|
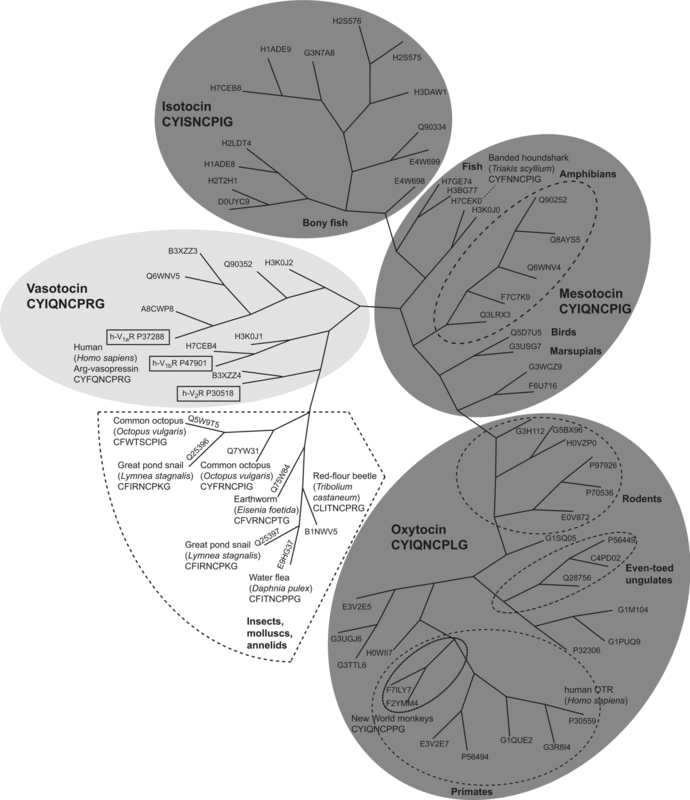
Oxytocin Receptor
The oxytocin receptor, also known as OXTR, is a protein which functions as receptor for the hormone and neurotransmitter oxytocin. In humans, the oxytocin receptor is encoded by the ''OXTR'' gene which has been localized to human chromosome 3p25. Function and location The OXTR protein belongs to the G-protein coupled receptor family, specifically Gq, and acts as a receptor for oxytocin. Its activity is mediated by G proteins that activate several different second messenger systems. Oxytocin receptors are expressed by the myoepithelial cells of the mammary gland, and in both the myometrium and endometrium of the uterus at the end of pregnancy. The oxytocin-oxytocin receptor system plays an important role as an inducer of uterine contractions during parturition and of milk ejection. OXTR is also associated with the central nervous system. The gene is believed to play a major role in social, cognitive, and emotional behavior. A decrease in OXTR expression by methylation of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring develops ( gestates) inside a woman's uterus (womb). A multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins. Pregnancy usually occurs by sexual intercourse, but can also occur through assisted reproductive technology procedures. A pregnancy may end in a live birth, a miscarriage, an induced abortion, or a stillbirth. Childbirth typically occurs around 40 weeks from the start of the last menstrual period (LMP), a span known as the gestational age. This is just over nine months. Counting by fertilization age, the length is about 38 weeks. Pregnancy is "the presence of an implanted human embryo or fetus in the uterus"; implantation occurs on average 8–9 days after fertilization. An '' embryo'' is the term for the developing offspring during the first seven weeks following implantation (i.e. ten weeks' gestational age), after which the term ''fetus'' is used until birth. Signs an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empathy
Empathy is the capacity to understand or feel what another person is experiencing from within their frame of reference, that is, the capacity to place oneself in another's position. Definitions of empathy encompass a broad range of social, cognitive, and emotional processes primarily concerned with understanding others (and others' emotions in particular). Types of empathy include cognitive empathy, emotional (or affective) empathy, somatic empathy, and spiritual empathy.Rothschild, B. (with Rand, M. L.). (2006). ''Help for the Helper: The psychophysiology of compassion fatigue and vicarious trauma''. Etymology The English word ''empathy'' is derived from the Ancient Greek (''empatheia'', meaning "physical affection or passion"). That word derives from (''en'', "in, at") and ('' pathos'', "passion" or "suffering"). Theodor Lipps adapted the German aesthetic term ("feeling into") to psychology in 1903, and Edward B. Titchener translated into English as "empathy" i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intron
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e. a region inside a gene."The notion of the cistron .e., gene... must be replaced by that of a transcription unit containing regions which will be lost from the mature messenger – which I suggest we call introns (for intragenic regions) – alternating with regions which will be expressed – exons." (Gilbert 1978) The term ''intron'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and the corresponding RNA sequence in RNA transcripts. The non-intron sequences that become joined by this RNA processing to form the mature RNA are called exons. Introns are found in the genes of most organisms and many viruses and they can be located in both protein-coding genes and genes that function as RNA (noncoding genes). There are four main types of introns: tRNA introns, group I introns, group II introns, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymorphism (biology)
In biology, polymorphism is the occurrence of two or more clearly different morphs or forms, also referred to as alternative ''phenotypes'', in the population of a species. To be classified as such, morphs must occupy the same habitat at the same time and belong to a panmictic population (one with random mating). Ford E.B. 1965. ''Genetic polymorphism''. Faber & Faber, London. Put simply, polymorphism is when there are two or more possibilities of a trait on a gene. For example, there is more than one possible trait in terms of a jaguar's skin colouring; they can be light morph or dark morph. Due to having more than one possible variation for this gene, it is termed 'polymorphism'. However, if the jaguar has only one possible trait for that gene, it would be termed "monomorphic". For example, if there was only one possible skin colour that a jaguar could have, it would be termed monomorphic. The term polyphenism can be used to clarify that the different forms arise from the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
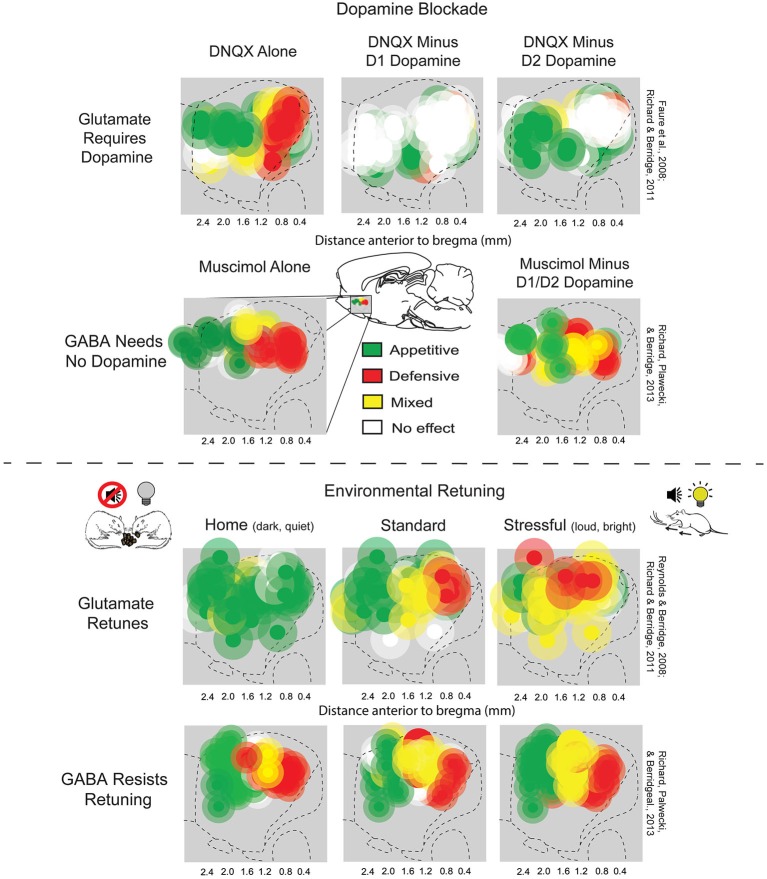
Mesolimbic Pathway
The mesolimbic pathway, sometimes referred to as the reward pathway, is a dopaminergic pathway in the brain. The pathway connects the ventral tegmental area in the midbrain to the ventral striatum of the basal ganglia in the forebrain. The ventral striatum includes the nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle. The release of dopamine from the mesolimbic pathway into the nucleus accumbens regulates incentive salience (e.g. motivation and desire for rewarding stimuli) and facilitates reinforcement and reward-related motor function learning; it may also play a role in the subjective perception of pleasure. The dysregulation of the mesolimbic pathway and its output neurons in the nucleus accumbens plays a significant role in the development and maintenance of an addiction. Anatomy The mesolimbic pathway is a collection of dopaminergic (i.e., dopamine-releasing) neurons that project from the ventral tegmental area (VTA) to the ventral striatum, which includes the nucleus accumben ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleus Accumbens
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for "nucleus adjacent to the septum") is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypothalamus. The nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle collectively form the ventral striatum. The ventral striatum and dorsal striatum collectively form the striatum, which is the main component of the basal ganglia. The dopaminergic neurons of the mesolimbic pathway project onto the GABAergic medium spiny neurons of the nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle. Each cerebral hemisphere has its own nucleus accumbens, which can be divided into two structures: the nucleus accumbens core and the nucleus accumbens shell. These substructures have different morphology and functions. Different NAcc subregions (core vs shell) and neuron subpopulations within each region (D1-type vs D2-type medium spiny neurons) are responsible for different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventral Tegmental Area
The ventral tegmental area (VTA) (tegmentum is Latin for ''covering''), also known as the ventral tegmental area of Tsai, or simply ventral tegmentum, is a group of neurons located close to the midline on the floor of the midbrain. The VTA is the origin of the dopaminergic cell bodies of the mesocorticolimbic dopamine system and other dopamine pathways; it is widely implicated in the drug and natural reward circuitry of the brain. The VTA plays an important role in a number of processes, including reward cognition ( motivational salience, associative learning, and positively-valenced emotions) and orgasm, among others, as well as several psychiatric disorders. Neurons in the VTA project to numerous areas of the brain, ranging from the prefrontal cortex to the caudal brainstem and several regions in between. Structure Neurobiologists have often had great difficulty distinguishing the VTA in humans and other primate brains from the substantia nigra (SN) and surrounding nucl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraventricular Hypothalamic Nucleus
The paraventricular nucleus (PVN, PVA, or PVH) is a nucleus in the hypothalamus. Anatomically, it is adjacent to the third ventricle and many of its neurons project to the posterior pituitary. These projecting neurons secrete oxytocin and a smaller amount of vasopressin, otherwise the nucleus also secretes corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) and thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). CRH and TRH are secreted into the hypophyseal portal system and act on different targets neurons in the anterior pituitary. PVN is thought to mediate many diverse functions through these different hormones, including osmoregulation, appetite, and the response of the body to stress. Location The paraventricular nucleus lies adjacent to the third ventricle. It lies within the periventricular zone and is not to be confused with the periventricular nucleus, which occupies a more medial position, beneath the third ventricle. The PVN is highly vascularised and is protected by the blood–brain barrier, althou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, acid–base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hydrogen, ammonium, potassium and uric acid. The nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Each adult human kidney contains around 1 million nephrons, while a mouse kidney contains on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulation Of Affect
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology and society, but the term has slightly different meanings according to context. For example: * in biology, gene regulation and metabolic regulation allow living organisms to adapt to their environment and maintain homeostasis; * in government, typically regulation means stipulations of the delegated legislation which is drafted by subject-matter experts to enforce primary legislation; * in business, industry self-regulation occurs through self-regulatory organizations and trade associations which allow industries to set and enforce rules with less government involvement; and, * in psychology, self-regulation theory is the study of how individuals regulate their thoughts and behaviors to reach goals. Social Regulation in the social, political, psychological, and economic domains can take many forms: legal restrictio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_2.jpg)