|
Outer Planet Flagship Mission
NASA's large strategic science missions or large strategic missions, formerly known as Flagship missions or Flagship-class missions, are the costliest and most capable NASA science spacecraft. Flagship missions exist within all four divisions of NASA's Science Mission Directorate (SMD): the astrophysics, Earth science, heliophysics and planetary science divisions. "Large" refers to the budget of each mission, typically the most expensive mission in the scientific discipline. Within the Astrophysics Division and the Planetary Science Division, the large strategic missions are usually in excess of US$1 billion. Within Earth Science Division and Heliophysics Division, the large strategic missions are usually in excess of US$500 million.Powering Science: NASA's Large Strategic Science Missions (20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JWST Spacecraft Model 2
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope which conducts infrared astronomy. As the largest optical telescope in space, its high resolution and sensitivity allow it to view objects too old, List of the most distant astronomical objects, distant, or faint for the Hubble Space Telescope. This will enable investigations across many fields of astronomy and cosmology, such as observation of the Population III star, first stars, the Galaxy formation and evolution, formation of the first galaxies, and detailed atmospheric characterization of potentially habitable exoplanets. The U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) led JWST's design and development and partnered with two main agencies: the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA). The NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) in Maryland managed telescope development, the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore on the Homewood Campus of Johns Hopkins University operates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
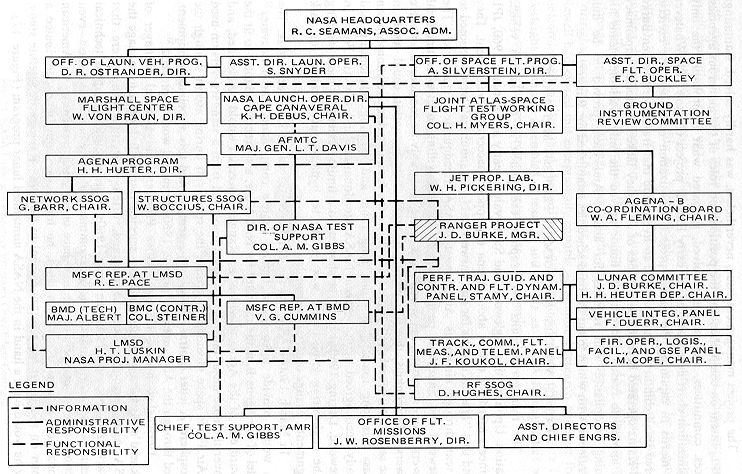
Ranger Program
The Ranger program was a series of unmanned space missions by the United States in the 1960s whose objective was to obtain the first close-up images of the surface of the Moon. The Ranger spacecraft were designed to take images of the lunar surface, transmitting those images to Earth until the spacecraft were destroyed upon impact. A series of mishaps, however, led to the failure of the first six flights. At one point, the program was called "shoot and hope". Congress launched an investigation into "problems of management" at NASA Headquarters and Jet Propulsion Laboratory. After two reorganizations of the agencies, Ranger 7 successfully returned images in July 1964, followed by two more successful missions. Ranger was originally designed, beginning in 1959, in three distinct phases, called "blocks". Each block had different mission objectives and progressively more advanced system design. The JPL mission designers planned multiple launches in each block, to maximize the engine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europa (moon)
Europa , or Jupiter II, is the smallest of the four Galilean moons orbiting Jupiter, and the sixth-closest to the planet of all the 80 known moons of Jupiter. It is also the sixth-largest moon in the Solar System. Europa was discovered in 1610 by Galileo Galilei and was named after Europa, the Phoenician mother of King Minos of Crete and lover of Zeus (the Greek equivalent of the Roman god Jupiter). Slightly smaller than Earth's Moon, Europa is primarily made of silicate rock and has a water-ice crust and probably an iron–nickel core. It has a very thin atmosphere, composed primarily of oxygen. Its white-beige surface is striated by light tan cracks and streaks, but craters are relatively few. In addition to Earth-bound telescope observations, Europa has been examined by a succession of space-probe flybys, the first occurring in the early 1970s. In September 2022, the ''Juno'' spacecraft flew within about 200 miles of Europa for a more recent close-up view. Europa ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter Europa Orbiter
As a part of the defunct Europa Jupiter System Mission – Laplace (EJSM-Laplace), the Jupiter Europa Orbiter (JEO) was a proposed orbiter probe slated for lift-off in 2020 and planned for detailed studies of Jupiter's moons Europa and Io as well as the Jovian magnetosphere. Its main goal would have been to look for evidence of a possible subsurface ocean. In June 2015, a more economical mission, the Europa Multiple-Flyby Mission (''Europa Clipper'') was approved by NASA and entered the formulation stage.Howell, Elizabeth (20 June 2015)"NASA's Europa Mission Approved for Next Development Stage"Space.com. Retrieved 2015-06-21. See also * Europa Orbiter (former NASA plan cancelled in 2002). * Europa Clipper (the next mission plan for Europa, non-nuclear orbiter for Jupiter doing Europa flybys). * Europa Lander (NASA) The Europa Lander is a proposed astrobiology mission concept by NASA to send a lander to Europa, an icy moon of Jupiter. If funded and develope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars Sample-return Mission
A Mars sample-return (MSR) mission is a proposed mission to collect rock and dust samples on Mars and return them to Earth. Such a mission would allow more extensive analysis than that allowed by onboard sensors. The three most recent concepts are a NASA–ESA proposal, a CNSA proposal, Tianwen-3, and a Roscosmos proposal, Mars-Grunt. Although NASA and ESA's plans to return the samples to Earth are still in the design stage as of 2022, samples have been gathered on Mars by the ''Perseverance'' rover. Risks of cross-contamination of the Earth biosphere from returned Martian samples have been raised, though the risk of this occurring is considered to be extremely low. Scientific value Once returned to Earth, stored samples can be studied with the most sophisticated science instruments available. Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for science at NASA Headquarters in Washington, expect such studies to allow several new discoveries at many fields. Samples may be reana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Space Agency
, owners = , headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France , coordinates = , spaceport = Guiana Space Centre , seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png , seal_size = 130px , image = Views in the Main Control Room (12052189474).jpg , size = , caption = , acronym = , established = , employees = 2,200 , administrator = Director General Josef Aschbacher , budget = €7.2 billion (2022) , language = English and French (working languages) , website = , logo = European Space Agency logo.svg , logo_caption = Logo , image_caption = European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) Main Control Room The European Space Agency (ESA; french: Agence spatiale européenne , it, Agenzia Spaziale Europea, es, Agencia Espacial Europea ASE; german: Europäische Weltraumorganisation) is an intergovernmental organisation of 22 member states dedicated to the exploration of space. Established in 1975 and headquartered i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ExoMars
ExoMars (Exobiology on Mars) is an astrobiology programme of the European Space Agency (ESA). The goals of ExoMars are to search for signs of past life on Mars, investigate how the Martian water and geochemical environment varies, investigate atmospheric trace gases and their sources and by doing so demonstrate the technologies for a future Mars sample-return mission. The first part of the programme is a mission launched in 2016 that placed the Trace Gas Orbiter into Mars orbit and released the ''Schiaparelli'' EDM lander. The orbiter is operational but the lander crashed on the planet's surface. The second part of the programme was planned to launch in July 2020, when the ''Kazachok'' lander would have delivered the ''Rosalind Franklin'' rover on the surface, supporting a science mission that was expected to last into 2022 or beyond. On 12 March 2020, it was announced that the second mission was being delayed to 2022 as a result of problems with the parachutes, which could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars Astrobiology Explorer-Cacher
The Mars Astrobiology Explorer-Cacher (MAX-C), also known as Mars 2018 mission was a NASA concept for a Mars rover mission, proposed to be launched in 2018 together with the European ExoMars rover.Mars Astrobiology Explorer-Cacher (MAX-C): A Potential Rover Mission for 2018 (September 15, 2009) The MAX-C rover concept was cancelled in April 2011 due to budget cuts. The rover would have been solar powered, with a maximum mass of 300 kg and based largely on the ''Curiosity'' rover components, but would have entailed a system tailored to the specific payload. The MA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary Science Decadal Survey
The Planetary Science Decadal Survey is a publication of the United States National Research Council produced for NASA and other United States Government Agencies such as the National Science Foundation.National Academy of Sciences, National Academies Press, http://www.nap.edu/download.php?record_id=13117 , ''Vision and Voyages for Planetary Science in the Decade 2013–2022'', 2011; . Retrieved February 23, 2015 The document identifies key questions facing planetary science and outlines recommendations for space and ground-based exploration ten years into the future. Missions to gather data to answer these big questions are described and prioritized, where appropriate. Similar decadal surveys cover astronomy and astrophysics, earth science, and heliophysics. As of 2022 there have been three "Decadals", one published in 2002 for the decade from 2003 to 2013, one in 2011 for 2013 to 2022, and one in 2022 for 2023 to 2032. The survey for 2023 to 2032 was released on April 19th, 2022. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titan Saturn System Mission
Titan Saturn System Mission (TSSM) was a joint NASA–ESA proposal for an exploration of Saturn and its moons Titan (moon), Titan and Enceladus (moon), Enceladus, where many complex phenomena were revealed by ''Cassini–Huygens, Cassini''. TSSM was proposed to launch in 2020, get gravity assists from Earth and Venus, and arrive at the Saturn system in 2029. The 4-year prime mission would include a two-year Saturn tour, a 2-month Titan aero-sampling phase, and a 20-month Titan orbit phase. In 2009, a EJSM, mission to Jupiter and its moons was given priority over ''Titan Saturn System Mission'', although TSSM will continued to be assessed for possible development and launch. Origin and status The Titan Saturn System Mission (TSSM) was officially created in January 2009 by the merging of the ESA's Titan and Enceladus Mission (TandEM) with NASA's Titan Explorer (2007) study, although plans to combine both concepts date at least back to early 2008. TSSM was competing against the Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europa Jupiter System Mission – Laplace
The Europa Jupiter System Mission – Laplace (EJSM-Laplace) was a proposed joint NASA/ESA uncrewed space mission slated to launch around 2020 for the in-depth exploration of Jupiter's moons with a focus on Europa, Ganymede and Jupiter's magnetosphere. The mission would have comprised at least two independent elements, NASA's Jupiter Europa Orbiter (JEO) and ESA's Jupiter Ganymede Orbiter (JGO), to perform coordinated studies of the Jovian system. The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and the Roscosmos (Russian Space Agency) had expressed their interest in contributing to EJSM-Laplace, although no deals had been finalized. JEO was estimated to cost US$4.7 billion, while ESA would spend US$1.0 billion (€710 million) on JGO. In April 2011, European Space Agency (ESA) stated that it seemed unlikely that a joint US–European mission will happen in the early 2020s given NASA's budget, so ESA continued with its initiative, called the Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravity, gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It Formation and evolution of the Solar System, formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. The solar mass, vast majority (99.86%) of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the Jupiter mass, remaining mass contained in the planet Jupiter. The four inner Solar System, inner system planets—Mercury (planet), Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars—are terrest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.png)

