|
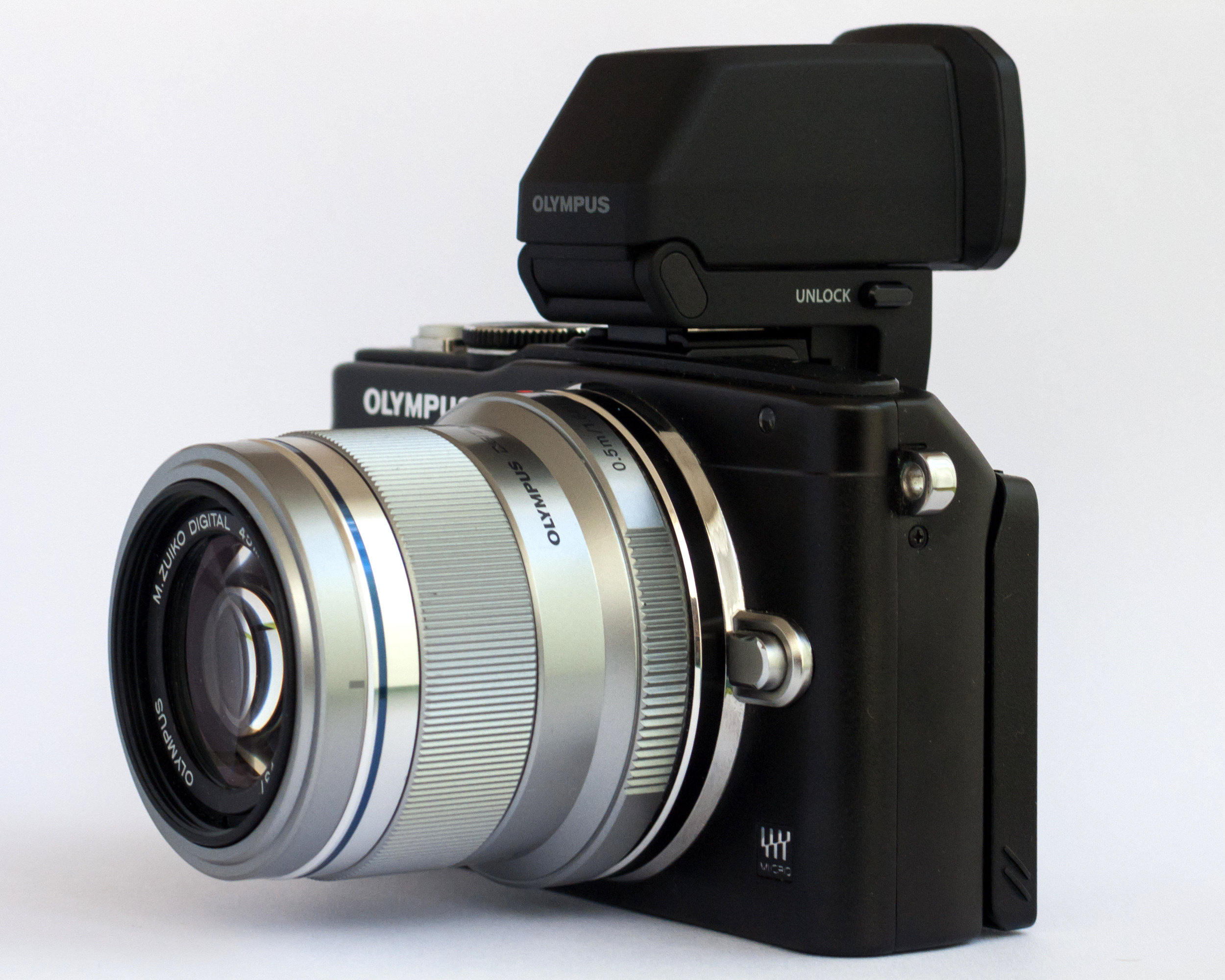
Olympus OM-D E-M10 Mark II
The Olympus OM-D E-M10 Mark II is a digital mirrorless system camera announced by Olympus Corporation on August 25, 2015. The E-M10 Mark II features a 5-axis in-body image stabilization system, an upgrade to the 3-axis design found in its predecessor, the original E-M10. The E-M10 Mark II was succeeded by the E-M10 Mark III, offering 4K video capabilities. Features * 16 megapixel Live MOS 4/3 size sensor * Micro Four Thirds system * SLR-style body * 2.3m dot electronic viewfinder * 8 fps burst rate * 1/4000s fastest shutter speed with mechanical shutter * 1/16000s fastest shutter speed with electronic shutter * 81 contrast detection autofocus points, no phase detection * 1080p/60 fps video with 77 Mbit/s bitrate * Built-in flash * Wi-Fi * Tilting touchscreen with a resolution of 1,040 million dots * 390g body weight Drawbacks * No minijack socket (impossible to connect an external microphone) Differences with the Olympus OM-D E-M10 * 5 axis sensor stabilization syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Live MOS
The Live MOS sensor is a brand name of an NMOS Image sensorOlympus E-330 EVOLT Review used by , Olympus and Leica in their |
Olympus OM-D E-M10
The Olympus OM-D E-M10 was the third model in the OM-D series of compact, mirrorless, interchangeable-lens cameras. It is of the Micro Four Thirds type and was introduced in January 2014. The model cost less than the OM-D E-M5 and OM-D E-M1 models that preceded it. Some features of the previous models, such as weather sealing, were not included. The E-M10 featured only a 3-way image stabilizer instead of the other models' 5-way stabilizer. The E-M10 used the BLS-1 battery first supplied with the earlier E-P1/2 compact mirrorless cameras rather than the BLN-1 used by the OM-D E-M5 and E-M1 models. It was succeeded by the Olympus OM-D E-M10 Mark II in 2015. Specification and features * Sensor: 16MP Live MOS sensor without AA filter * Image stabilisation: 3-axis image stabilisation * Tilting LCD screen, with capacitive touchscreen operation * TruePic VII processor with lens correction * ISO range: 200 - 25600 * Manual focus (with focus peaking) * Focus points: 81-area multi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olympus OM-D E-M10 Mark III
The Olympus OM-D E-M10 Mark III is a digital mirrorless interchangeable-lens camera released by Olympus Corporation in September 2017. It succeeded the Olympus OM-D E-M10 Mark II The Olympus OM-D E-M10 Mark II is a digital mirrorless system camera announced by Olympus Corporation on August 25, 2015. The E-M10 Mark II features a 5-axis in-body image stabilization system, an upgrade to the 3-axis design found in its predece ..., although it did not offer much of a hardware upgrade, instead focusing on an easier photography experience. Critics pointed out that the 16 megapixel sensor seemed dated at the time of the camera's release. The E-M10 Mark III won a Japan Parenting Award 2017. Differences with the Olympus OM-D E-M10 Mark II The Mark III uses a newer image processor TruePic VIII. It introduces 4K movie capabilities, has more autofocus points (121 instead of 81) and allows slightly faster sequential shooting. Some software features were introduced in the Mark III, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olympus Corporation
is a Japanese manufacturer of optics and reprography products. Olympus was established on 12 October 1919, initially specializing in microscopes and thermometers. Olympus holds roughly a 70-percent share of the global endoscope market, estimated to be worth approximately US$2.5 billion. Its global headquarters are located in Shinjuku, Tokyo, Japan. In 2011, Olympus attracted worldwide media scrutiny when it fired its CEO and the matter snowballed into a corporate corruption investigation with multiple arrests. It paid $646 million in kickback fines in 2016. Products Cameras and audio In 1936, Olympus introduced its first camera, the Semi-Olympus I, fitted with the first Zuiko-branded lens. The Olympus Chrome Six was a series of folding cameras made by Takachiho, and later Olympus, from 1948 to 1956, for 6×4.5 cm or 6×6 cm exposures on 120 film. The first innovative camera series from Olympus was the Pen, launched in 1959. It used a half-frame forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4K Resolution
4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. Digital television and digital cinematography commonly use several different 4K resolutions. In television and consumer media, 38402160 (4K UHD) is the dominant 4K standard, whereas the movie projection industry uses 40962160 (DCI 4K). The 4K television market share increased as prices fell dramatically during 2014 and 2015. 4K standards and terminology The term "4K" is generic and refers to any resolution with a horizontal pixel count of approximately 4,000. Several different 4K resolutions have been standardized by various organizations. The terms "4K" and "Ultra HD" are used more widely in marketing than "2160p". While typically referring to motion pictures, some digital camera vendors have used the term "4K photo" for still photographs, making it appear like an especially high resolution even though 3840×2160 pixels equal approximately 8.3 megapixels, which is not considered to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Sensor
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to make an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they pass through or reflect off objects) into signals, small bursts of current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronic imaging devices of both analog and digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, camera phones, optical mouse devices, medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technology changes, electronic and digital imaging tends to replace chemical and analog imaging. The two main types of electronic image sensors are the charge-coupled device (CCD) and the active-pixel sensor (CMOS sensor). Both CCD and CMOS sensors are based on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) technology, with CCDs based on MOS capacitors and CMOS senso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Viewfinder
An electronic viewfinder (EVF) is a camera viewfinder where the image captured by the lens is displayed on a small screen (usually LCD or OLED) which the photographer can look through when composing their shot. It differs from a live preview screen in being smaller and shaded from ambient light, and may also use less power. The sensor records the view through the lens, the view is processed, and finally projected on a miniature display which is viewable through the eyepiece. Digital viewfinders are used in digital still cameras and in video cameras. Some cameras (such as Panasonic, Sony, Fujifilm) have an automatic eye sensor which switches the display from screen to EVF when the viewfinder is near the eye. More modest cameras use a button to switch the display. Some have no button at all. While many cameras come with a built-in EVF, this is fixed in place and can only be used while holding the camera to the user's eye, which may not be convenient. Other cameras don't come ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autofocus
An autofocus (or AF) optical system uses a sensor, a control system and a motor to focus on an automatically or manually selected point or area. An electronic rangefinder has a display instead of the motor; the adjustment of the optical system has to be done manually until indication. Autofocus methods are distinguished as active, passive or hybrid types. Autofocus systems rely on one or more sensors to determine correct focus. Some AF systems rely on a single sensor, while others use an array of sensors. Most modern SLR cameras use through-the-lens optical sensors, with a separate sensor array providing light metering, although the latter can be programmed to prioritize its metering to the same area as one or more of the AF sensors. Through-the-lens optical autofocusing is usually speedier and more precise than manual focus with an ordinary viewfinder, although more precise manual focus can be achieved with special accessories such as focusing magnifiers. Autofocus accu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flash (photography)
A flash is a device used in photography that produces a brief burst of light (typically lasting 1/1000 to 1/200 of a second) at a color temperature of about 5500 K to help illuminate a scene. A major purpose of a flash is to illuminate a dark scene. Other uses are capturing quickly moving objects or changing the quality of light. ''Flash'' refers either to the flash of light itself or to the electronic flash unit discharging the light. Most current flash units are electronic, having evolved from single-use flashbulbs and flammable powders. Modern cameras often activate flash units automatically. Flash units are commonly built directly into a camera. Some cameras allow separate flash units to be mounted via a standardized accessory mount bracket (a ''hot shoe''). In professional studio equipment, flashes may be large, standalone units, or studio strobes, powered by special battery packs or connected to mains power. They are either synchronized with the camera using a fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi () is a family of wireless network protocols, based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. These are the most widely used computer networks in the world, used globally in home and small office networks to link desktop and laptop computers, tablet computers, smartphones, smart TVs, printers, and smart speakers together and to a wireless router to connect them to the Internet, and in wireless access points in public places like coffee shops, hotels, libraries and airports to provide visitors with Internet access for their mobile devices. ''Wi-Fi'' is a trademark of the non-profit Wi-Fi Alliance, which restricts the use of the term ''Wi-Fi Certified'' to products that successfully complete interoperability certification testing. the Wi-Fi Alliance consisted of more than 800 companies from around the world. over 3.05 billio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Touchscreen
A touchscreen or touch screen is the assembly of both an input ('touch panel') and output ('display') device. The touch panel is normally layered on the top of an electronic visual display of an information processing system. The display is often an LCD, AMOLED or OLED display while the system is usually used in a laptop, tablet, or smartphone. A user can give input or control the information processing system through simple or multi-touch gestures by touching the screen with a special stylus or one or more fingers. Some touchscreens use ordinary or specially coated gloves to work while others may only work using a special stylus or pen. The user can use the touchscreen to react to what is displayed and, if the software allows, to control how it is displayed; for example, zooming to increase the text size. The touchscreen enables the user to interact directly with what is displayed, rather than using a mouse, touchpad, or other such devices (other than a stylus, which is opt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |