|
Oil And Gas (Enterprise) Act 1982
The Oil and Gas (Enterprise) Act 1982 (1982 chapter 23) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which started the process of privatisation of the oil and gas industries in the UK. It empowered the government to float off and sell shares in Britoil the upstream production side of the British National Oil Corporation. It ended the British Gas Corporation’s monopoly on the transportation and supply of gas, opening up the gas market to other gas suppliers. The Act made miscellaneous provisions relating to the oil and gas industries concerning Petroleum Licences and Offshore Installations. Background The British gas industry had been in state ownership since nationalisation of the industry in 1949. The Gas Act 1972 had established the British Gas Corporation to exercise full responsibility for the oversight, control and operation of the gas industry. The government had established the British National Oil Corporation (BNOC) in 1975 under the provision of the Petroleum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Act Of Parliament
Acts of Parliament, sometimes referred to as primary legislation, are texts of law passed by the Legislature, legislative body of a jurisdiction (often a parliament or council). In most countries with a parliamentary system of government, acts of parliament begin as a Bill (law), bill, which the legislature votes on. Depending on the structure of government, this text may then be subject to assent or approval from the Executive (government), executive branch. Bills A draft act of parliament is known as a Bill (proposed law), bill. In other words, a bill is a proposed law that needs to be discussed in the parliament before it can become a law. In territories with a Westminster system, most bills that have any possibility of becoming law are introduced into parliament by the government. This will usually happen following the publication of a "white paper", setting out the issues and the way in which the proposed new law is intended to deal with them. A bill may also be introduced in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Offshore Petroleum Development (Scotland) Act 1975
The Offshore Petroleum Development (Scotland) Act 1975 (c. 8) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which facilitated the onshore construction of offshore oil platforms for the UK Continental Shelf. Its provisions permitted the acquisition of land; the regulation of sea-based operations; the granting of licences for construction; the reinstatement of land; and financial provisions. Background In 1975 the UK government recognised that the development of offshore oil resources would make an important contribution to the UK economy, particularly at a time when the cost of imported crude oil was increasing rapidly. An immediate objective for the government and the oil industry was the building of offshore oil platforms; their construction required significant areas of coastal land. The 1975 Act addressed these issues; it had three purposes: to ensure that land was available for onshore construction; to ensure that construction was properly regulated; and that land was r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
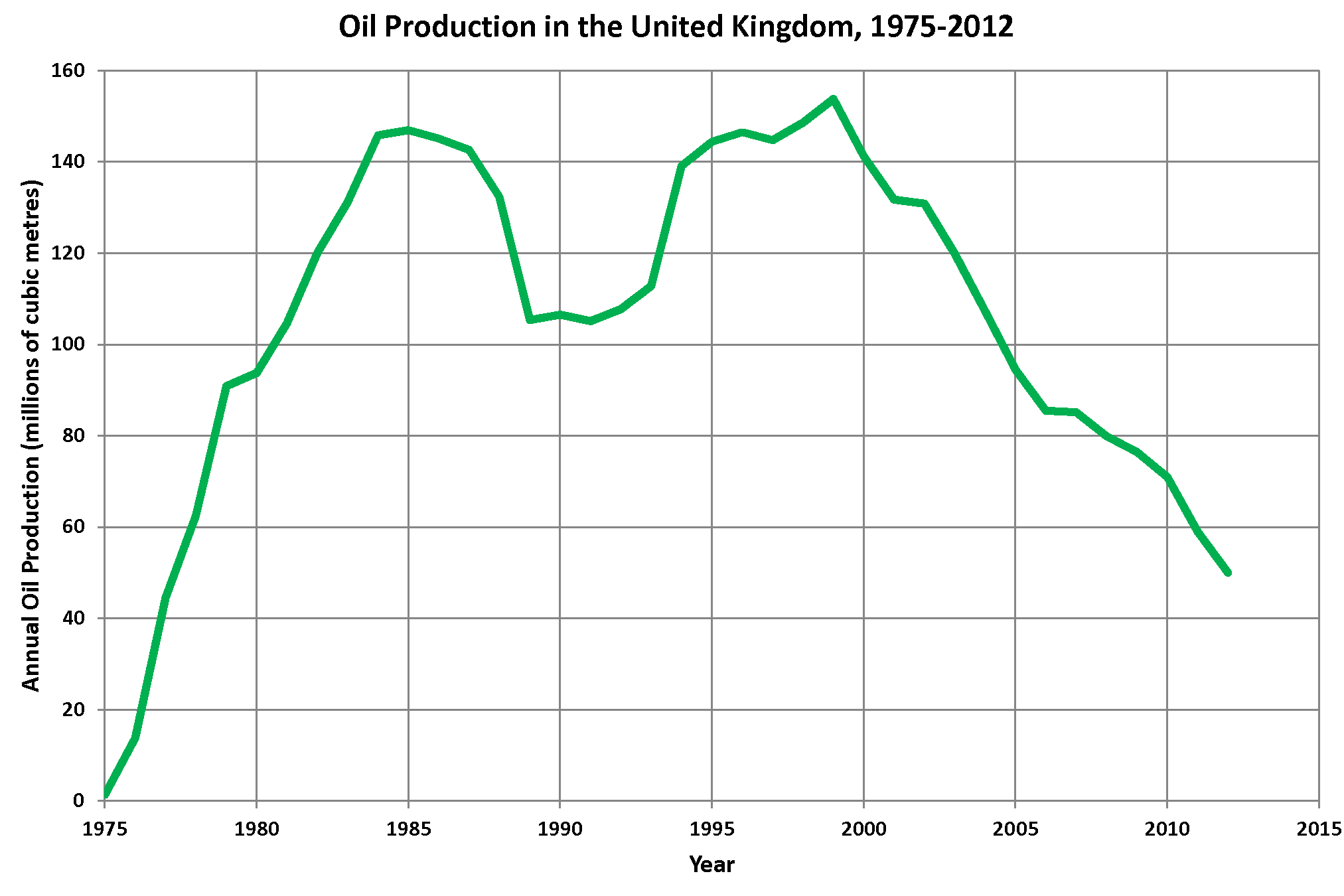
North Sea Oil
North Sea oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons, comprising liquid petroleum and natural gas, produced from petroleum reservoirs beneath the North Sea. In the petroleum industry, the term "North Sea" often includes areas such as the Norwegian Sea and the area known as "West of Shetland", "the Atlantic Frontier" or "the Atlantic Margin" that is not geographically part of the North Sea. Brent crude is still used today as a standard benchmark for pricing oil, although the contract now refers to a blend of oils from fields in the northern North Sea. From the 1960s to 2014 it was reported that 42 billion barrels of oil equivalent (BOE) had been extracted from the North Sea since when production began, and there is still a potential of 24 billion BOE left remaining there, which is equivalent to about 35 years worth of production, the North Sea will remain as an important petroleum reservoir for years to come. History 1851–1963 Commercial extraction of oil on the shores of the North Sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil And Gas Industry In The United Kingdom
The oil and gas industry plays a central role in the economy of the United Kingdom. Oil and gas account for more than three-quarters of the UK's total primary energy needs. Oil provides 97 per cent of the fuel for transport, and gas is a key fuel for heating and electricity generation. Transport, heating and electricity each account for about one-third of the UK's primary energy needs. Oil and gas are also major feedstocks for the petrochemicals industries producing pharmaceuticals, plastics, cosmetics and domestic appliances. Although UK Continental Shelf production peaked in 1999, in 2016 the sector produced 62,906,000 cubic metres of oil and gas, meeting more than half of the UK's oil and gas needs. There could be up to 3.18 billion cubic metres of oil and gas still to recover from the UK's offshore fields. In 2017, capital investment in the UK offshore oil and gas industry was £5.6 billion. Since 1970 the industry has paid almost £330 billion in production tax. About 280,000 j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineral Working (Offshore Installations) Act 1971
The Mineral Workings (Offshore Installations) Act 1971 (1971 chapter 61) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which provided for the safety, health and welfare of people on installations undertaking the exploitation of, and exploration for, mineral resources in UK offshore waters. Background The exploration for natural gas under the United Kingdom’s sector of the North Sea began in 1964. The first gas was found in September 1965 by the self-elevating drilling rig ''Sea Gem''. Tragically, on 27 December 1965 ''Sea Gem'' collapsed and sank 43 miles east of the Humber. Thirteen of the crew of 32 were killed. A tribunal was appointed in February 1967 to establish the circumstances of the accident. The hearing lasted 29 days, and the tribunal report was published on 26 July 1967. The report identified that statutory provisions for regulating the safety of offshore installations, together with credible sanctions, should be available for installations working on the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil And Pipelines Agency
The Oil and Pipelines Agency (OPA) is a statutory corporation of the Ministry of Defence (MoD) in the United Kingdom. Its current role is to operate six coastal Oil Fuel Depots on behalf of the MoD. The OPA was also previously responsible for the management of the Government Pipelines and Storage System (GPSS), until its sale in 2015. The OPA is the MoD's professional expert on bulk fuel storage and transportation by pipeline. History The OPA was formed at the end of 1985 under the Oil and Pipelines Act 1985 (c. 62). It was the successor organisation to the British National Oil Corporation (BNOC) in its responsibility for managing the Department of Energy's pipelines and storage depots. It was not initially responsible for either the Ministry of Defence spur pipelines or storage depots. Its statutory role was to be responsible for the safe, efficient, economic and effective management of the GPSS. The OPA's tasks included maximising private sector usage of the GPSS provided this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil And Pipelines Act 1985
The Oil and Pipelines Act 1985 (c. 62) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which established the Oil and Pipelines Agency to buy, sell or deal in petroleum and to manage on behalf of the Crown petroleum pipelines and storage installations. The act abolished the British National Oil Corporation and transferred its assets to the Agency. Background The government had established the British National Oil Corporation (BNOC) in 1975 under the provisions of the Petroleum and Submarine Pipe-lines Act 1975. BNOC, as constituted, was effectively two businesses: firstly for the production of oil and petroleum, and secondly for trading in oil. The Oil and Gas (Enterprise) Act 1982 enabled the government to transfer the upstream oil exploration and production side of the BNOC's business into Britoil, a limited liability company. Britoil was floated on the stock market in November 1982 and again in August 1985. The downstream trading side of the business remained within BNOC. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Office Of Gas And Electricity Markets
, type = Non-ministerial government department , nativename = , nativename_a = , nativename_r = , logo = Ofgem logo.svg , logo_width = 124px , logo_caption = , seal = , seal_width = , seal_caption = , picture = , picture_width = , picture_caption = , formed = , preceding1 = Office of Electricity Regulation , preceding2 = Office of Gas Supply , dissolved = , superseding = , jurisdiction = Great Britain , headquarters = 10 South Colonnade, Canary Wharf, London, , region_code = GB , coordinates = , employees = 1,187 , budget = For 2015–2016 Parliament approved through the Main Estimate a gross resource budget of £89.5 million , minister1_name = Grant Shapps , minister1_pfo = Secretary of State for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy , chief1_name = Jonathan Brearley , chief1_position = Chief Executive , chief2_name = , chief2_position = , chief3_name = , chief3_position = , chief4_name = , chief4_position = , chief5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Gas Plc
British Gas plc was an energy and home services provider in the United Kingdom. It was formed when the British Gas Corporation was privatised as a result of the Gas Act 1986, instigated by the government of Margaret Thatcher and superseding the Gas Act 1972. History The company was formed when the Conservative Government privatised the British Gas Corporation in December 1986, with its shares floated on the London stock market. To encourage individuals to become shareholders, the offer was intensely advertised with the "If you see Sid...Tell him!" campaign. The privatisation was criticised by Baron Gray of Contin who said it broke a key part of the Conservative's 1983 manifesto that the party would not simply replace one monopoly with another; at the time, British Gas was the only organisation that could supply gas to anyone in the country. In June 1991, chairman Robert Evans Robert Evans (born Robert J. Shapera; June 29, 1930October 26, 2019) was an American film producer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Assent
Royal assent is the method by which a monarch formally approves an act of the legislature, either directly or through an official acting on the monarch's behalf. In some jurisdictions, royal assent is equivalent to promulgation, while in others that is a separate step. Under a modern constitutional monarchy, royal assent is considered little more than a formality. Even in nations such as the United Kingdom, Norway, the Netherlands, Liechtenstein and Monaco which still, in theory, permit their monarch to withhold assent to laws, the monarch almost never does so, except in a dire political emergency or on advice of government. While the power to veto by withholding royal assent was once exercised often by European monarchs, such an occurrence has been very rare since the eighteenth century. Royal assent is typically associated with elaborate ceremony. In the United Kingdom the Sovereign may appear personally in the House of Lords or may appoint Lords Commissioners, who announce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliament Of The United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative supremacy and thereby ultimate power over all other political bodies in the UK and the overseas territories. Parliament is bicameral but has three parts, consisting of the sovereign ( King-in-Parliament), the House of Lords, and the House of Commons (the primary chamber). In theory, power is officially vested in the King-in-Parliament. However, the Crown normally acts on the advice of the prime minister, and the powers of the House of Lords are limited to only delaying legislation; thus power is ''de facto'' vested in the House of Commons. The House of Commons is an elected chamber with elections to 650 single-member constituencies held at least every five years under the first-past-the-post system. By constitutional convention, all governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander L
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history. Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Aleksander and Aleksandr. Related names and diminutives include Iskandar, Alec, Alek, Alex, Alexandre, Aleks, Aleksa and Sander; feminine forms include Alexandra, Alexandria, and Sasha. Etymology The name ''Alexander'' originates from the (; 'defending men' or 'protector of men'). It is a compound of the verb (; 'to ward off, avert, defend') and the noun (, genitive: , ; meaning 'man'). It is an example of the widespread motif of Greek names expressing "battle-prowess", in this case the ability to withstand or push back an enemy battle line. The earliest attested form of the name, is the Mycenaean Greek feminine anthroponym , , (/Alexandra/), written in the Linear B syllabic script. Alaksandu, alternatively called ''Alakasandu'' or ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |