|
Oxidative Addition
Oxidative addition and reductive elimination are two important and related classes of reactions in organometallic chemistry. Oxidative addition is a process that increases both the oxidation state and coordination number of a metal centre. Oxidative addition is often a step in catalytic cycles, in conjunction with its reverse reaction, reductive elimination. Role in transition metal chemistry For transition metals, oxidative reaction results in the decrease in the d''n'' to a configuration with fewer electrons, often 2e fewer. Oxidative addition is favored for metals that are (i) basic and/or (ii) easily oxidized. Metals with a relatively low oxidation state often satisfy one of these requirements, but even high oxidation state metals undergo oxidative addition, as illustrated by the oxidation of Pt(II) with chlorine: : tCl4sup>2− + Cl2 → tCl6sup>2− In classical organometallic chemistry, the formal oxidation state of the metal and the electron count of the complex both in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reductive Elimination
Reductive elimination is an elementary step in organometallic chemistry in which the oxidation state of the metal center decreases while forming a new covalent bond between two ligands. It is the microscopic reverse of oxidative addition, and is often the product-forming step in many catalytic processes. Since oxidative addition and reductive elimination are reverse reactions, the same mechanisms apply for both processes, and the product equilibrium depends on the thermodynamics of both directions. General information Reductive elimination is often seen in higher oxidation states, and can involve a two-electron change at a single metal center (mononuclear) or a one-electron change at each of two metal centers (binuclear, dinuclear, or bimetallic). For mononuclear reductive elimination, the oxidation state of the metal decreases by two, while the d-electron count of the metal increases by two. This pathway is common for d8 metals Ni(II), Pd(II), and Au(III) and d6 metals Pt(I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
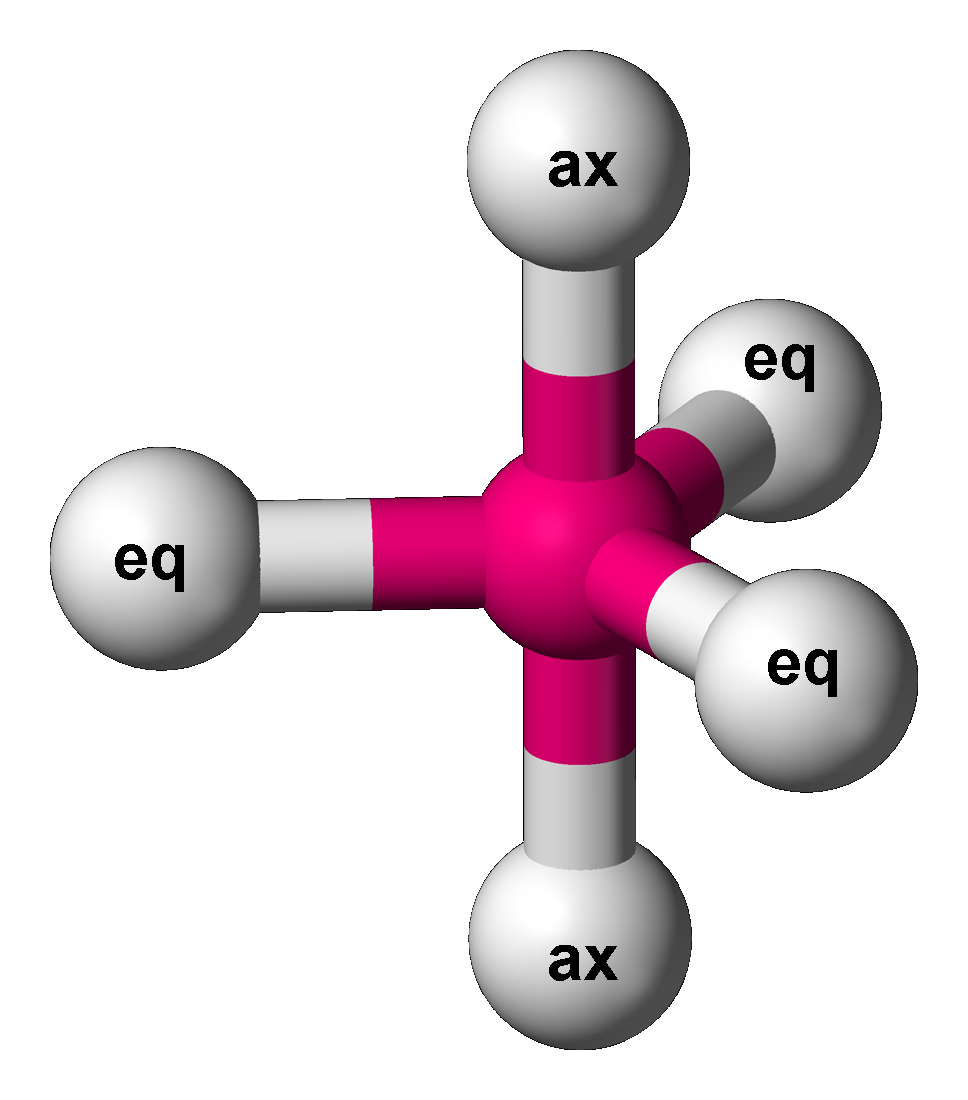
Trigonal Bipyramidal
In chemistry, a trigonal bipyramid formation is a molecular geometry with one atom at the center and 5 more atoms at the corners of a triangular bipyramid. This is one geometry for which the bond angles surrounding the central atom are not identical (see also pentagonal bipyramid), because there is no geometrical arrangement with five terminal atoms in equivalent positions. Examples of this molecular geometry are phosphorus pentafluoride (), and phosphorus pentachloride () in the gas phase. Axial (or apical) and equatorial positions The five atoms bonded to the central atom are not all equivalent, and two different types of position are defined. For phosphorus pentachloride as an example, the phosphorus atom shares a plane with three chlorine atoms at 120° angles to each other in ''equatorial'' positions, and two more chlorine atoms above and below the plane (''axial'' or ''apical'' positions). According to the VSEPR theory of molecular geometry, an axial position is more crowd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monsanto Process
The Monsanto process is an industrial method for the manufacture of acetic acid by catalytic carbonylation of methanol. The Monsanto process has largely been supplanted by the Cativa process, a similar iridium-based process developed by BP Chemicals Ltd which is more economical and environmentally friendly. This process operates at a pressure of 30–60 atm and a temperature of 150–200 °C and gives a selectivity greater than 99%. It was developed in 1960 by the German chemical company, BASF, and improved by the Monsanto Company in 1966, which introduced a new catalyst system. Catalytic cycle The catalytically active species is the anion ''cis''- h(CO)2I2sup>− (top of scheme). The first organometallic step is the oxidative addition of methyl iodide to ''cis''- h(CO)2I2sup>− to form the hexacoordinate species CH3)Rh(CO)2I3sup>−. This anion rapidly transforms, via the migration of a methyl group to an adjacent carbonyl ligand, affording the pentacoordinate acetyl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homogeneous Catalysis
In chemistry, homogeneous catalysis is catalysis by a soluble catalyst in a solution. Homogeneous catalysis refers to reactions where the catalyst is in the same phase as the reactants, principally in solution. In contrast, heterogeneous catalysis describes processes where the catalysts and substrate are in distinct phases, typically solid-gas, respectively. The term is used almost exclusively to describe solutions and implies catalysis by organometallic compounds. Homogeneous catalysis is an established technology that continues to evolve. An illustrative major application is the production of acetic acid. Enzymes are examples of homogeneous catalysts. Examples Acid catalysis The proton is a pervasive homogeneous catalyst because water is the most common solvent. Water forms protons by the process of self-ionization of water. In an illustrative case, acids accelerate (catalyze) the hydrolysis of esters: :CH3CO2CH3 + H2O CH3CO2H + CH3OH At neutral pH, aqueous solutions of most e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azobisisobutyronitrile
Azobisisobutyronitrile (abbreviated AIBN) is an organic compound with the formula CH3)2C(CN)sub>2N2. This white powder is soluble in alcohols and common organic solvents but is insoluble in water. It is often used as a foamer in plastics and rubber and as a radical initiator. As an azo initiator, radicals resulting from AIBN have multiple benefits over common organic peroxides. For example, they do not have oxygenated byproducts or much yellow discoloration. Additionally, they do not cause too much grafting and therefore are often used when making adhesives, acrylic fibers, detergents, etc. Mechanism of decomposition In its most characteristic reaction, AIBN decomposes, eliminating a molecule of nitrogen gas to form two 2-cyanoprop-2-yl radicals: : Because azobisisobutyronitrile readily gives off free radicals, it is often used as a radical initiator. This happens at temperatures above 40 °C, but in experiments is more commonly done at temperatures between 66 °C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalton Transactions
''Dalton Transactions'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing original (primary) research and review articles on all aspects of the chemistry of inorganic, bioinorganic, and organometallic compounds. It is published weekly by the Royal Society of Chemistry. The journal was named after the English chemist, John Dalton, best known for his work on modern atomic theory. Authors can elect to have accepted articles published as open access. The editor is Andrew Shore. ''Dalton Transactions'' was named a "rising star" by ''In-cites'' from Thomson Scientific in 2006. Publication history The journal was established as the ''Journal of the Chemical Society A: Inorganic, Physical, Theoretical'' in 1966. In 1972, the journal was divided into three separate journals: ''Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions'' (covering inorganic and organometallic chemistry), '' Journal of the Chemical Society, Faraday Transactions 1: Physical Chemistry in Condensed Phases'', and '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical (chemistry)
In chemistry, a radical, also known as a free radical, is an atom, molecule, or ion that has at least one unpaired valence electron. With some exceptions, these unpaired electrons make radicals highly chemically reactive. Many radicals spontaneously dimerize. Most organic radicals have short lifetimes. A notable example of a radical is the hydroxyl radical (HO·), a molecule that has one unpaired electron on the oxygen atom. Two other examples are triplet oxygen and triplet carbene (꞉) which have two unpaired electrons. Radicals may be generated in a number of ways, but typical methods involve redox reactions. Ionizing radiation, heat, electrical discharges, and electrolysis are known to produce radicals. Radicals are intermediates in many chemical reactions, more so than is apparent from the balanced equations. Radicals are important in combustion, atmospheric chemistry, polymerization, plasma chemistry, biochemistry, and many other chemical processes. A majority of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halogens
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of five or six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group is known as group 17. The word "halogen" means "salt former" (or "salt maker"). When halogens react with metals, they produce a wide range of salts, including calcium fluoride, sodium chloride (common table salt), silver bromide and potassium iodide. The group of halogens is the only periodic table group that contains elements in three of the main states of matter at standard temperature and pressure. All of the halogens form acids when bonded to hydrogen. Most halogens are typically produced from minerals or salts. The middle halogens—chlorine, bromine, and iodine—are often used as disinfectants. Organobromides are the most important class of flame retardants, while elemental halogens are dangerous and can be toxic. History The fluo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkyl Halides
The haloalkanes (also known as halogenoalkanes or alkyl halides) are alkanes containing one or more halogen substituents. They are a subset of the general class of halocarbons, although the distinction is not often made. Haloalkanes are widely used commercially. They are used as flame retardants, fire extinguishants, refrigerants, propellants, solvents, and pharmaceuticals. Subsequent to the widespread use in commerce, many halocarbons have also been shown to be serious pollutants and toxins. For example, the chlorofluorocarbons have been shown to lead to ozone depletion. Methyl bromide is a controversial fumigant. Only haloalkanes that contain chlorine, bromine, and iodine are a threat to the ozone layer, but fluorinated volatile haloalkanes in theory may have activity as greenhouse gases. Methyl iodide, a naturally occurring substance, however, does not have ozone-depleting properties and the United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the compound a non-ozone l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General SN2-type Oxidative Addition Reaction
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry. In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. March 2021. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/77489?rskey=dCKrg4&result=1 (accessed May 11, 2021) The term ''general'' is used in two ways: as the generic title for all grades of general officer and as a specific rank. It originates in the 16th century, as a shortening of ''captain general'', which rank was taken from Middle French ''capitaine général''. The adjective ''general'' had been affixed to officer designations since the late medieval period to indicate relative superiority or an extended jurisdiction. Today, the title of ''general'' is known in some countries as a four-star rank. However, different countries use different systems of stars or other insignia for senior ranks. It has a NATO rank sca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methyl Iodide
Iodomethane, also called methyl iodide, and commonly abbreviated "MeI", is the chemical compound with the formula CH3I. It is a dense, colorless, volatile liquid. In terms of chemical structure, it is related to methane by replacement of one hydrogen atom by an atom of iodine. It is naturally emitted by rice plantations in small amounts. It is also produced in vast quantities estimated to be greater than 214,000 tons annually by algae and kelp in the world's temperate oceans, and in lesser amounts on land by terrestrial fungi and bacteria. It is used in organic synthesis as a source of methyl groups. Preparation and handling Iodomethane is formed via the exothermic reaction that occurs when iodine is added to a mixture of methanol with red phosphorus. The iodinating reagent is phosphorus triiodide that is formed ''in situ:'' :3 CH3OH + PI3 → 3 CH3I + H2PO3H Alternatively, it is prepared from the reaction of dimethyl sulfate with potassium iodide in the presence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical ( in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied in organic chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but also containing other elements, especially oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus (included in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_Reaction.png)



