|
Owslebury And Morestead
Owslebury is a village and civil parish in the county of Hampshire, in the south of England approximately southeast of Winchester. It lies within the administrative district of the City of Winchester. Geography The village lies at the top of a hill, on the Roman road from Winchester to the south coast near Portchester. Marwell Zoological Park is towards the south of the parish. Owslebury lies on the Pilgrims' Trail from Winchester to Mont Saint-Michel and the Monarch's Way from Worcester to Shoreham-by-Sea. The village is relatively geographically concentrated along the road that runs through the village. It has a public house and cricket ground that has probably been in use for 150 year an infrequent bus service, a local school, church (St Andrew's Church) and village hall. There were formerly several small shops in the village. Marwell Wildlife Marwell Wildlife (formerly Marwell Zoological Park) is within the boundaries of the parish. Swing Riots On 23 November 1830 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meon Valley (UK Parliament Constituency)
Meon Valley () is a parliamentary constituency in Hampshire represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament by Flick Drummond, a Conservative, since 2019. It had previously been represented since its 2010 creation by George Hollingbery. Constituency profile It is a generally rural constituency, and an affluent safe seat for the Conservatives. The largest towns in the constituency are Waterlooville and Horndean. Output areas in the area in 2001 displayed higher than average incomes overall compared to the national average. In the 2011 census, incidence of home ownership and incidence of semi-detached and detached properties all exceeded the national average and were some of the highest figures for the region. Boundaries This seat has been formed by the Boundary Commission for England as an extra constituency in Hampshire, with electoral wards from East Hampshire, Havant and Winchester districts. *From East Hampshire - the wards of Clanfield and Finchdean, Horndean Cat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palaiós'' meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch (which succeeds the Paleocene), translating to "the old part of the Eocene". The epoch is bracketed by two major events in Earth's history. The K–Pg extinction event, brought on by an asteroid impact and possibly volcanism, marked the beginning of the Paleocene and killed off 75% of living species, most famously the non-avian dinosaurs. The end of the epoch was marked by the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which was a major climatic event wherein about 2,500–4,500 gigatons of carbon were released into the atmosphere and ocean systems, causing a spike in global temperatures and ocean acidification. In the Paleocene, the continents of the Northern Hemisphere were still connected via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colden Common
Colden Common is a civil parish in the Winchester District of Hampshire, England, approximately 5 miles south of the city of Winchester, covering an area of with a resident population of approximately 4,000 people. It includes the village of Colden Common and the hamlets of Hensting, Fisher's Pond, Nob's Crook, Highbridge and Brambridge. Part of the parish lies within the South Downs National Park. History Known in the 13th Century as Colvedene, the origin of the name is uncertain but may come from Old English ''clofa'' (cleft) and ''denu'' (valley). The area that is now known as Colden Common is referred to as Golding Common in the First Edition Ordnance Survey Map of Winchester and Solent. The area was a major centre of palaeolithic flint tool manufacture, with evidence of a "factory" covering 400 square metres discovered during a 1915 excavation in Highbridge. The parish was originally part of the manors of Twyford, Hampshire, Twyford and Owslebury. The Ecclesiastical Parish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dry Valley
A dry valley may develop on many kinds of permeable rock, such as limestone and chalk, or sandy terrains that do not regularly sustain surface water flow. Such valleys do not hold surface water because it sinks into the permeable bedrock. There are many examples of chalk dry valleys along the North and South Downs in Southern England. Notably the National Trust-owned Devil's Dyke near Brighton covers some of downland scarp, and includes the deepest dry valley in the world – created when melting water eroded the chalk downland to the permafrost layer after the last ice age. The three-quarter mile long curved dry valley is around in height and attracts tourists with its views of Sussex, Hampshire and Kent. Other examples include the Alkham Valley near Dover, and the Hartley Bottom and Fawkham valleys near Dartford in north Kent. There are many examples of limestone dry valleys in the Peak District and the Yorkshire Wolds. A notable example is the valley of the River Manifold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hampshire Basin
The Hampshire Basin is a geological basin of Palaeogene age in southern England, underlying parts of Hampshire, the Isle of Wight, Dorset, and Sussex. Like the London Basin to the northeast, it is filled with sands and clays of Paleocene and younger ages and it is surrounded by a broken rim of chalk hills of Cretaceous age. Extent The Hampshire Basin is the traditional name for the landward section of a basin underlying the northern English Channel and much of central southern England, known more fully as the Hampshire-Dieppe Basin. It stretches a little over 100 miles (160 km) from the Dorchester area in the west to Beachy Head in the east. Its southern boundary is marked by a monocline, the Purbeck Monocline, resulting in a near-vertical chalk ridge which forms the Purbeck Hills of Dorset, running under the sea from Old Harry Rocks to The Needles and the central spine of the Isle of Wight and continuing under the English Channel as the Wight- Bray monocline. The northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalk
Chalk is a soft, white, porous, sedimentary carbonate rock. It is a form of limestone composed of the mineral calcite and originally formed deep under the sea by the compression of microscopic plankton that had settled to the sea floor. Chalk is common throughout Western Europe, where deposits underlie parts of France, and steep cliffs are often seen where they meet the sea in places such as the Dover cliffs on the Kent coast of the English Channel. Chalk is mined for use in industry, such as for quicklime, bricks and builder's putty, and in agriculture, for raising pH in soils with high acidity. It is also used for " blackboard chalk" for writing and drawing on various types of surfaces, although these can also be manufactured from other carbonate-based minerals, or gypsum. Description Chalk is a fine-textured, earthy type of limestone distinguished by its light color, softness, and high porosity. It is composed mostly of tiny fragments of the calcite shells or skeletons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia and Anta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
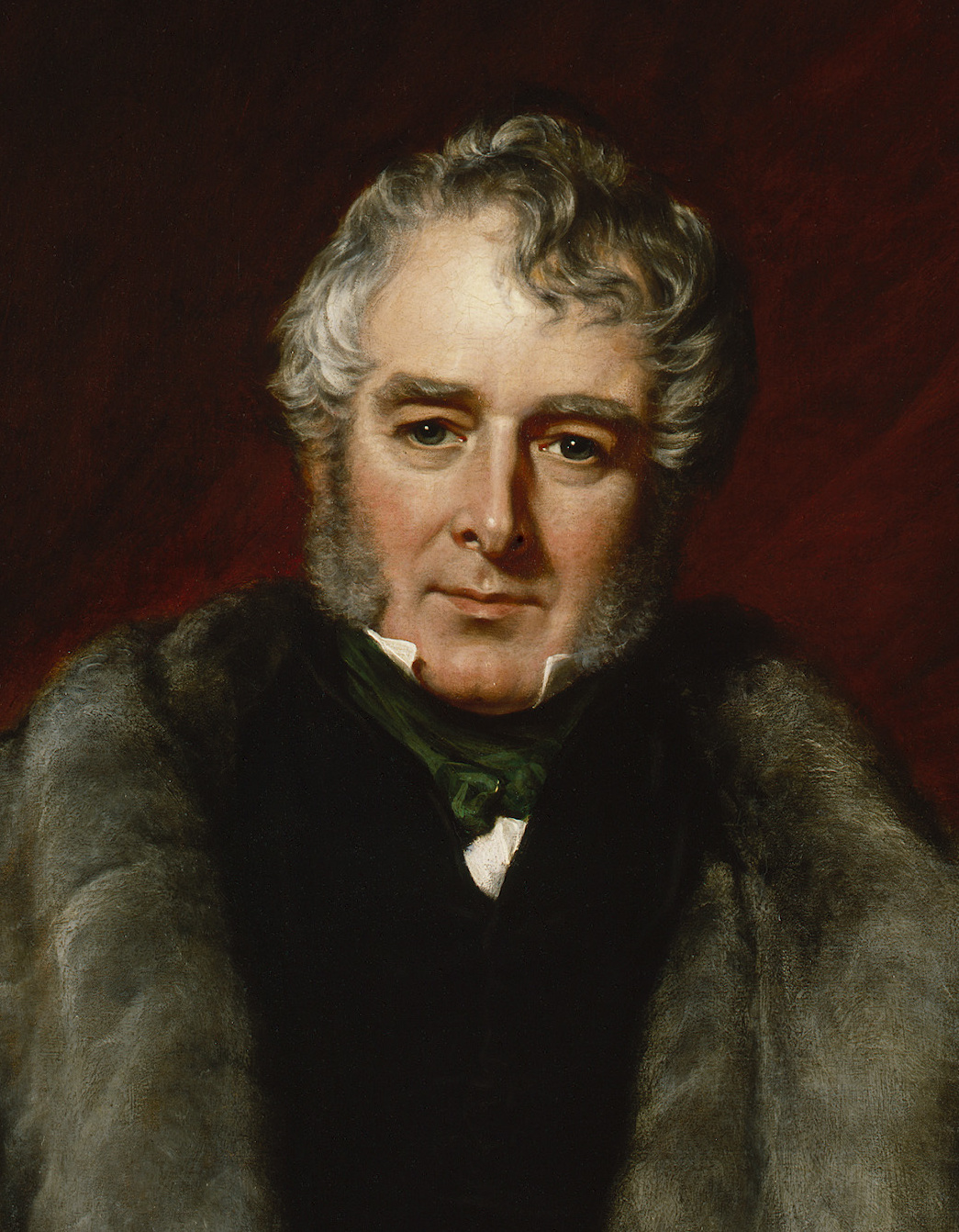
William Lamb, 2nd Viscount Melbourne
William Lamb, 2nd Viscount Melbourne, (15 March 177924 November 1848), in some sources called Henry William Lamb, was a British Whig politician who served as Home Secretary (1830–1834) and Prime Minister (1834 and 1835–1841). His first premiership ended when he was dismissed by King William IV in 1834, the last British prime minister to be dismissed by a monarch. Five months later he was re-appointed and served for six more years, into the reign of Queen Victoria. He is best known for coaching the Queen in the ways of politics, acting almost as her private secretary. Historians do not rank Melbourne's tenure as prime minister favourably, as he had no great foreign wars or domestic issues to handle, and he was involved in several political scandals in the early years of Victoria's reign. Early life Born in London in 1779 to an aristocratic Whig family, William Lamb was the son of the 1st Viscount Melbourne and Elizabeth, Viscountess Melbourne (1751–1818). However, his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
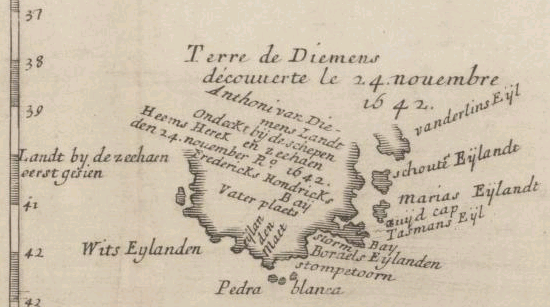
Van Diemen's Land
Van Diemen's Land was the colonial name of the island of Tasmania used by the British during the European exploration of Australia in the 19th century. A British settlement was established in Van Diemen's Land in 1803 before it became a separate colony in 1825. Its penal colonies became notorious destinations for the transportation of convicts due to the harsh environment, isolation and reputation for being inescapable. Macquarie Harbour and Port Arthur are among the most well-known penal settlements on the island. With the passing of the Australian Constitutions Act 1850, Van Diemen's Land (along with New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Victoria, and Western Australia) was granted responsible self-government with its own elected representative and parliament. On 1 January 1856, the colony of Van Diemen's Land was officially changed to Tasmania. The last penal settlement was closed in Tasmania in 1877. Toponym The island was named in honour of Anthony van Die ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penal Transportation
Penal transportation or transportation was the relocation of convicted criminals, or other persons regarded as undesirable, to a distant place, often a colony, for a specified term; later, specifically established penal colonies became their destination. While the prisoners may have been released once the sentences were served, they generally did not have the resources to return home. Origin and implementation Banishment or forced exile from a polity or society has been used as a punishment since at least the 5th century BC in Ancient Greece. The practice of penal transportation reached its height in the British Empire during the 18th and 19th centuries. Transportation removed the offender from society, mostly permanently, but was seen as more merciful than capital punishment. This method was used for criminals, debtors, military prisoners, and political prisoners. Penal transportation was also used as a method of colonization. For example, from the earliest days of English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winnowing Machine
Winnowing is a process by which chaff is separated from grain. It can also be used to remove pests from stored grain. Winnowing usually follows threshing in grain preparation. In its simplest form, it involves throwing the mixture into the air so that the wind blows away the lighter chaff, while the heavier grains fall back down for recovery. Techniques included using a winnowing fan (a shaped basket shaken to raise the chaff) or using a tool (a winnowing fork or shovel) on a pile of harvested grain. In Greek culture The winnowing-fan (λίκνον [''líknon''], also meaning a "cradle") featured in the rites accorded Dionysus and in the Eleusinian Mysteries: "it was a simple agricultural implement taken over and mysticized by the religion of Dionysus," Jane Ellen Harrison remarked. ''Dionysus Liknites'' ("Dionysus of the winnowing fan") was wakened by the Dionysian women, in this instance called ''Thyiades'', in a cave on Mount Parnassus, Parnassus high above Delphi; the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




%2C_Western_Negev%2C_Israel.jpg)