|
Owasso High School (Michigan)
Owasso High School is a high school located within Tulsa County in Owasso, Oklahoma, United States. It is among the largest high schools in Oklahoma by enrollment with nearly 3,000 students. In 2024, the school received international attention following the death of Nex Benedict. The district (of which this is the sole comprehensive high school) includes Owasso, a small portion of Tulsa, Limestone, and a small portion of Valley Park. It is located within the 7,000 square-mile Cherokee Nation reservation in northeastern Oklahoma. History ''Owasso Independent School District v. Falvo'' In October 1998, Kristja Falvo filed suit in the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of Oklahoma, alleging that the use of " peer-grading" within Owasso Public Schools violated the Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA). FERPA authorizes the withholding of federal funds from public school districts that "release any information from a student's education record" wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oklahoma
Oklahoma (; Choctaw language, Choctaw: ; chr, ᎣᎧᎳᎰᎹ, ''Okalahoma'' ) is a U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States, bordered by Texas on the south and west, Kansas on the north, Missouri on the northeast, Arkansas on the east, New Mexico on the west, and Colorado on the northwest. Partially in the western extreme of the Upland South, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 20th-most extensive and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 28th-most populous of the 50 United States. Its residents are known as Oklahomans and its capital and largest city is Oklahoma City. The state's name is derived from the Choctaw language, Choctaw words , 'people' and , which translates as 'red'. Oklahoma is also known informally by its List of U.S. state and territory nicknames, nickname, "Sooners, The Sooner State", in reference to the settlers who staked their claims on land before the official op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
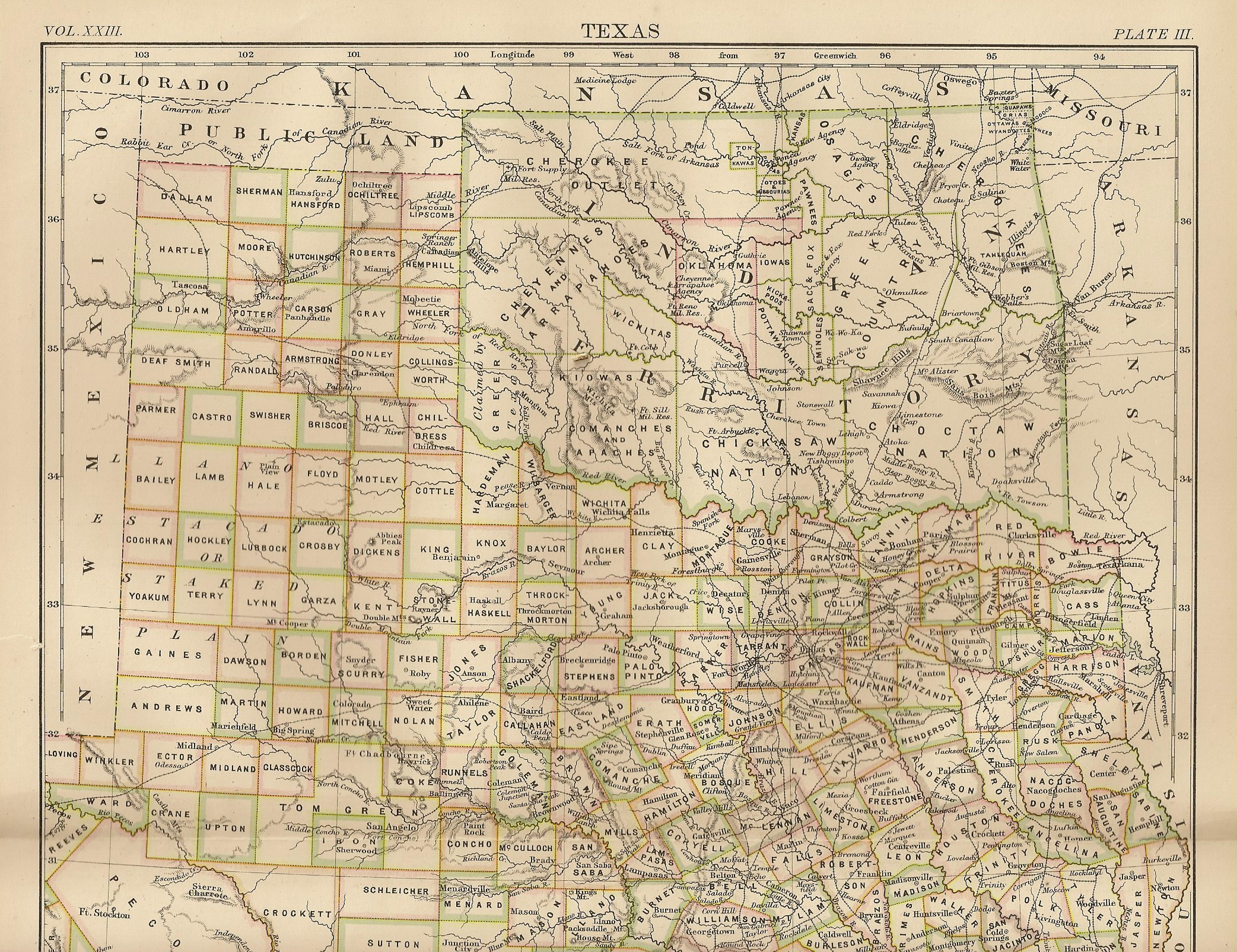
Limestone, Oklahoma
Limestone is a census-designated place (CDP) in Rogers County, Oklahoma, United States, at an elevation of 705 feet. It is located less than 10 miles west of Claremore, Oklahoma on Oklahoma State Highway 20. The population was 753 as of July 2020. Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP has a total area of , all land. Demographics As of the census of 2000, there were 745 people, 252 households, and 214 families residing in the CDP. The population density was . There were 258 housing units at an average density of . The racial makeup of the CDP was 85.23% White, 4.97% Native American, 0.54% Asian, 1.07% from other races, and 8.19% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 1.34% of the population. There were 252 households, out of which 40.5% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 76.2% were married couples living together, 6.0% had a female householder with no husband present, and 14.7% were non-families. 11.5% of all ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disciplinary Action
In a deliberative assembly, disciplinary procedures are used to punish members for violating the rules of the assembly. Codes and rules According to Robert's Rules of Order Newly Revised (RONR), discipline could include censure, fine, suspension, or expulsion. The officers may be removed from their position, including the position of the chair. If an offense occurs in a meeting, the assembly, having witnessed it themselves, can vote on a punishment without the need for a trial. The chair has no authority to impose a penalty or to order the offending member to be removed from the hall, but the assembly has that power. Mason's Manual of Legislative Procedure states that the power of discipline is within the assembly as a whole and not the presiding officer acting alone. A trial is required if the offense occurs outside a meeting and the organization's rules do not describe the disciplinary procedures. The Standard Code of Parliamentary Procedure (TSC) states that in trials of di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grade Point Averages
Grading in education is the process of applying standardized measurements for varying levels of achievements in a course. Grades can be assigned as letters (usually A through F), as a range (for example, 1 to 6), as a percentage, or as a number out of a possible total (often out of 100). In some countries, grades are averaged to create a grade point average (GPA). GPA is calculated by using the number of grade points a student earns in a given period of time. GPAs are often calculated for high school, undergraduate, and graduate students, and can be used by potential employers or educational institutions to assess and compare applicants. A cumulative grade point average (CGPA), sometimes referred to as just GPA, is a measure of performance for all of a student's courses. History Yale University historian George Wilson Pierson writes: "According to tradition the first grades issued at Yale (and possibly the first in the country) were given out in the year 1785, when Preside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amicus Curiae
An ''amicus curiae'' (; ) is an individual or organization who is not a party to a legal case, but who is permitted to assist a court by offering information, expertise, or insight that has a bearing on the issues in the case. The decision on whether to consider an ''amicus'' brief lies within the discretion of the court. The phrase is legal Latin and the origin of the term has been dated to 1605–1615. The scope of ''amici curiae'' is generally found in the cases where broad public interests are involved and concerns regarding civil rights are in question. In American law, an ''amicus curiae'' typically refers to what in some other jurisdictions is known as an intervenor: a person or organization who requests to provide legal submissions so as to offer a relevant alternative or additional perspective regarding the matters in dispute. In the American courts, the amicus may be referred to as an ''amicus'' brief. In other jurisdictions, such as Canada, an ''amicus curiae'' is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthony Kennedy
Anthony McLeod Kennedy (born July 23, 1936) is an American lawyer and jurist who served as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1988 until his retirement in 2018. He was nominated to the court in 1987 by President Ronald Reagan, and sworn in on February 18, 1988. After the retirement of Sandra Day O'Connor in 2006, he was the swing vote on many of the Roberts Court's 5–4 decisions. Born in Sacramento, California, Kennedy took over his father's legal practice in Sacramento after graduating from Harvard Law School. In 1975, President Gerald Ford appointed Kennedy to the United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit. In November 1987, after two failed attempts at nominating a successor to Associate Justice Lewis F. Powell Jr., President Reagan nominated Kennedy to the Supreme Court. Kennedy won unanimous confirmation from the United States Senate in February 1988. Following the death of Antonin Scalia in February 2016, Kennedy becam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Court Justice
The Supreme Court of the United States is the highest-ranking judicial body in the United States. Its membership, as set by the Judiciary Act of 1869, consists of the chief justice of the United States and eight Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, associate justices, any six of whom constitute a quorum. Appointments Clause, Article II, Section 2, Clause 2 of the Constitution grants plenary power to the President of the United States to nominate, and with the advice and consent of the United States Senate, appoint justices to the Supreme Court; justices have life tenure. Background The Supreme Court was created by Article Three of the United States Constitution, Article III of the Constitution of the United States, United States Constitution, which stipulates that the "judicial power of the United States, shall be vested in one Supreme Court," and was organized by the 1st United States Congress. Through the Judiciary Act of 1789, Congress specified the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appellate Court
A court of appeals, also called a court of appeal, appellate court, appeal court, court of second instance or second instance court, is any court of law that is empowered to hear an appeal of a trial court or other lower tribunal. In much of the world, court systems are divided into at least three levels: the trial court, which initially hears cases and reviews evidence and testimony to determine the facts of the case; at least one intermediate appellate court; and a supreme court (or court of last resort) which primarily reviews the decisions of the intermediate courts, often on a discretionary basis. A particular court system's supreme court is its highest appellate court. Appellate courts nationwide can operate under varying rules. Under its standard of review, an appellate court decides the extent of the deference it would give to the lower court's decision, based on whether the appeal were one of fact or of law. In reviewing an issue of fact, an appellate court ordina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Court Of Appeals For The Tenth Circuit
The United States Court of Appeals for the Tenth Circuit (in case citations, 10th Cir.) is a federal court with appellate jurisdiction over the district courts in the following districts: * District of Colorado * District of Kansas * District of New Mexico * Eastern District of Oklahoma * Northern District of Oklahoma * Western District of Oklahoma * District of Utah * District of Wyoming These districts were part of the Eighth Circuit until 1929. The court is composed of twelve active judges and is based at the Byron White U.S. Courthouse in Denver, Colorado. It is one of thirteen United States courts of appeals and has jurisdiction over 560,625 square miles, or roughly one seventh of the country's land mass. History Congress created a new judicial circuit in 1929 to accommodate the increased caseload in the federal courts. Between 1866 and 1912, twelve new states had entered the Union and been incorporated into the Eighth and Ninth Circuits. The Eighth Circuit e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
School District
A school district is a special-purpose district that operates local public primary and secondary schools in various nations. North America United States In the U.S, most K–12 public schools function as units of local school districts, which usually operate several schools, and the largest urban and suburban districts operate hundreds of schools. While practice varies significantly by state (and in some cases, within a state), most American school districts operate as independent local governmental units under a grant of authority and within geographic limits created by state law. The executive and legislative power over locally controlled policies and operations of an independent school district are, in most cases, held by a school district's board of education. Depending on state law, members of a local board of education (often referred to informally as a school board) may be elected, appointed by a political office holder, serve ex officio, or a combination of any of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family Educational Rights And Privacy Act
The Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act of 1974 (FERPA or the Buckley Amendment) is a United States federal law that governs the access to educational information and records by public entities such as potential employers, publicly funded educational institutions, and foreign governments. The act is also referred to as the ''Buckley Amendment'', for one of its proponents, Senator James L. Buckley of New York. Overview FERPA gives parents access to their child's education records, an opportunity to seek to have the records amended, and some control over the disclosure of information from the records. With several exceptions, schools must have a student's consent prior to the disclosure of education records ''after that student is 18 years old''. The law applies only to educational agencies and institutions that receive funds under a program administered by the U.S. Department of Education. Other regulations under this Act, effective starting January 3, 2012, allow for gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)
