|
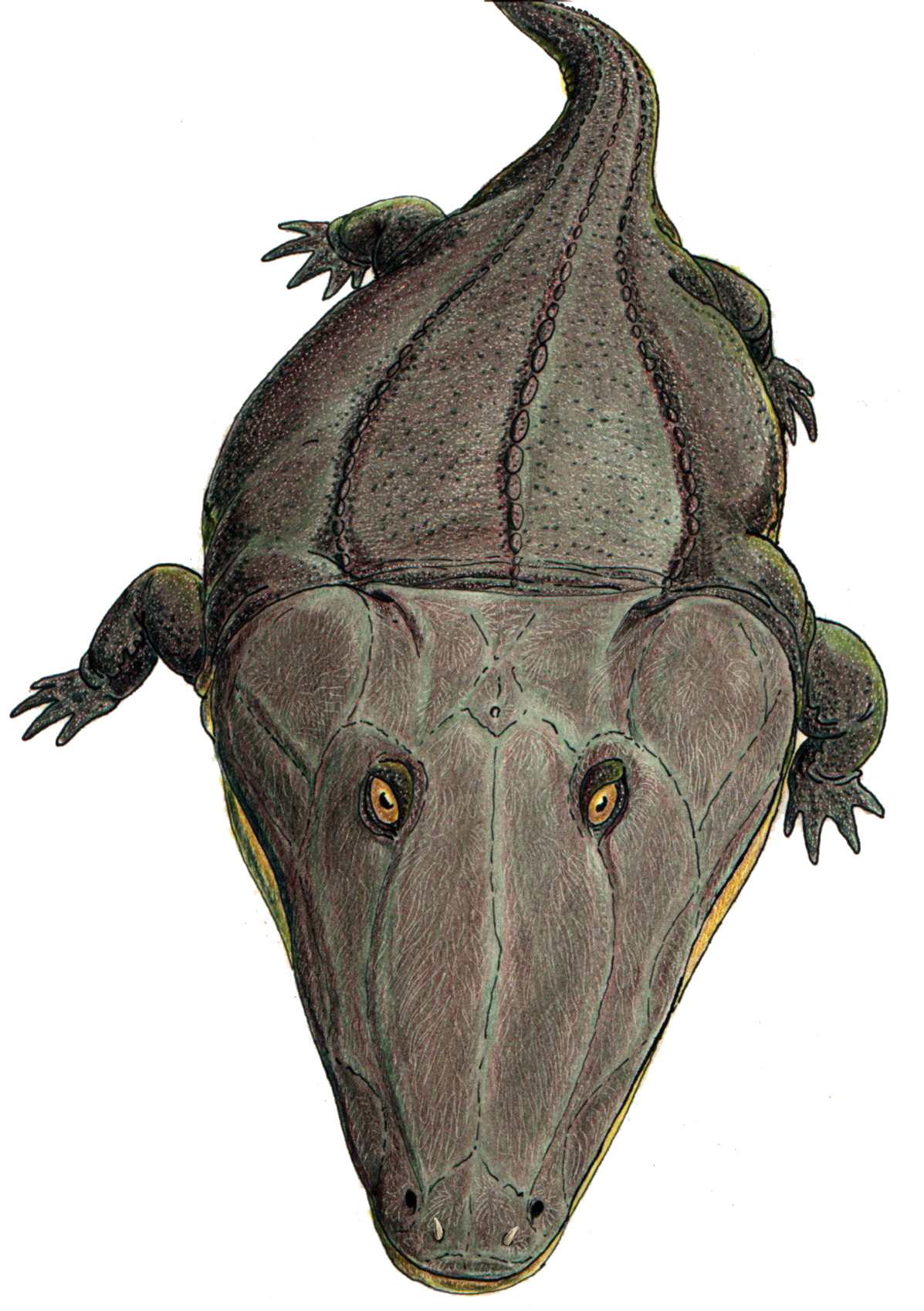
Odenwaldia
''Odenwaldia'' is an extinct genus of mastodonsauroid temnospondyl within the family Heylerosauridae. History of study ''Odenwaldia'' is only known from one species, ''O. heidelbergensis'', and was named by Morales & Kamphausen (1984). The holotype, a skull roof and counterpiece cast, were collected from the Middle Bundsandstein (Oberes Konglomerat) near Heidelberg, Germany and were first described by Wilhelm Simon in 1961, who thought that the specimen belonged to the trematosaur ''Trematosaurus''. It was then redescribed by Schoch (2008). Description The holotype is the only uncontroversial specimen of this taxon, although others have been referred to the species. ''Odenwaldia'' is diagnosed by several autapomorphies, including (1) small orbits combined with broad interorbital distance; (2) preorbital region slender, with nasals and lacrimals narrower than frontals; and (3) dermal ornament consists of small, similarly sized polygons, but no elongated ridges. In contrast t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odenwaldia Heidelbergensis
''Odenwaldia'' is an extinct genus of mastodonsauroid temnospondyl within the family Heylerosauridae. History of study ''Odenwaldia'' is only known from one species, ''O. heidelbergensis'', and was named by Morales & Kamphausen (1984). The holotype, a skull roof and counterpiece cast, were collected from the Middle Bundsandstein (Oberes Konglomerat) near Heidelberg, Germany and were first described by Wilhelm Simon in 1961, who thought that the specimen belonged to the trematosaur ''Trematosaurus''. It was then redescribed by Schoch (2008). Description The holotype is the only uncontroversial specimen of this taxon, although others have been referred to the species. ''Odenwaldia'' is diagnosed by several autapomorphies, including (1) small orbits combined with broad interorbital distance; (2) preorbital region slender, with nasals and lacrimals narrower than frontals; and (3) dermal ornament consists of small, similarly sized polygons, but no elongated ridges. In contrast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladlenosaurus Alexeyevi
''Vladlenosaurus'' is an extinct genus of capitosaur from Russia. It lived during the late Vetlugian (Early Triassic). Based on the type of deposits it was found in, ''Vladlenosaurus'' probably inhabited lacustrine, or lake, habitats. The type species is ''V. alexeyevi'', named in 2000. Description Unlike the flatter, more rounded snouts of other capitosaurs, ''Vladlenosaurus'' had a wedge-shaped snout. This characteristic is also seen in trematosaurians, although it was independently acquired in both cases as a result of convergent evolution. Classification ''Vladlenosaurus'' is similar in appearance to the benthosuchids, a group of trematosauroid temnospondyls, but is more closely related to mastodonsauroids. Among capitosaurs, it shares many features with the basal form ''Wetlugasaurus'', also from the Early Triassic of Russia. ''Vladlenosaurus alexeyevi'' was even considered to be a species of ''Wetlugasaurus'' in a 2006 study. In a 2011 phylogenetic analysis, the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heylerosauridae
Heylerosauridae is a family of mastodonsauroid temnospondyls. It was first named in 1980 to include the genera '' Odenwaldia'' and '' Quasicyclotosaurus''. In addition to these genera, the family now includes '' Eocyclotosaurus'' and '' Yuanansuchus''. Recent phylogenetic analyses have not found a close relationship between ''Odenwaldia'' and other heylerosaurids and place it outside the family. Heylerosaurids are generally regarded as the sister taxon In phylogenetics, a sister group or sister taxon, also called an adelphotaxon, comprises the closest relative(s) of another given unit in an evolutionary tree. Definition The expression is most easily illustrated by a cladogram: Taxon A and ... of the stenotosaurids. References Triassic temnospondyls Middle Triassic first appearances Late Triassic extinctions {{temnospondyli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capitosauria
Capitosauria is an extinct group of large temnospondyl amphibians with simplified stereospondyl vertebrae. Mainly living as piscivores in lakes and rivers, the Capitosauria and its sister taxon Trematosauria were the only major labyrinthodonts that existed during the Mesozoic in ecological niches broadly similar to those of modern crocodiles, and some grew to very large sizes. At 6 meters in length, the Mid-Triassic '' Mastodonsaurus giganteus'' is not only thought to have been the largest capitosaur, but possibly also the largest amphibian to have lived. The latest known remains are from the Rhaetian of Germany and are referred to ''Cyclotosaurus''. Capitosauria was first named by Schoch and Milner (2000) and further described by Yates and Warren (2000), who assigned ''Lydekkerina'' and Mastodonsauroidea to it. It was described by Damiani (2001) under the name Mastodonsauroidea. In their phylogenetic analysis of temnospondyls, Ruta ''et al.'' (2007) placed ''Lydekkerina'' and it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edingerella Madagascariensis
''Edingerella'' is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian from the Early Triassic of Madagascar. It is a basal capitosaur closely related to ''Watsonisuchus''. Phylogeny Below is a cladogram A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to d ... from Fortuny ''et al.'' (2011): References Triassic temnospondyls of Africa Prehistoric animals of Madagascar Capitosaurs Early Triassic amphibians of Africa Prehistoric amphibian genera {{triassic-animal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benthosuchus
''Benthosuchus'' (meaning "deep water crocodile") is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian from the Early Triassic of Russia. It was primarily aquatic, living in rivers and lakes. Multiple species are known, with the largest reaching about 2.5 meters in length. Russian paleontologist Ivan Yefremov fremovcalled the genus ''Benthosaurus'' "deep water lizard" (from Ancient Greek βένθος (''benthos'') "depth, deep water") in his original 1929 description, "in view of its clearly indicated adaptation to life in deep water" shown by "the position of the orbits and the flatness of the skull." The type species ''B. sushkini'' honored his late teacher Petr Sushkin. The generic name was preoccupied by ''Benthosaurus'' Goode & Bean, 1886, a fish, and he renamed the genus ''Benthosuchus'' ("deep water crocodile") in 1937.Efremov, I. A. (1929). ''Benthosaurus sushkini'', ein neuer Labyrinthodont der permotriassischen Ablagerungen der Sharschenga Flusses. ''Bulletin of the Acad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhinesuchidae
Rhinesuchidae is a family of tetrapods that lived primarily in the Permian period. They belonged to the broad group Temnospondyli, a successful and diverse collection of semiaquatic tetrapods which modern amphibians are probably descended from. Rhinesuchids can be differentiated from other temnospondyls by details of their skulls, most notably the interior structure of their otic notches at the back of the skull. They were among the earliest-diverging members of the Stereospondyli, a subgroup of temnospondyls with flat heads and aquatic habits. Although more advanced stereospondyls evolved to reach worldwide distribution in the Triassic period, rhinesuchids primarily lived in the high-latitude environments of Gondwana (what is now South America and Africa) during the Guadalupian and Lopingian epochs of the Permian. The taxonomy of this family has been convoluted, with more than twenty species having been named in the past; a 2017 review recognized only eight of them (distributed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanocephalosaurus Birdi
''Stanocephalosaurus'' (stano from Greek stenos, meaning “narrow”, cephalo from Greek kephalē, meaning “head”) is an extinct genus of large-sized temnospondyl amphibians living through the early to mid Triassic. The etymology of its name most likely came from its long narrow skull when compared to other temnospondyls. ''Stanocephalosaurus'' lived an aquatic lifestyle, with some species even living in salt lakes. There are currently three recognized species and another that needs further material to establish its legitimacy. The three known species are ''Stanocephalosaurus pronus'' from the Middle Triassic in Tanzania, ''Stanocephalosaurus amenasensis'' from the Lower Triassic in Algeria, and ''Stanocephalosaurus birdi'', from the middle Triassic in Arizona. ''Stanocephalosaurus rajareddyi'' from the Middle Triassic in central India needs further evidence in order to establish its relationship among other Stanocephalosaurs. Like other temnospondyls, ''Stanocephalosaurus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanocephalosaurus Pronus
''Stanocephalosaurus'' (stano from Greek stenos, meaning “narrow”, cephalo from Greek kephalē, meaning “head”) is an extinct genus of large-sized temnospondyl amphibians living through the early to mid Triassic. The etymology of its name most likely came from its long narrow skull when compared to other temnospondyls. ''Stanocephalosaurus'' lived an aquatic lifestyle, with some species even living in salt lakes. There are currently three recognized species and another that needs further material to establish its legitimacy. The three known species are ''Stanocephalosaurus pronus'' from the Middle Triassic in Tanzania, ''Stanocephalosaurus amenasensis'' from the Lower Triassic in Algeria, and ''Stanocephalosaurus birdi'', from the middle Triassic in Arizona. ''Stanocephalosaurus rajareddyi'' from the Middle Triassic in central India needs further evidence in order to establish its relationship among other Stanocephalosaurs. Like other temnospondyls, ''Stanocephalosaurus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracyclotosaurus Crookshanki
''Paracyclotosaurus'' (meaning "Near Wheeled Lizard") is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian, which would have appeared similar to today's salamander – but much larger, measuring up to long and weighing between . It lived in the Middle Triassic period, about 235 million years ago, and fossils have been found in Australia, India, and South Africa. Although they could live on dry land, ''Paracyclotosaurus'' probably spent most of its time in water. They had flattened bodies and elongated heads, almost long, that vaguely resembled those of modern crocodiles. Discovery and naming The type species ''P. davidi'' is only known from one complete specimen recovered from Australia. It was discovered by quarry miners in a brick pit in St. Peters in Sydney, New South Wales. The discovery, made in 1910, was from a large ironstone nodule within Ashfield Shale which contained the nearly complete skeleton. The reconstruction was finished in July 1914, and was initially determin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherninia Denwai
''Cherninia'' is an extinct genus of mastodonsaurid temnospondyl. The type species, ''Cherninia denwai'', is known from the Denwa Formation of India. It is based on a massive skull, ISI A 54, which was originally considered a species of ''Parotosuchus ''Parotosuchus'' is an extinct genus of capitosaurian temnospondyl amphibians within the family Mastodonsauridae. Fossils are known from the Early Triassic of Europe, Africa, Australia, and Antarctica. It was about long and likely lived in aqu ...'' in 1998 before being given its own genus in 2001. Another species, ''Cherninia megarhina'', is known from the Upper Ntawere Formation of Zambia. ''C. megarhina'' is based on another large skull, BP/1/4223, which had also been previously referred to ''Parotosuchus''. Though not as well-preserved as the skull of ''C. denwai'', BP/1/4233 was described earlier in 1974. It was described by Sharon Chernin, a paleontologist at the Bernard Price Institute and the namesake of the genus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenotosuchus Africanus
''Xenotosuchus'' is an extinct genus of mastodonsaurid temnospondyl within the family Mastodonsauridae known from the Triassic of South Africa. The genus is based on a skull originally described as ''Parotosuchus'', an animal which it resembled in general build and habit. Description Like many mastodontosaurids, it was a large animal with a large head. Its amphibian life history meant that the distinct shape of the skull roof would change from a generalized tadpole-like skull type through to the distinct adult shape. The head bones are covered in large pits and grooves, indicating extensive dermal armour on the head. Both the upper and lower jaw had tusks, those of the upper jaw being situated on a 2nd row of teeth on the vomer and palatine bone. Contrary to related forms like ''Mastodonsaurus'', the tusks of the lower jaw were of moderate size and did not penetrate the premaxilla. See also * Prehistoric amphibian * List of prehistoric amphibians This list of prehistoric amph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |