaurus'' at |
Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and . The largest settlement is Longyearbyen. The islands were first used as a base by the whalers who sailed far north in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which they were abandoned. Coal mining started at the beginning of the 20th century, and several permanent communities were established. The Svalbard Treaty of 1920 recognizes Norwegian sovereignty, and the 1925 Svalbard Act made Svalbard a full part of the Kingdom of Norway. They also established Svalbard as a free economic zone and a demilitarized zone. The Norwegian Store Norske and the Russian remain the only mining companies in place. Res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symphysis
A symphysis (, pl. symphyses) is a fibrocartilaginous fusion between two bones. It is a type of cartilaginous joint, specifically a secondary cartilaginous joint. # A symphysis is an amphiarthrosis, a slightly movable joint. # A growing together of parts or structures. Unlike synchondroses, symphyses are permanent. Examples The more prominent symphyses are: * the pubic symphysis * sacrococcygeal symphysis * intervertebral disc between two vertebrae * in the sternum, between the manubrium and body Body may refer to: In science * Physical body, an object in physics that represents a large amount, has mass or takes up space * Body (biology), the physical material of an organism * Body plan, the physical features shared by a group of anima ... * mandibular symphysis, in the jaw Symphysis disorders Pubic symphysis diastasis Pubic symphysis diastasis, is an extremely rare complication that occurs in women who are giving birth. Separation of the two pubic bones during deli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anisian
In the geologic timescale, the Anisian is the lower stage or earliest age of the Middle Triassic series or epoch and lasted from million years ago until million years ago. The Anisian Age succeeds the Olenekian Age (part of the Lower Triassic Epoch) and precedes the Ladinian Age. Stratigraphic definitions The stage and its name were established by Austrian geologists Wilhelm Heinrich Waagen and Carl Diener in 1895. The name comes from ''Anisus'', the Latin name of the river Enns. The original type locality is at Großreifling in the Austrian state of Styria. The base of the Anisian Stage (also the base of the Middle Triassic series) is sometimes laid at the first appearance of conodont species '' Chiosella timorensis'' in the stratigraphic record. Other stratigraphers prefer to use the base of magnetic chronozone MT1n. There is no accepted global reference profile for the base, but one ( GSSP or golden spike) was proposed at a flank of the mountain Deşli Caira in the Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humboldt Range
The Humboldt Range is a largely north-south running range of mountains in northwest Nevada, USA, that extend from the town of Imlay in the north to the junction with the West Humboldt Range in the south. It is bordered continuously by Interstate 80 and the Humboldt River, largely expanded in the form of the Rye Patch Reservoir in this area, on the west side and by a long and fairly broad Buena Vista Valley to the east, in a typical basin-and-range pattern. The Humboldts are ostensibly visible to travelers along Interstate 80, especially with respect to the highest point of the range, Star Peak, which with a quite nicely defined tip reaches an elevation of 9,836 feet (2,998 m), located in the center of the north range section. The midpoint of the range is in the area of Fourth of July Flat.DeLorme Atlas, p. 36. The Humboldt Range is also noteworthy for having a famous historical town at its base on the eastern side called Unionville, which, for a brief period, was home to Samu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |