|
Ovarian Serous Cystadenoma
Ovarian serous cystadenoma, also (less precisely) known as serous cystadenoma, is the most common ovarian neoplasm, representing 20% of ovarian neoplasms, and is benign. It has a very superficial resemblance to the most common type of ovarian cancer (serous carcinoma of the ovary) under the microscope; however, (1) it is virtually impossible to mix-up with its malignant counterpart (serous carcinoma), and (2) does not share genetic traits of indeterminate serous tumours, also called ''serous borderline tumours'', that may transform into serous carcinoma. Serous cystadenomas (of the ovary) are not related to serous cystadenomas of the pancreas, i.e. the presence of an ovarian ''or'' pancreatic one does ''not'' suggest an increased risk for the other one. Diagnostic Procedures includes initially ultrasound or colour doppler study to know about size and nature of mass and sometimes CECT. Blood investigation includes CA-125 level for screening and further CEA, beta hCG levels, AFP, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
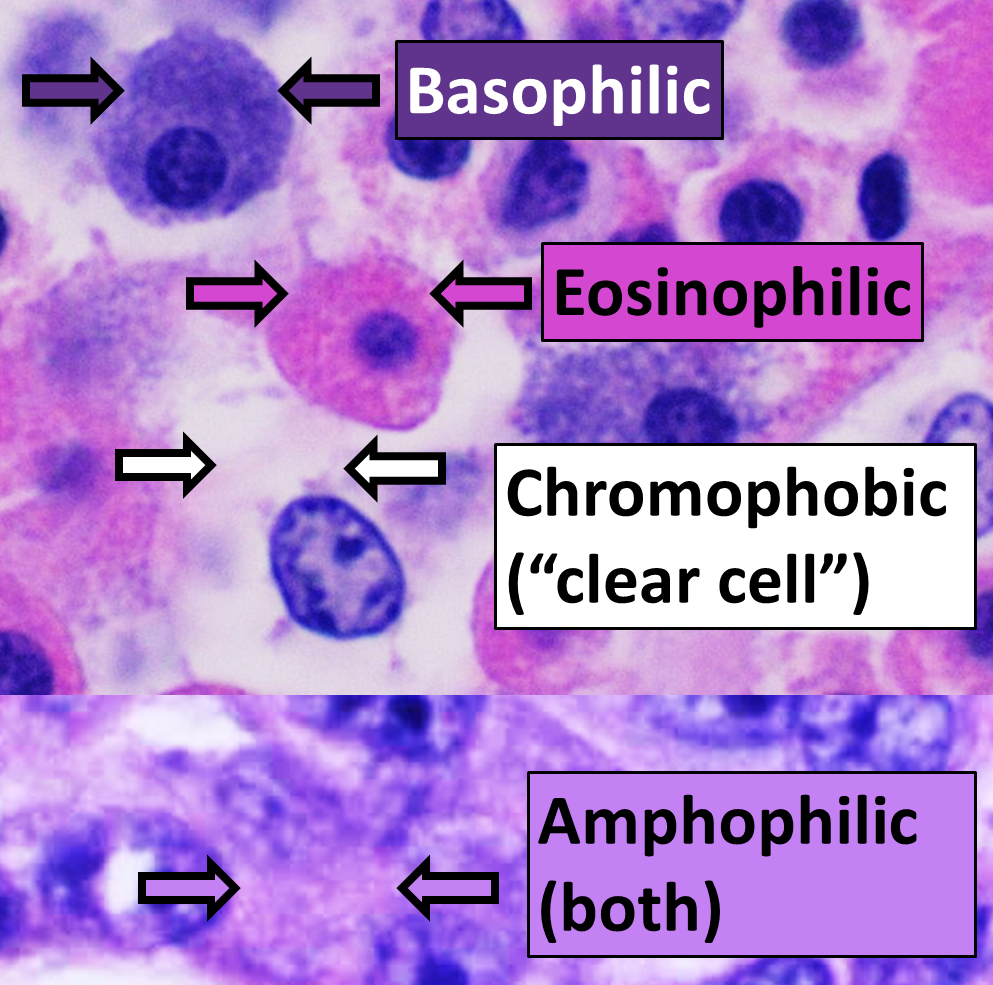
H&E Stain
Hematoxylin and eosin stain ( or haematoxylin and eosin stain or hematoxylin-eosin stain; often abbreviated as H&E stain or HE stain) is one of the principal tissue stains used in histology. It is the most widely used stain in medical diagnosis and is often the gold standard. For example, when a pathologist looks at a biopsy of a suspected cancer, the histological section is likely to be stained with H&E. H&E is the combination of two histological stains: hematoxylin and eosin. The hematoxylin stains cell nuclei a purplish blue, and eosin stains the extracellular matrix and cytoplasm pink, with other structures taking on different shades, hues, and combinations of these colors. Hence a pathologist can easily differentiate between the nuclear and cytoplasmic parts of a cell, and additionally, the overall patterns of coloration from the stain show the general layout and distribution of cells and provides a general overview of a tissue sample's structure. Thus, pattern recogniti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histomorphology
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and ''cytology'', the study of cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these four principal tissue types (fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
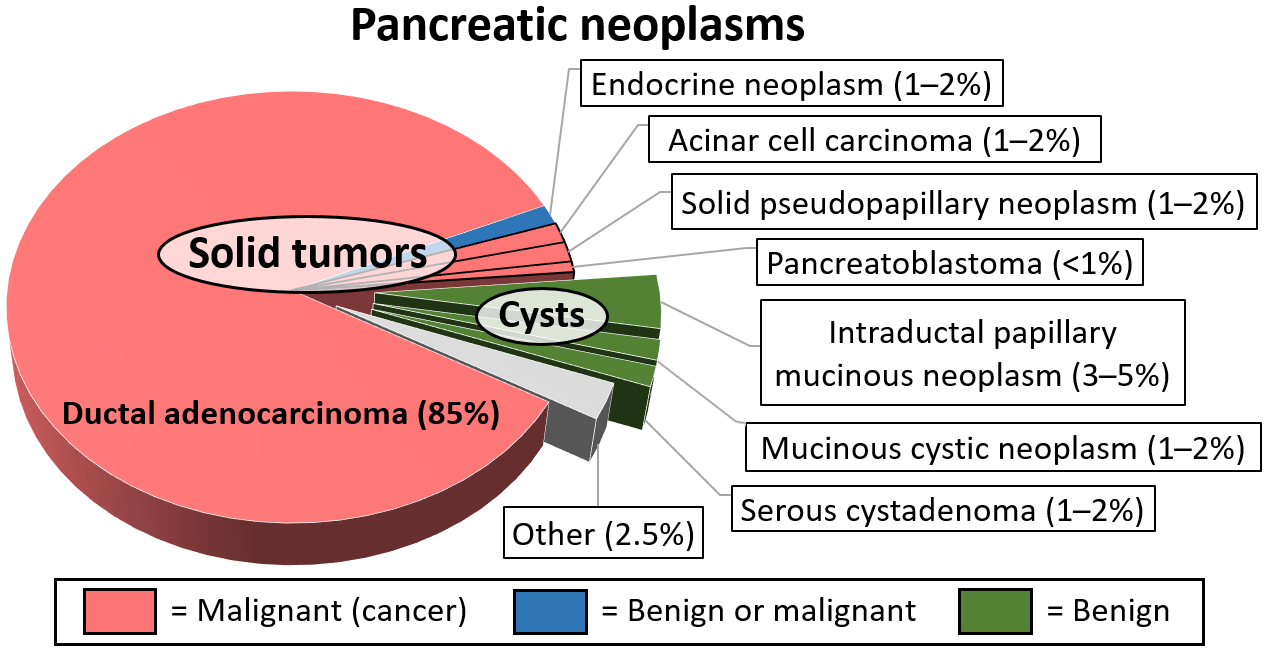
Pancreatic Serous Cystadenoma
Pancreatic serous cystadenoma is a benign tumour of the pancreas. It is usually found in the tail of the pancreas, and may be associated with von Hippel–Lindau syndrome. In contrast to some of the other cyst-forming tumors of the pancreas (such as the intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm and the pancreatic mucinous cystadenoma), serous cystic neoplasms are almost always entirely benign. There are some exceptions; rare case reports have described isolated malignant serous cystadenocarcinomas. In addition, serous cystic neoplasms slowly grow, and if they grow large enough they can press on adjacent organs and cause symptoms. Signs and symptoms In most cases, serous cystadenomas of the pancreas are asymptomatic. However, large cysts may cause symptoms related to their size. Classification Pathologists classify serous cystic neoplasms into two broad groups. Those that are benign, that have not spread to other organs, are designated "serous cystadenoma". Serous cystadenomas can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous tumor of an ovary. It may originate from the ovary itself or more commonly from communicating nearby structures such as fallopian tubes or the inner lining of the abdomen. The ovary is made up of three different cell types including epithelial cells, germ cells, and stromal cells. When these cells become abnormal, they have the ability to divide and form tumors. These cells can also invade or spread to other parts of the body. When this process begins, there may be no or only vague symptoms. Symptoms become more noticeable as the cancer progresses. These symptoms may include bloating, vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, abdominal swelling, constipation, and loss of appetite, among others. Common areas to which the cancer may spread include the lining of the abdomen, lymph nodes, lungs, and liver. The risk of ovarian cancer increases with age. Most cases of ovarian cancer develop after menopause. It is also more common in women who have ovulated m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cilia
The cilium, plural cilia (), is a membrane-bound organelle found on most types of eukaryotic cell, and certain microorganisms known as ciliates. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. The cilium has the shape of a slender threadlike projection that extends from the surface of the much larger cell body. Eukaryotic flagella found on sperm cells and many protozoans have a similar structure to motile cilia that enables swimming through liquids; they are longer than cilia and have a different undulating motion. There are two major classes of cilia: ''motile'' and ''non-motile'' cilia, each with a subtype, giving four types in all. A cell will typically have one primary cilium or many motile cilia. The structure of the cilium core called the axoneme determines the cilium class. Most motile cilia have a central pair of single microtubules surrounded by nine pairs of double microtubules called a 9+2 axoneme. Most non-motile cilia have a 9+0 axoneme that lacks the central pair of mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epitheli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microscopically
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical microscope, optical, electron microscope, electron, and scanning probe microscopy, along with the emerging field of X-ray microscopy. Optical microscopy and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection (physics), reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the Laboratory specimen, specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscope, transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross Pathology
Gross pathology refers to macroscopic manifestations of disease in organs, tissues, and body cavities. The term is commonly used by anatomical pathologists to refer to diagnostically useful findings made during the gross examination portion of surgical specimen processing or an autopsy An autopsy (post-mortem examination, obduction, necropsy, or autopsia cadaverum) is a surgical procedure that consists of a thorough examination of a corpse by dissection to determine the cause, mode, and manner of death or to evaluate any di .... It is vital to systematically explain the gross appearance of a pathological state, for example, a malignant tumor, noting the site, size, shape, consistency, presence of a capsule and appearance on cut section whether well circumscribed or diffusely infiltrating, homogeneous or variegated, cystic, necrotic, hemorrhagic areas, as well as papillary projections. {{pathology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathologist
Pathology is the study of the causal, causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area which includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue (biology), tissue, human cell, cell, and body fluid samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases (as in the statement "the many different forms of cancer have diverse pathologies", in which case a more proper choice of word would be "Pathophysiology, pathophysiologies"), and the affix ''pathy'' is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a hormone for the maternal recognition of pregnancy produced by trophoblast cells that are surrounding a growing embryo (syncytiotrophoblast initially), which eventually forms the placenta after implantation. The presence of hCG is detected in some pregnancy tests (HCG pregnancy strip tests). Some cancerous tumors produce this hormone; therefore, elevated levels measured when the patient is not pregnant may lead to a cancer diagnosis and, if high enough, paraneoplastic syndromes, however, it is not known whether this production is a contributing cause, or an effect of carcinogenesis. The pituitary analog of hCG, known as luteinizing hormone (LH), is produced in the pituitary gland of males and females of all ages. Various endogenous forms of hCG exist. The measurement of these diverse forms is used in the diagnosis of pregnancy and a variety of disease states. Preparations of hCG from various sources have also been used therapeutically, by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovary
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. The ovaries also secrete hormones that play a role in the menstrual cycle and fertility. The ovary progresses through many stages beginning in the prenatal period through menopause. It is also an endocrine gland because of the various hormones that it secretes. Structure The ovaries are considered the female gonads. Each ovary is whitish in color and located alongside the lateral wall of the uterus in a region called the ovarian fossa. The ovarian fossa is the region that is bounded by the external iliac artery and in front of the ureter and the internal iliac artery. This area is about 4 cm x 3 cm x 2 cm in size.Daftary, Shirish; Chakravarti, Sudip (2011). Manual of Obstetrics, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1-16. . The ovari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CA-125
Mucin-16 (MUC-16) also known as Ovarian cancer-related tumor marker CA125 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''MUC16'' gene. MUC-16 is a member of the mucin family glycoproteins. MUC-16 has found application as a tumor marker or biomarker that may be elevated in the blood of some patients with specific types of cancers, most notably ovarian cancer, or other conditions that are benign. Structure Mucin 16 is a membrane associated mucin that possesses a single transmembrane domain. A unique property of MUC16 is its large size. MUC16 is more than twice as long as MUC1 and MUC4 and contains about 22,000 amino acids, making it the largest membrane-associated mucin. MUC16 is composed of three different domains: * An N-terminal domain * A tandem repeat domain * A C-terminal domain The N-terminal and tandem repeat domains are both entirely extracellular and highly O-glycosylated. All mucins contain a tandem repeat domain that has repeating amino acid sequences high in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
