|
Ojos De Mar
Ojos de Mar is a group of 3–6 small water bodies close to the town of Tolar Grande in Argentina and an important tourist attraction there. They are inhabited by extremophile microorganisms of interest to biotechnology; stromatolites have also been found there. The lakes The Ojos de Mar are six or three small deep ponds characterized by a blue-turquoise colour in a white salty desert landscape under a bright blue sky. Their water is extremely salty and alkaline and their colour changes depending on the angle of the sun impacting the clear waters. The water bodies are filled by water coming from surrounding rocks that evaporates in the Ojos de Mar. The name may refer to the colour and saltiness of the water that resembles the sea; it is possible that the water bodies were encountered by the Spanish on their way through the Andes. They are also referred to as Ojo de Tolar. Despite their name and appearance, they are not remnants of the sea. Water temperatures of have been mea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aracar
Aracar is a large conical stratovolcano in northwestern Argentina, just east of the Chilean border. It has a main summit crater about in diameter which sometimes contains crater lakes, and a secondary crater. The volcano has formed, starting during the Pliocene, on top of a lava platform and an older basement. Constructed on a base with an altitude of , it covers a surface area of and has a volume of . The only observed volcanic activity was a possible steam or ash plume on March 28, 1993, seen from the village of Tolar Grande about southeast of the volcano, but with no evidence of deformation of the volcano from satellite observations. Inca archeological sites are found on the volcano. Geology Aracar is located in the Salta province, north of the Salar de Taca Taca and Arizaro and east of the Salar de Incahuasi and the Sierra de Taca Taca, close to the Chilean border. Volcanoes in the territory rise above the endorheic sinks and landscape. Cerro Arizaro (9.0 ± 1.3 mya) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salta
Salta () is the capital and largest city in the Argentine province of the same name. With a population of 618,375 according to the 2010 census, it is also the 7th most-populous city in Argentina. The city serves as the cultural and economic center of the Valle de Lerma Metropolitan Area (Spanish: ''Área Metropolitana del Valle de Lerma'', AMVL), which is home to over 50.9% of the population of Salta Province and also includes the municipalities of La Caldera, Vaqueros, Campo Quijano, Rosario de Lerma, Cerrillos, La Merced and San Lorenzo. Salta is the seat of the Capital Department, the most populous department in the province. History Salta was founded on April 16, 1582 by the Spanish conquistador Hernando de Lerma, who intended the settlement to be an outpost between Lima, Peru and Buenos Aires. The origin of the name ''Salta'' is a matter of conjecture, with several theories being advanced to explain it. During the war of independence, the city became a commercial an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
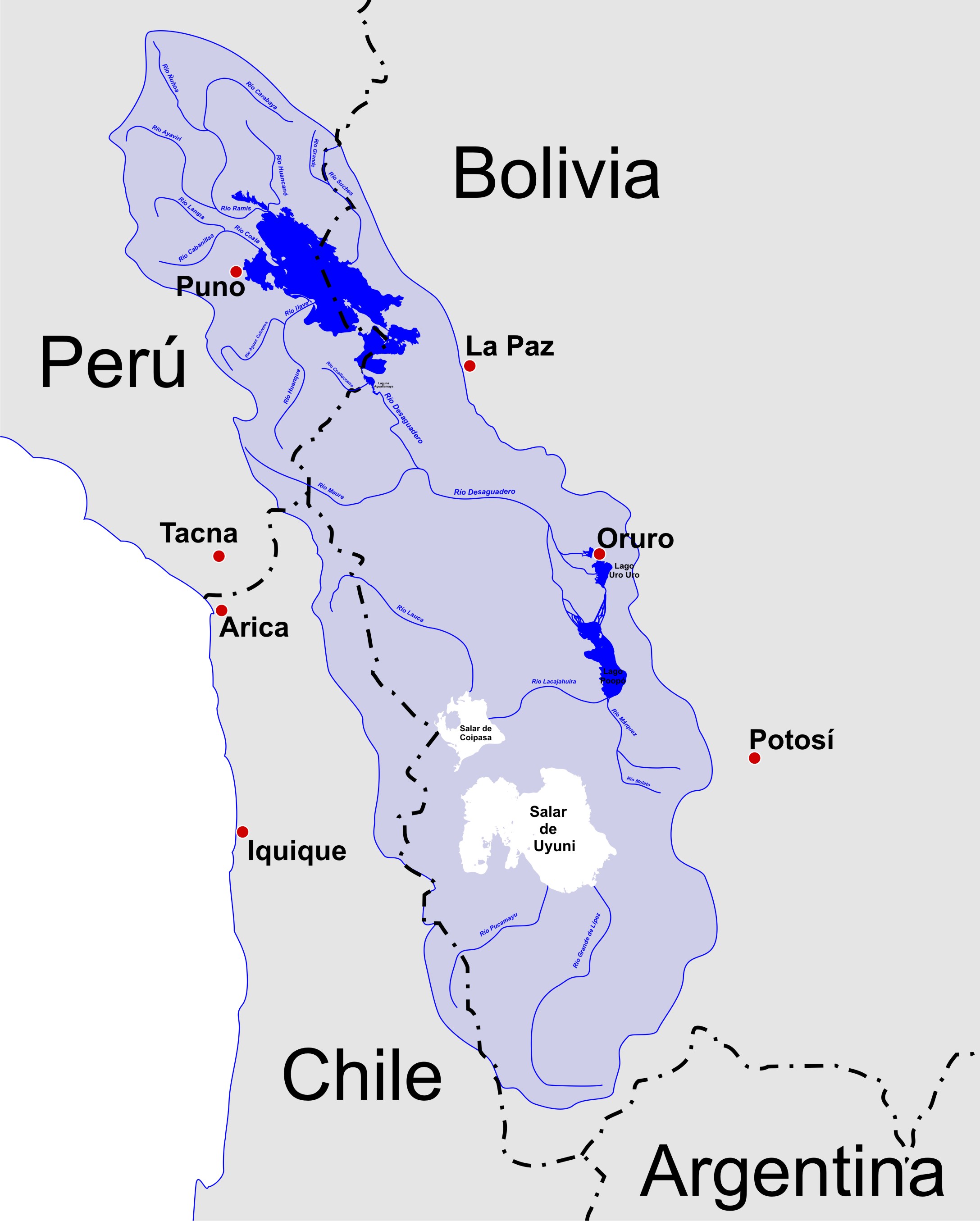
Altiplano
The Altiplano (Spanish for "high plain"), Collao (Quechua and Aymara: Qullaw, meaning "place of the Qulla") or Andean Plateau, in west-central South America, is the most extensive high plateau on Earth outside Tibet. The plateau is located at the latitude of the widest part of the north-south-trending Andes. The bulk of the Altiplano lies in Bolivia, but its northern parts lie in Peru, and its southwestern fringes lie in Chile. There are on the plateau several cities in each of these three nations, including El Alto, La Paz, Oruro, and Puno. The northeastern part of the Altiplano is more humid than the southwestern part, which has several salares (salt flats), due to its aridity. At the Bolivia–Peru border lies Lake Titicaca, the largest lake in South America. Farther south, in Bolivia, there was until recently a lake, Lake Poopó, but by December 2015 it had completely dried up, and was declared defunct. It is unclear whether that lake, which had been the second-largest in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evaporite
An evaporite () is a water-soluble sedimentary mineral deposit that results from concentration and crystallization by evaporation from an aqueous solution. There are two types of evaporite deposits: marine, which can also be described as ocean deposits, and non-marine, which are found in standing bodies of water such as lakes. Evaporites are considered sedimentary rocks and are formed by chemical sediments. Formation of evaporite rocks Although all water bodies on the surface and in aquifers contain dissolved salts, the water must evaporate into the atmosphere for the minerals to precipitate. For this to happen, the water body must enter a restricted environment where water input into this environment remains below the net rate of evaporation. This is usually an arid environment with a small basin fed by a limited input of water. When evaporation occurs, the remaining water is enriched in salts, and they precipitate when the water becomes supersaturated. Evaporite depositi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
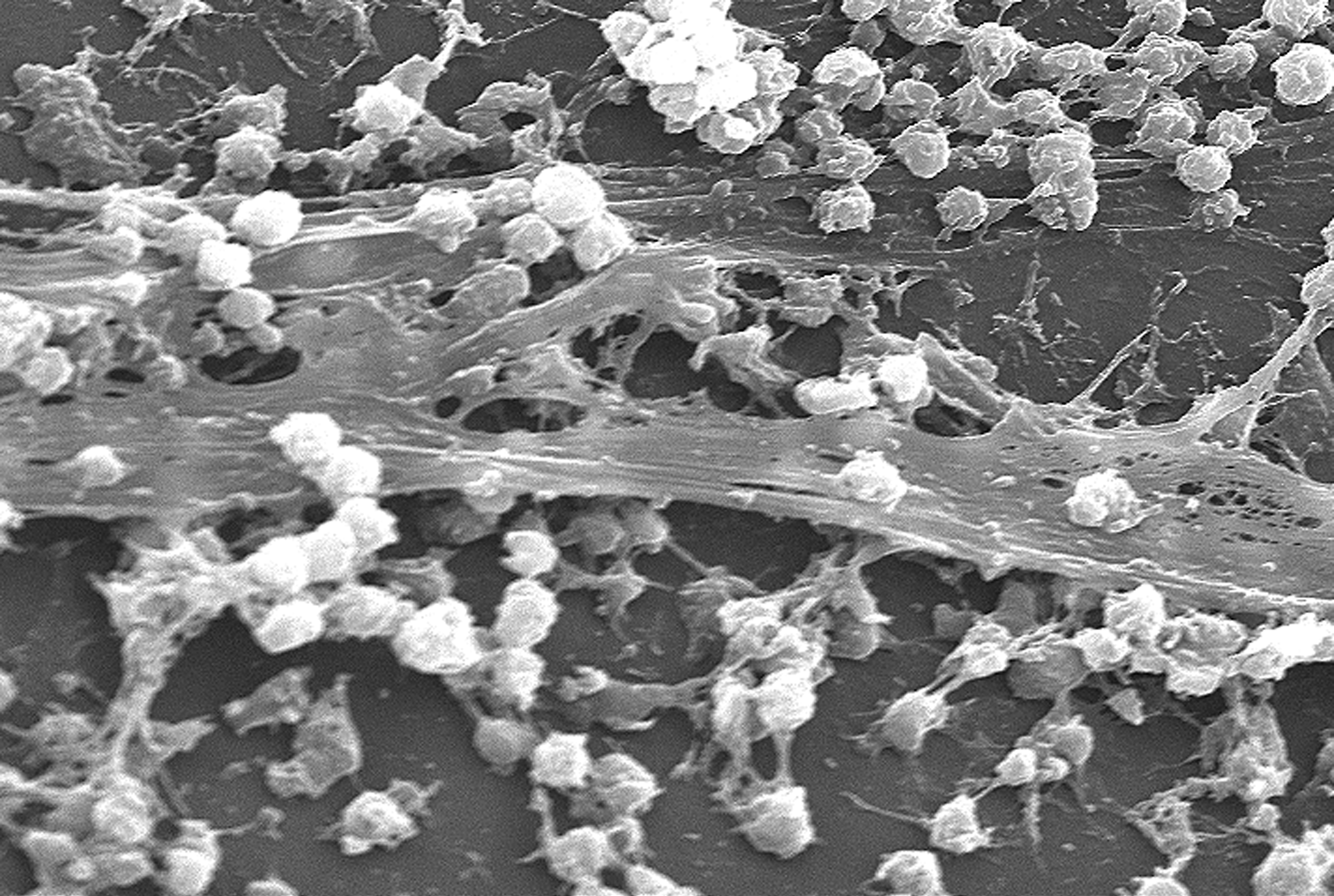
Endolithic
An endolith or endolithic is an organism ( archaeon, bacterium, fungus, lichen, algae or amoeba) that is able to acquire the necessary resources for growth in the inner part of a rock, mineral, coral, animal shells, or in the pores between mineral grains of a rock. Many are extremophiles, living in places long imagined inhospitable to life. The distribution, biomass, and diversity of endolith microorganisms are determined by the physical and chemical properties of the rock substrate, including the mineral composition, permeability, the presence of organic compounds, the structure and distribution of pores, water retention capacity, and the pH. Normally, the endoliths colonize the areas within lithic substrates to withstand intense solar radiation, temperature fluctuations, wind, and desiccation. They are of particular interest to astrobiologists, who theorize that endolithic environments on Mars and other planets constitute potential refugia for extraterrestrial microbial co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biofilm
A biofilm comprises any syntrophic consortium of microorganisms in which cells stick to each other and often also to a surface. These adherent cells become embedded within a slimy extracellular matrix that is composed of extracellular polymeric substances (EPSs). The cells within the biofilm produce the EPS components, which are typically a polymeric conglomeration of extracellular polysaccharides, proteins, lipids and DNA. Because they have three-dimensional structure and represent a community lifestyle for microorganisms, they have been metaphorically described as "cities for microbes". Biofilms may form on living or non-living surfaces and can be prevalent in natural, industrial, and hospital settings. They may constitute a microbiome or be a portion of it. The microbial cells growing in a biofilm are physiologically distinct from planktonic cells of the same organism, which, by contrast, are single cells that may float or swim in a liquid medium. Biofilms can form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioinformatic
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, in particular when the data sets are large and complex. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combines biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret the biological data. Bioinformatics has been used for ''in silico'' analyses of biological queries using computational and statistical techniques. Bioinformatics includes biological studies that use computer programming as part of their methodology, as well as specific analysis "pipelines" that are repeatedly used, particularly in the field of genomics. Common uses of bioinformatics include the identification of candidates genes and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Often, such identification is made with the aim to better understand the genetic basis of disease, unique adaptations, desirable properties (esp. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicuña
The vicuña (''Lama vicugna'') or vicuna (both , very rarely spelled ''vicugna'', its former genus name) is one of the two wild South American camelids, which live in the high alpine areas of the Andes, the other being the guanaco, which lives at lower elevations. Vicuñas are relatives of the llama, and are now believed to be the wild ancestor of domesticated alpacas, which are raised for their coats. Vicuñas produce small amounts of extremely fine wool, which is very expensive because the animal can only be shorn every three years and has to be caught from the wild. When knitted together, the product of the vicuña's wool is very soft and warm. The Inca valued vicuñas highly for their wool, and it was against the law for anyone but royalty to wear vicuña garments; today, the vicuña is the national animal of Peru and appears on the Peruvian coat of arms. Both under the rule of the Inca and today, vicuñas have been protected by law, but they were heavily hunted in the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yareta
__NOTOC__ Yareta or llareta (''Azorella compacta'', known historically as ''Azorella yareta'', from ''yarita'' in the Quechua language) is a velvety, chartreuse cushion plant in the family Apiaceae which is native to South America. It grows in the Puna grasslands of the Andes in Peru, Bolivia, northern Chile and western Argentina at altitudes between . Description Yareta is an evergreen perennial with a low, mat-like shape and hemispherical growth form that grows to around 6 m (~20 ft) in diameter. The self-fertile, pink or lavender flowers are hermaphroditic and are pollinated by insects. The plant prefers sandy, well-drained soils. It can grow in nutritionally poor soils that are acidic, neutral or basic (alkaline) at altitudes of up to . Yareta is well-adapted to high insolation rates typical of the Andes highlands and cannot grow in shade. The plant's leaves grow into an extremely compact, dense mat that reduces heat and water loss. This mat grows near the ground whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parastrephia Lepidophylla
''Parastrephia lepidophylla'', commonly known as tola or tola tola, is a species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae. It is native to South America and has been recorded from Argentina, Bolivia, Chile and Peru where it is characteristic of the puna grassland ecoregion. It is a resinous shrub, growing up to 2 m in height, that is typically found in semi-arid central Andean dry, or tola heath, puna habitats, at altitudes of 3500–5000 m above sea level, and in the undergrowth of central Andean ''Polylepis ''Polylepis'' is a genus comprising 28 recognised shrub and tree species, that are endemic to the mid- and high-elevation regions of the tropical Andes. This group is unique in the rose family in that it is predominantly wind-pollinated. They are ...'' forest. Uses In north-western Argentina the smoke from burning the leaves of the plant has been used externally as an aid in hastening childbirth. References Astereae Taxa named by Ángel Lulio Cabrera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cono De Arita
Cono may refer to * Cono Christian School, a Presbyterian church near Walker, Iowa * City of New Orleans (train), a passenger train operated by Amtrak from New Orleans, Louisiana, to Chicago, Illinois * Cono Township, Buchanan County, Iowa Cono Township is one of sixteen townships in Buchanan County, Iowa, United States The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America ..., one of sixteen townships in Buchanan County, Iowa See also * Cuno (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socompa
Socompa is a large stratovolcano at the border of Argentina and Chile with an elevation of metres. Part of the Chilean and Argentine Andean Volcanic Belt (AVB), it is part of the Central Volcanic Zone, one of the various segments of the AVB. This part of the Andean volcanic arc begins in Peru and runs first through Bolivia and Chile, and then through Argentina and Chile, and contains about 44 active volcanoes. Socompa lies close to the pass of the same name, where the Salta-Antofagasta railway crosses the border. Socompa is known for its large debris avalanche, which was formed 7,200 years ago when most of the northwestern slope collapsed and slid down, forming an extensive deposit. It was at first considered to be either a moraine or a nuee ardende deposit, until the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens prompted awareness of the instability of volcanic edifices and the existence of large scale collapses on them. The Socompa collapse is among the largest known with a volume of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)