|
Olaf The White
Olaf the White ( non, Óláfr hinn Hvíti) was a viking sea-king who lived in the latter half of the 9th century. Life Olaf was born around 820, in Ireland. His father was the Hiberno-Norse warlord Ingjald Helgasson. Some traditional sources portray Olaf as a descendant of Ragnar Lodbrok – for instance, the '' Eyrbyggja Saga'', claims that Olaf's paternal grandmother (Thora) was a daughter of Ragnar's son Sigurd Snake-in-the-Eye. However, this connection seems unlikely, given that Sigurd appears to have lived in the mid-9th Century and Ragnar himself may have lived until the 860s. Irish fragments provide a different genealogy, suggesting that Olaf's father was Godfred, son of Ragnall, son of Godfred, son of Godfred. He was named King of Dublin around 853. According to Irish sources, Olaf ruled jointly with his kinsman Ímar. Olaf married Aud the Deep-minded (''Auðr''), daughter of Ketil Flatnose, the ruler of the Hebrides, according to Icelandic traditions (''Landnámab� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden), who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9–22. They also voyaged as far as the Mediterranean, North Africa, Volga Bulgaria, the Middle East, and North America. In some of the countries they raided and settled in, this period is popularly known as the Viking Age, and the term "Viking" also commonly includes the inhabitants of the Scandinavian homelands as a collective whole. The Vikings had a profound impact on the early medieval history of Scandinavia, the British Isles, France, Estonia, and Kievan Rus'. Expert sailors and navigators aboard their characteristic longships, Vikings established Norse settlements and governments in the British Isles, the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Greenland, Normandy, and the Baltic coast, as well as alon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinland
Vinland, Vineland, or Winland ( non, Vínland ᚠᛁᚾᛚᛅᚾᛏ) was an area of coastal North America explored by Vikings. Leif Erikson landed there around 1000 AD, nearly five centuries before the voyages of Christopher Columbus and John Cabot. The name appears in the Vinland Sagas, and describes Newfoundland and the Gulf of Saint Lawrence as far as northeastern New Brunswick. Much of the geographical content of the sagas corresponds to present-day knowledge of transatlantic travel and North America. In 1960, archaeological evidence of the only known Norse site in North America, L'Anse aux Meadows, was found on the northern tip of the island of Newfoundland. Before the discovery of archaeological evidence, Vinland was known only from the sagas and medieval historiography. The 1960 discovery further proved the pre-Columbian Norse exploration of mainland North America. L'Anse aux Meadows has been hypothesized to be the camp ''Straumfjörð'' mentioned in the '' Saga of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
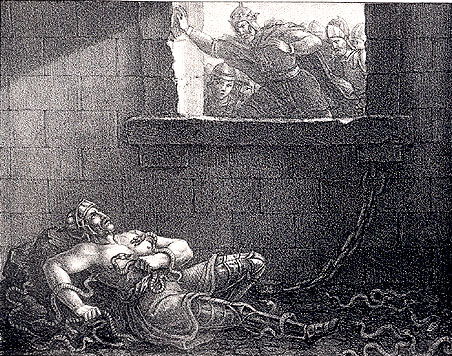
Ælla Of Northumbria
Ælla (or Ælle or Aelle, fl. 866; died 21 March 867) was King of Northumbria, a kingdom in medieval England, during the middle of the 9th century. Sources on Northumbrian history in this period are limited, and so Ælla's ancestry is not known and the dating of the beginning of his reign is questionable. In addition to the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'', Ælla is also mentioned in Scandinavian sources, such as the Norse sagas. According to the latter, Ælla captured the legendary Swedish-Danish Viking king Ragnar Lodbrok and put him to death in a pit of snakes. The historical invasion of Northumbria in 866 occurred in retaliation for Ragnar's execution, according to '' Ragnarssona þáttr'' (''The Tale of Ragnar's Sons''). While Norse sources claim that Ragnar's sons tortured Ælla to death by the method of the blood eagle, Anglo-Saxon accounts maintain that he died in battle at York on 21 March 867. Concerning the Norse claim, Roberta Frank reviewed the historical evidence for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aslaug
Aslaug ( non, Áslaug ), also called Aslög, Kráka (O.N.: ) or Kraba, is a figure in Norse mythology who appears in Snorri's Edda, the Völsunga saga and in the saga of Ragnar Lodbrok as one of his wives. Aslaug in legend According to the 13th-century ''Tale of Ragnar Lodbrok'', Aslaug was the daughter of Sigurd and the shieldmaiden Brynhildr, but was raised by Brynhildr's foster father Heimer. At the deaths of Sigurd and Brynhildr, Heimer was concerned about Aslaug's security, so he made a harp large enough to hide the girl. He then traveled as a poor harp player carrying the harp containing the girl. They arrived at Spangereid at Lindesnes in Norway, where they stayed for the night in the house of the peasants Áke and Grima. Áke believed the harp contained valuable items and told his wife Grima. Grima then persuaded him to murder Heimer as he was sleeping. However, when they broke the harp open, they discovered a little girl, whom they raised as their own, calling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gudrød The Hunter
Gudrød the Hunter (Old Norse: ''Guðrøðr veiðikonungr'', Norwegian: ''Gudrød Veidekonge'', literally ''Gudrod Hunter-king''; died 820 AD), also known as Gudrød the Magnificent (Old Norse: ''enn gǫfugláti'', Norwegian: ''den gjeve''), is a legendary character portrayed in the Norse sagas as a Norwegian petty king in the early 9th century. According to the sagas, he was the father of Halfdan the Black, and thus the grandfather of Harald Fairhair, the first king of unified Norway. He is considered by modern historians to be of a more mythical nature than other ancestors of Harald and Halfdan, and he can not be identified historically. Historians have in turn made a number of proposals seeking to identify him with various would-be contemporary historical figures. Background Gudrød was a member of the House of Yngling. He was the son of Halfdan the Mild, king of Romerike and Vestfold, and Liv, daughter of King Dag of Vestmar. Gudrød is mentioned in the skaldic poem '' Yn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olaf Geirstad-Alf
Olaf Gudrødsson (c. 810 – c. 860), known after his death as Olaf Geirstad-Alf "Olaf, Elf of Geirstad" (Old Norse Ólafr Geirstaðaalfr), was a semi-legendary petty king in Norway. A member of the House of Yngling, he was the son of Gudrød the Hunter and according to the late ''Heimskringla'', a half-brother of Halfdan the Black. Gudrød and Olaf ruled a large part of Raumarike. The ''Þáttr Ólafs Geirstaða Alfs'' in Flateyjarbók records a fantastical story of how he was worshipped after his death and on his own instructions, his body was then decapitated so that he could be reborn as Olaf II of Norway (St. Olaf). Two not necessarily conflicting hypotheses identify Geirstad with Gjerstad, formerly ''Geirekstad'' in Agder, and with Gokstad (possibly also a contraction of ''Geirekstad'') in Vestfold, the location of the mound Gokstadhaugen, where the Gokstad Ship was excavated. The theory that Olaf thus had a connection with the ship burial is unproven. ''Ynglinga s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olaf Guthfrithsson
Olaf Guthfrithson or Anlaf Guthfrithson ( non, Óláfr Guðrøðsson ; oe, Ánláf; sga, Amlaíb mac Gofraid; died 941) was a Hiberno-Scandinavian (Irish-Viking) leader who ruled Dublin and Viking Northumbria in the 10th century. He was the son of Gofraid ua Ímair and great-grandson of Ímar, making him one of the Uí Ímair. Olaf succeeded his father as King of Dublin in 934 and succeeded in establishing dominance over the Vikings of Limerick when he captured their king, Amlaíb Cenncairech, in 937. That same year he allied with Constantine II of Scotland in an attempt to reclaim the Kingdom of Northumbria which his father had ruled briefly in 927. The forces of Olaf and Constantine were defeated by the English led by Æthelstan at the Battle of Brunanburh in 937. Olaf returned to Ireland in 938 but after Æthelstan's death the following year Olaf left for York where he was quickly able to establish himself as king, with his brother Blácaire mac Gofraid being left to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heimskringla
''Heimskringla'' () is the best known of the Old Norse kings' sagas. It was written in Old Norse in Iceland by the poet and historian Snorre Sturlason (1178/79–1241) 1230. The name ''Heimskringla'' was first used in the 17th century, derived from the first two words of one of the manuscripts (''kringla heimsins'', "the circle of the world"). ''Heimskringla'' is a collection of sagas about Swedish and Norwegian kings, beginning with the saga of the legendary Swedish dynasty of the Ynglings, followed by accounts of historical Norwegian rulers from Harald Fairhair of the 9th century up to the death of the pretender Eystein Meyla in 1177. The exact sources of the Snorri's work are disputed, but they include earlier kings' sagas, such as Morkinskinna, Fagrskinna and the 12th-century Norwegian synoptic histories and oral traditions, notably many skaldic poems. He explicitly names the now lost work '' Hryggjarstykki'' as his source for the events of the mid-12th century. Althou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestfold
Vestfold is a traditional region, a former county and a current electoral district in Eastern Norway. In 2020 the county became part of the much larger county of Vestfold og Telemark. Located on the western shore of the Oslofjord, it bordered the previous Buskerud and Telemark counties. The county administration was located in Tønsberg, Norway's oldest city, and the largest city is Sandefjord. With the exception of the city-county of Oslo, Vestfold was the smallest county in Norway by area. Vestfold was the only county in which all municipalities had declared Bokmål to be their sole official written form of the Norwegian language. Vestfold is located west of the Oslofjord, as the name indicates. It includes many smaller, but well-known towns in Norway, such as Larvik, Sandefjord, Tønsberg and Horten; these towns run from Oslo in an almost constant belt of urban areas along the coast, ending in Grenland in neighbouring region Telemark. The river Numedalslågen runs thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gwyn Jones (author)
Gwyn Jones (24 May 1907 – 6 December 1999) was a Welsh novelist and story writer, and a scholar and translator of Nordic literature and history. Personal life and academic career Gwyn Jones was born on 24 May 1907 in New Tredegar, Monmouthshire, the second child of George Henry Jones (1874–1970), a miner, and his second wife, Lily Florence, née Nethercott (1877–1960), a midwife. He was brought up in nearby Blackwood. He attended Tredegar county school and studied at University College, Cardiff as an undergraduate and a postgraduate. After six years he was a schoolteacher in Wigan and Manchester, in 1935 he returned to University College, Cardiff as a lecturer. In 1940 was appointed Professor of English of the University College of Wales, Aberystwyth, where he taught until his appointment as Professor of English at University College, Cardiff in 1964, a position he held until his retirement in 1975. In 1939 Jones registered as a conscientious objector to military servic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alba
''Alba'' ( , ) is the Scottish Gaelic name for Scotland. It is also, in English language historiography, used to refer to the polity of Picts and Scots united in the ninth century as the Kingdom of Alba, until it developed into the Kingdom of Scotland of the late Middle Ages following the absorption of Strathclyde and English-speaking Lothian in the 12th century. It is cognate with the Irish term ' (gen. ', dat. ') and the Manx term ', the two other Goidelic Insular Celtic languages, as well as contemporary words used in Cornish (') and Welsh ('), both of which are Brythonic Insular Celtic languages. The third surviving Brythonic language, Breton, instead uses ', meaning 'country of the Scots'. In the past, these terms were names for Great Britain as a whole, related to the Brythonic name Albion. Etymology The term first appears in classical texts as ' or ' (in Ptolemy's writings in Greek), and later as ' in Latin documents. Historically, the term refers to Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |