|
Octopus Hubbsorum
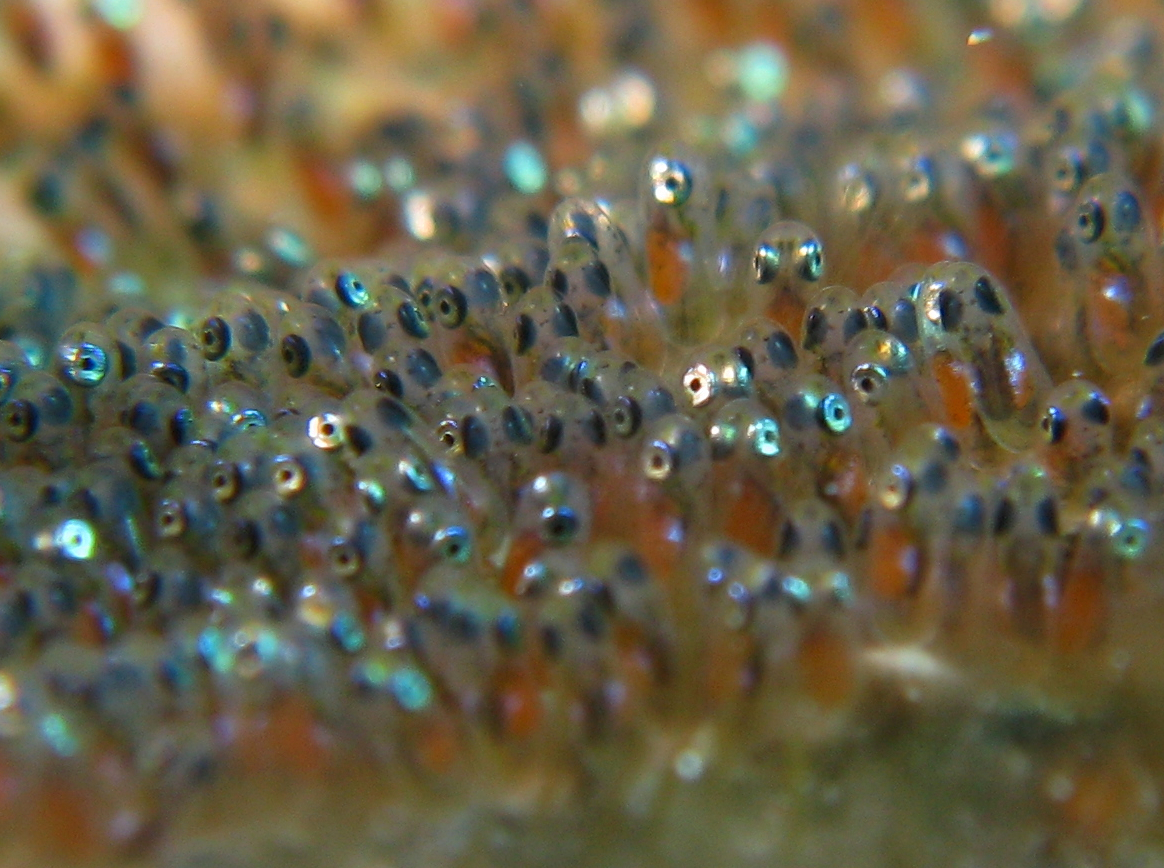
''Octopus hubbsorum'' (also known as Hubb's octopus), is an octopus in the family Octopodidae. It is commonly found along tropical waters along the central Pacific Coast of Mexico. Here, they are one of the most commonly caught cephalopods and are commercially extremely important for the economy. Ecology General ''O. hubbsorum'' is a benthic free-swimming octopus commonly found in intertidal and shallow subtidal zones of the Mexico pacific. Typically, they are found hiding in small places along coral reefs in shallow waters. Additionally, they do not stay in one area, rather they display seasonal movement due to changes in diet patterns. The typical mantle length is medium sized at with an average weight of . It has been found that there is a continuous mature population, which can be accredited to the warmer waters they live in. Additionally, mature males were typically smaller than mature females. It is interesting to note that the species was noticed to have no ocelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manzanillo, Colima
Manzanillo () is a city and seat of Manzanillo Municipality, in the Mexican state of Colima. The city, located on the Pacific Ocean, contains Mexico's busiest port, responsible for handling Pacific cargo for the Mexico City area. It is the largest-producing municipality for the business sector and tourism in the small state of Colima. The city has been referred to as the "sailfish capital of the world". Since 1957, it has hosted national and international fishing competitions, such as the Dorsey Tournament.Manzanillo info at visitmexico.com . Ritrieved 5 August 2011. Manzanillo has developed as a destination for . History |
Octopus Mimus
''Octopus mimus'' (Gould octopus) is commonly found between northern Peru and northern Chile.Tresierra, A., P. Ramirez, S. Alfaro, S. Campos & L. De Lucio. 2009. Catalogo de Invertebrados Marinos de La Región La Libertad. Inst. Mar del Peru. 114 pp. The species is relatively large with a round sacciform mantle without fins.Cardosa, F., P. Villegas y C. Estrella. 2004. Observaciones sobre la biologia de Octopus mimus (Cephalopoda: Octopoda) en la costa peruana. Rev. Peru. Biol. 11(1): 45-50. The tentacles are moderately large, approximately 4 times longer than the mantle. The 3rd tentacle on the right holds the short, thin copulatory organ in males. The color ranges, with individuals commonly speckled a mix of gray, yellow, black, green. It is primarily benthic, living in rocky substrates and kelp forests until depths of 200 m.Zúñiga, O., A. Olivares Paz & I. Torres. 2011. Evaluación del crecimiento del pulpo común Octopus mimus del norte de Chile alimentado con dietas form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hectocotylus
A hectocotylus (plural: ''hectocotyli'') is one of the arms of male cephalopods that is specialized to store and transfer spermatophores to the female. Structurally, hectocotyli are muscular hydrostats. Depending on the species, the male may use it merely as a conduit to the female, analogously to a penis in other animals, or he may wrench it off and present it to the female. The hectocotyl arm was first described in Aristotle's biological works. Although Aristotle knew of its use in mating, he was doubtful that a tentacle could deliver sperm. The name ''hectocotylus'' was devised by Georges Cuvier, who first found one embedded in the mantle of a female argonaut. Supposing it to be a parasitic worm, in 1829 Cuvier gave it a generic name, combining the Greek word for "hundred" and Latin word for "hollow thing". Anatomy Generalized anatomy of squid and octopod hectocotyli: Variability Hectocotyli are shaped in many distinctive ways, and vary considerably between species. The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hectocotylus
A hectocotylus (plural: ''hectocotyli'') is one of the arms of male cephalopods that is specialized to store and transfer spermatophores to the female. Structurally, hectocotyli are muscular hydrostats. Depending on the species, the male may use it merely as a conduit to the female, analogously to a penis in other animals, or he may wrench it off and present it to the female. The hectocotyl arm was first described in Aristotle's biological works. Although Aristotle knew of its use in mating, he was doubtful that a tentacle could deliver sperm. The name ''hectocotylus'' was devised by Georges Cuvier, who first found one embedded in the mantle of a female argonaut. Supposing it to be a parasitic worm, in 1829 Cuvier gave it a generic name, combining the Greek word for "hundred" and Latin word for "hollow thing". Anatomy Generalized anatomy of squid and octopod hectocotyli: Variability Hectocotyli are shaped in many distinctive ways, and vary considerably between species. The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fecundity
Fecundity is defined in two ways; in human demography, it is the potential for reproduction of a recorded population as opposed to a sole organism, while in population biology, it is considered similar to fertility, the natural capability to produce offspring, measured by the number of gametes (eggs), seed set, or asexual propagules. Superfecundity refers to an organism's ability to store another organism's sperm (after copulation) and fertilize its own eggs from that store after a period of time, essentially making it appear as though fertilization occurred without sperm (i.e. parthenogenesis). Human demography Human demography considers only human fecundity, at its culturally differing rates, while population biology studies all organisms. The term ''fecundity'' in population biology is often used to describe the rate of offspring production after one time step (often annual). In this sense, fecundity may include both birth rates and survival of young to that time step. Whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spawn (biology)
Spawn is the Egg cell, eggs and Spermatozoa, sperm released or deposited into water by aquatic animals. As a verb, ''to spawn'' refers to the process of releasing the eggs and sperm, and the act of both sexes is called spawning. Most aquatic animals, except for aquatic mammals and marine reptile, reptiles, reproduce through the process of spawning. Spawn consists of the reproductive cells (gametes) of many aquatic animals, some of which will become fertilized and produce offspring. The process of spawning typically involves females releasing Ovum, ova (unfertilized eggs) into the water, often in large quantities, while males simultaneously or sequentially release spermatozoa (milt) to fertilize the eggs. Most fish reproduce by spawning, as do most other aquatic animals, including crustaceans such as crabs and shrimps, molluscs such as oysters and squid, echinoderms such as sea urchins and sea cucumbers, amphibians such as frogs and newts, aquatic insects such as mayflies and mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
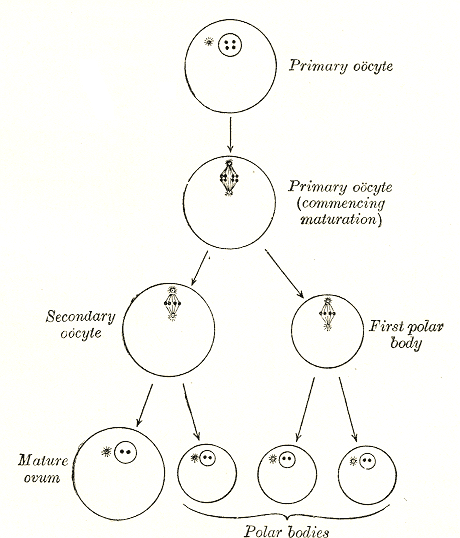
Oocyte
An oocyte (, ), oöcyte, or ovocyte is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female germ cells produce a primordial germ cell (PGC), which then undergoes mitosis, forming oogonia. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Formation The formation of an oocyte is called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and of secondary oocytes after it as part of ovulation. Characteristics Cytoplasm Oocytes are rich in cytoplasm, which contains yolk granules to nourish the cell early in development. Nucleus During the primary oocyte stage of oogenesis, the nucleus is called a germinal vesicle. The only normal human type of secondary oocyte has t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovulation
Ovulation is the release of eggs from the ovaries. In women, this event occurs when the ovarian follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the egg will be available to be fertilized by sperm. In addition, the uterine lining ( endometrium) is thickened to be able to receive a fertilized egg. If no conception occurs, the uterine lining as well as the egg will be shed during menstruation. Process Ovulation occurs about midway through the menstrual cycle, after the follicular phase. The days in which a person is most fertile can be calculated based on the date of the last menstrual period and the length of a typical menstrual cycle. The few days surrounding ovulation (from approximately days 10 to 18 of a 28-day cycle), constitute the most fertile phase. The time from the beginning of the last menstrual period (LMP) until ovulation is, on average, 14.6 days, but with substantial variation among females and betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunting Strategy
A hunting strategy, or hunting method, is a tactic that is used to target, pursue, and hunt an animal. The hunting strategy that a hunter uses depends mainly on the type of terrain, as well as game being hunted. Climate, local hunting techniques, and local hunting laws are also taken in consideration. Some of the most common hunting methods that are used include: still hunting, stalking, driving, stand hunting, calling, baiting, hunting with dogs and falconry. Still hunting Still hunting is a common method of hunting used to hunt North American big game species such as deer, elk, bear, and feral hogs. Still hunting is the process of hunting an animal by sneaking into habitats where the animal lives and trying to spot the animal before the animal spots you. The process emulates the final procedure of spot and stalk hunting throughout throughout the entire process. The still hunting method of hunting is not the most popular hunting technique because it takes a fair amount of skill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polychaete
Polychaeta () is a paraphyletic class (biology), class of generally marine invertebrate, marine annelid worms, common name, commonly called bristle worms or polychaetes (). Each body segment has a pair of fleshy protrusions called parapodia that bear many bristles, called chaetae, which are made of chitin. More than 10,000 species are described in this class. Common representatives include the lugworm (''Arenicola marina'') and the Alitta virens, sandworm or Alitta succinea, clam worm ''Alitta''. Polychaetes as a class are robust and widespread, with species that live in the coldest ocean temperatures of the abyssal plain, to forms which tolerate the extremely high temperatures near hydrothermal vents. Polychaetes occur throughout the Earth's oceans at all depths, from forms that live as plankton near the surface, to a 2- to 3-cm specimen (still unclassified) observed by the robot ocean probe Nereus (underwater vehicle), ''Nereus'' at the bottom of the Challenger Deep, the deepes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
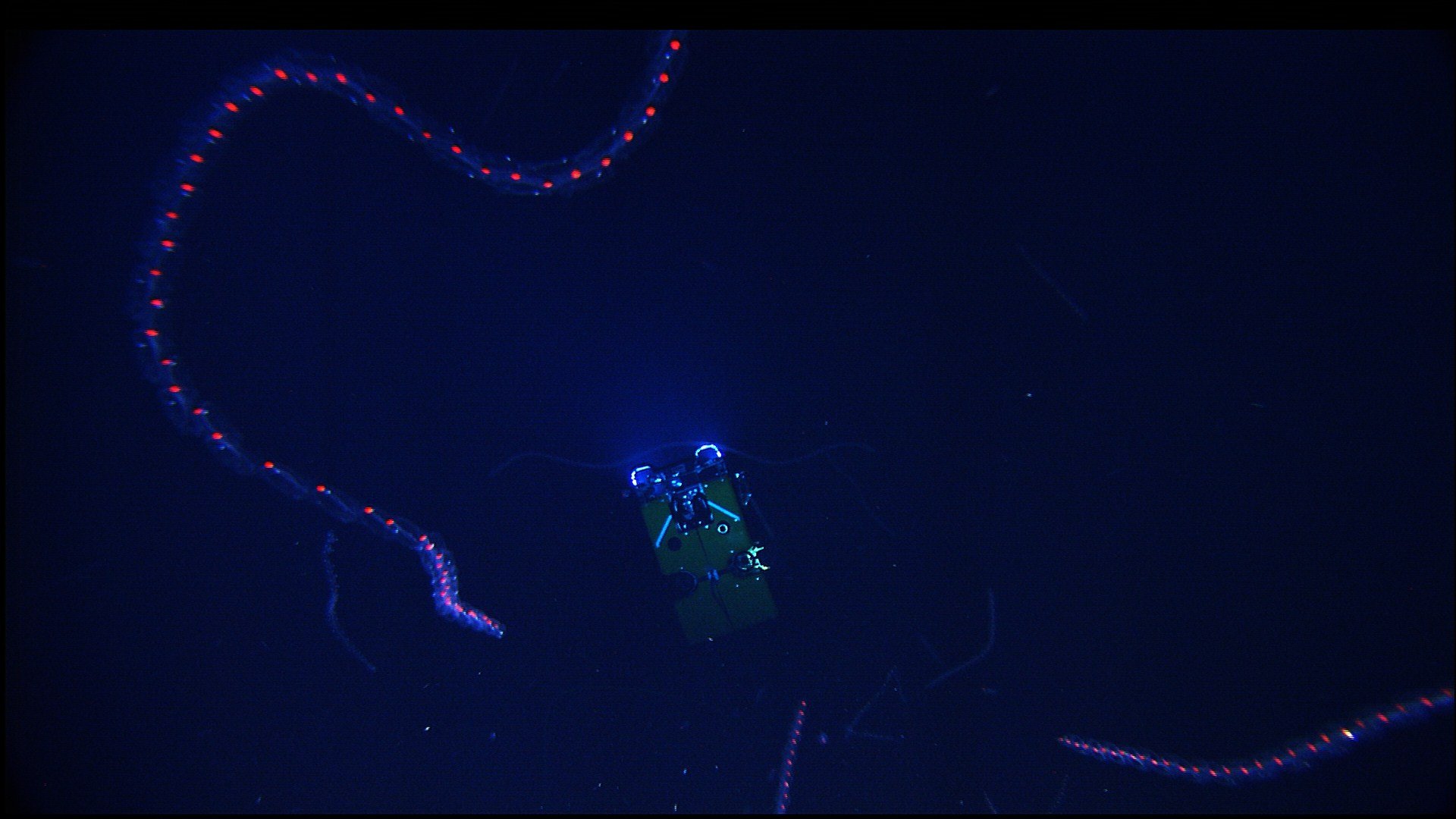
Siphonophorae
Siphonophorae (from Greek ''siphōn'' 'tube' + ''pherein'' 'to bear') is an order within Hydrozoa, which is a class of marine organisms within the phylum Cnidaria. According to the World Register of Marine Species, the order contains 175 species thus far. Although a siphonophore may appear to be an individual organism, each specimen is in fact a colonial organism composed of medusoid and polypoid zooids that are morphologically and functionally specialized. Zooids are multicellular units that develop from a single fertilized egg and combine to create functional colonies able to reproduce, digest, float, maintain body positioning, and use jet propulsion to move. Most colonies are long, thin, transparent floaters living in the pelagic zone. Like other hydrozoans, some siphonophores emit light to attract and attack prey. While many sea animals produce blue and green bioluminescence, a siphonophore in the genus ''Erenna'' was only the second life form found to produce a red li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaetognatha
The Chaetognatha or chaetognaths (meaning ''bristle-jaws'') are a phylum of predatory marine worms that are a major component of plankton worldwide. Commonly known as arrow worms, about 20% of the known Chaetognatha species are benthic, and can attach to algae and rocks. They are found in all marine waters, from surface tropical waters and shallow tide pools to the deep sea and polar regions. Most chaetognaths are transparent and are torpedo shaped, but some deep-sea species are orange. They range in size from . There are more than 120 modern species assigned to over 20 genera. Despite the limited diversity of species, the number of individuals is large. Arrow worms are usually considered a type of protostome that do not belong to either Ecdysozoa or Lophotrochozoa. Anatomy Chaetognaths are transparent or translucent dart-shaped animals covered by a cuticle. The body is divided into a distinct head, trunk, and tail. There are between four and fourteen hooked, grasping spines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |