|
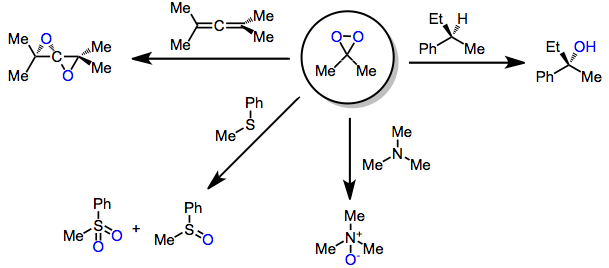
Oxidation With Dioxiranes
Oxidation with dioxiranes refers to the introduction of oxygen into organic molecules through the action of a dioxirane. Dioxiranes are well known for their oxidation of alkenes to epoxides; however, they are also able to oxidize other unsaturated functionality, heteroatoms, and alkane C-H bonds. Introduction Dioxiranes may be produced through the action of KHSO5 on carbonyl compounds. Because of their low-lying σ*O-O orbital, they are highly electrophilic oxidants and react with unsaturated functional groups, Y-H bonds (yielding oxygen insertion products), and heteroatoms. The most common dioxiranes employed for organic synthesis are dimethyldioxirane (DMD) and trifluoromethyl-methyldioxirane (TFD). The latter is effective for chemoselective oxidations of C-H and Si-H bonds. Although this class of reagents is most famous for the epoxidation of alkenes, dioxiranes have been used extensively for other kinds of oxidations as well. Mechanism and stereochemistry Prevailing mechanisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dioxirane
In chemistry, dioxirane is a compound with formula , whose molecule consists of a ring with one carbon and two oxygen atoms, and two hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon. It is a heterocyclic compound, the smallest cyclic organic peroxide. The compound itself is highly unstable and has never been observed at room temperature. Derivatives in which the hydrogens are replaced by other functional groups are called dioxiranes, and may be more stable. Some of them, such as dimethyldioxirane (DMDO) and the more reactive methyl(trifluoromethyl)dioxirane, are used in organic synthesis as oxidizing reagents, most notably as the key catalytic intermediate in the Shi epoxidation reaction. Difluorodioxirane, which boils at about –80 to –90 °C, is one of the very few dioxirane derivatives that is stable in pure form at room temperature. Synthesis Dioxirane is highly unstable and the majority of studies of it have been computational; it has been detected during the low tempera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adamantane
Adamantane is an organic compound with a formula C10H16 or, more descriptively, (CH)4(CH2)6. Adamantane molecules can be described as the fusion of three cyclohexane rings. The molecule is both rigid and virtually stress-free. Adamantane is the most stable isomer of C10H16. The spatial arrangement of carbon atoms in the adamantane molecule is the same as in the diamond crystal. This similarity led to the name ''adamantane'', which is derived from the Greek ''adamantinos'' (relating to steel or diamond). It is a white solid with a camphor-like odor. It is the simplest diamondoid. The discovery of adamantane in petroleum in 1933 launched a new field of chemistry dedicated to the synthesis and properties of polyhedral organic compounds. Adamantane derivatives have found practical application as drugs, polymeric materials, and thermally stable lubricants. History and synthesis In 1924, H. Decker suggested the existence of adamantane, which he called decaterpene. The first attempted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trifluoroacetone
Trifluoroacetone (1,1,1-trifluoroacetone) is an organofluorine compound with the chemical formula CF3C(O)CH3. The compound is a colorless liquid with chloroform-like odour. Preparation, reactions, uses Trifluoroacetone is produced by decarboxylation of trifluoroacetoacetic acid: :CF3C(O)CH2CO2H → CF3C(O)CH3 + CO2 The acetoacetic acid in turn is obtained via condensation of acetate and trifluoroacetate esters. Trifluoroacetone has been examined as oxidizing agent in Oppenauer oxidation, in which case hydroxyl groups of secondary alcohols can be oxidized in the presence of hydroxy groups of primary alcohols. Trifluoracetone is also used in a synthesis of 2-trifluoromethyl-7-azaindoles starting with 2,6-dihalopyridines. The derived chiral imine is used to prepare enantiopure α-trifluoromethyl alanines and diamines by a Strecker reaction followed by either nitrile hydrolysis or reduction. See also *Hexafluoroacetone Hexafluoroacetone (HFA) is a chemical compound with the formu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |