|
Outbuilding Of The Town Estate Of Savva Mamontov
The Outbuilding of the town estate of Savva Mamontov (russian: link=no, Флигель городской усадьбы С. И. Мамонтова) is a house in Moscow on the Garden Ring (, Building 6, Building 2). The only surviving building of the city manor. Built in the 1870s, it was built in the beginning of the 1890s to the design of artist Mikhail Vrubel, who after that lived there for some time. The building has the status of an object of cultural heritage of federal significance. History The town manor on was built in 1816 by court adviser Praskovya Esaulova. In 1867 it was significantly rebuilt, after which the well-known philanthropist Savva Mamontov settled there.Садовая-Спасская, 6 // Московский Журнал. № 11. Ноябрь 1999. In his |
Mikhail Vrubel
Mikhail Aleksandrovich Vrubel (russian: Михаил Александрович Врубель; March 17, 1856 – April 14, 1910, all New Style, n.s.) was a Russian Painting, painter, Drawing, draughtsman, and sculptor. A prolific and innovative master in various media such as painting, drawing, decorative sculpture, and theatrical art, Vrubel is generally characterized as one of the most important artists in Russian symbolism, Russian Symbolist tradition and a pioneering figure of Modernist art. In a 1990 biography of Vrubel, the Soviet art historian considered his life and art as a three-act drama with prologue and epilogue, while the transition between acts was rapid and unexpected. The "Prologue" refers to his earlier years of studying and choosing a career path. The "first act" peaked in the 1880s when Vrubel was studying at the Imperial Academy of Arts and then moved to Kiev to study Byzantine art, Byzantine and Christian art. The "second act" corresponded to the so- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garden Ring
The Garden Ring, also known as the "B" Ring (russian: Садо́вое кольцо́, кольцо́ "Б"; transliteration: ''Sadovoye Koltso''), is a circular ring road Avenue (landscape), avenue around central Moscow, its course corresponding to what used to be the city ramparts surrounding Zemlyanoy Gorod in the 17th century. The Ring consists of seventeen individually named streets and fifteen squares. It has a circumference of . At its narrowest point, Krymsky Bridge, the Ring has six lanes. After finishing reconstruction, all sections of the Ring will not have more than 10 lanes. In 2018, more than 50 % of sections of the Garden Ring are reconstructed, including Zubovskaya square, which was the widest section, there were about 18 lanes before. The Ring emerged in the 1820s, replacing fortifications, in the form of defensive wall, ramparts, that were no longer of military value. History Skorodom The Garden Ring is a direct descendant of the Skorodom (Скородом, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savva Mamontov
Savva Ivanovich Mamontov (russian: Са́вва Ива́нович Ма́монтов, ; 3 October 1841 (15 October N.S.), Yalutorovsk – 6 April 1918, Moscow) was a Russian industrialist, merchant, entrepreneur and patron of the arts. Business career He was a son of the wealthy merchant and industrialist Ivan Feodorovich Mamontov and Maria Tikhonovna (Lakhitina). In 1841, the family moved to Moscow. From 1852, he studied in St. Petersburg, and later at the Moscow University. In 1862 his father sent him to Baku to engage in business with the elder Mamontov's Trans-Caspian Trade Partnership. In 1864, Savva visited Italy where he began to take lessons in singing. There he was introduced to the daughter of Moscow merchant Grigory Sapozhnikov, 17-year-old Elizabeth, who subsequently became his wife. The wedding took place in 1865 at the Kireevo estate, near Khimki, just northwest of Moscow. Upon his father's death in 1869, he succeeded to his share in the Moscow-Yaroslavl Rail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salon (gathering)
A salon is a gathering of people held by an inspiring host. During the gathering they amuse one another and increase their knowledge through conversation. These gatherings often consciously followed Horace's definition of the aims of poetry, "either to please or to educate" (Latin: ''aut delectare aut prodesse''). Salons in the tradition of the French literary and philosophical movements of the 17th and 18th centuries were carried on until as recently as the 1920s in urban settings. Historical background The salon was an Italian invention of the 16th century, which flourished in France throughout the 17th and 18th centuries. The salon continued to flourish in Italy throughout the 19th century. In 16th-century Italy, some brilliant circles formed in the smaller courts which resembled salons, often galvanized by the presence of a beautiful and educated patroness such as Berta Zuckerkandl, Isabella d'Este or Elisabetta Gonzaga. Salons were an important place for the exchange of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
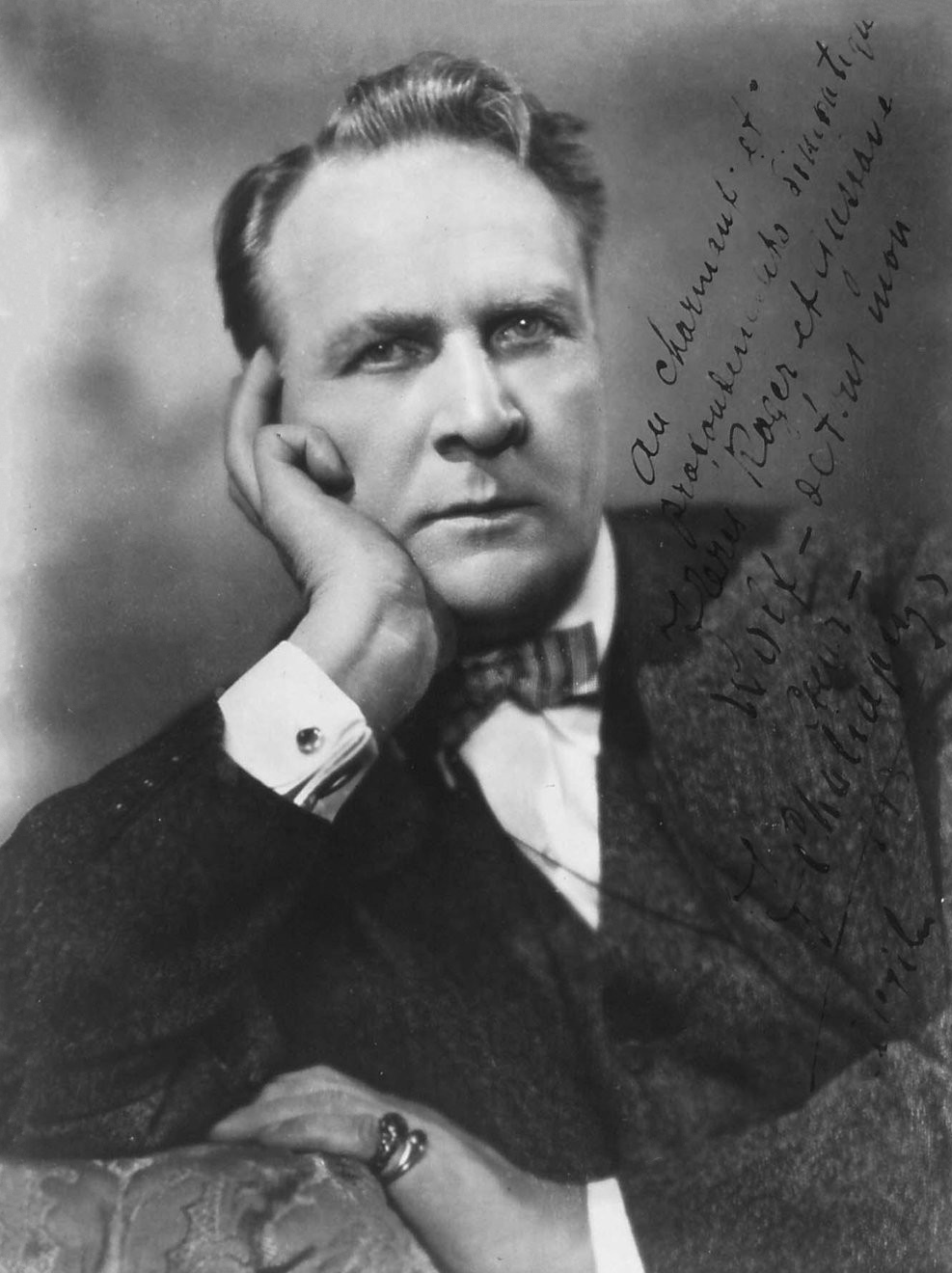
Feodor Chaliapin
Feodor Ivanovich Chaliapin ( rus, Фёдор Ива́нович Шаля́пин, Fyodor Ivanovich Shalyapin, ˈfʲɵdər ɪˈvanəvʲɪtɕ ʂɐˈlʲapʲɪn}; April 12, 1938) was a Russian opera singer. Possessing a deep and expressive bass voice, he enjoyed an important international career at major opera houses and is often credited with establishing the tradition of naturalistic acting in his chosen art form. During the first phase of his career, Chaliapin endured direct competition from three other great basses: the powerful (1869–1942), the more lyrical (1871–1948), and Dmitri Buchtoyarov (1866–1918), whose voice was intermediate between those of Sibiriakov and Kastorsky. The fact that Chaliapin is far and away the best remembered of this magnificent quartet of rival basses is a testament to the power of his personality, the acuteness of his musical interpretations, and the vividness of his performances. Spelling note He himself spelled his surname, French-style ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
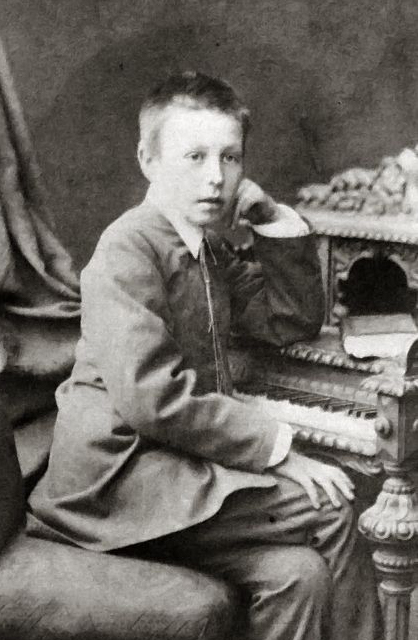
Viktor Vasnetsov
Viktor Mikhaylovich Vasnetsov (russian: Ви́ктор Миха́йлович Васнецо́в; May 15 ( N.S.), 1848 – July 23, 1926) was a Russian artist who specialized in mythological and historical subjects. He is considered the co-founder of Russian folklorist and romantic nationalistic painting (see also neo-romanticism), and a key figure in the Russian revivalist movement. Biography Childhood (1848–1858) Viktor Vasnetsov was born in the remote village of Lopyal in Vyatka Governorate in 1848, the second of the seven children (his only sister died 4 months after her birth). His father Mikhail Vasilievich Vasnetsov (1823–1870), known to be philosophically inclined, was a member of the priesthood, and a scholar of the natural sciences and astronomy. His grandfather was an icon painter. Two of Mikhail Vasnetsov's six sons, Viktor and Apollinary, became remarkable painters, three becoming schoolteachers and one a Russian folklorist. It was in Lopyal that Viktor sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Rachmaninoff
Sergei Vasilyevich Rachmaninoff; in Russian pre-revolutionary script. (28 March 1943) was a Russian composer, virtuoso pianist, and conductor. Rachmaninoff is widely considered one of the finest pianists of his day and, as a composer, one of the last great representatives of Romanticism in Russian classical music. Early influences of Tchaikovsky, Rimsky-Korsakov, and other Russian composers gave way to a thoroughly personal idiom notable for its song-like melodicism, expressiveness and rich orchestral colours. The piano is featured prominently in Rachmaninoff's compositional output and he made a point of using his skills as a performer to fully explore the expressive and technical possibilities of the instrument. Born into a musical family, Rachmaninoff took up the piano at the age of four. He studied with Anton Arensky and Sergei Taneyev at the Moscow Conservatory and graduated in 1892, having already composed several piano and orchestral pieces. In 1897, following the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Majolica
In different periods of time and in different countries, the term ''majolica'' has been used for two distinct types of pottery. Firstly, from the mid-15th century onwards, was ''maiolica'', a type of pottery reaching Italy from Spain, Majorca and beyond. This was made by a tin-glaze process (dip, dry, paint, fire), resulting in an opaque white glazed surface decorated with brush-painting in metal oxide enamel colour(s). During the 17th century, the English added the letter '' j'' to their alphabet. ''Maiolica'' was commonly anglicized to ''majolica'' thereafter. The second style of pottery known as ''majolica'' is the mid- to late-19th century Victorian style made by a simpler process (painting and then firing) whereby coloured lead silicate glazes were applied directly to an unfired clay mould, typically relief-moulded, resulting in brightly coloured, hard-wearing, inexpensive wares that were both useful and decorative, typically in naturalistic style. This type of majolica wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abramtsevo Colony
Abramtsevo (russian: Абра́мцево) is a former country estate and now museum-reserve located north of Moscow, in the proximity of Khotkovo, that became a centre for the Slavophile movement and an artists' colony in the 19th century. The estate is located in the village of Abramtsevo, in Sergiyevo-Posadsky District of Moscow Oblast. The Abramtsevo Museum-reserve site is an object of cultural heritage in Russia. History Originally owned by the author Sergei Aksakov, other writers and artists — such as Nikolai Gogol — at first came there as his guests. Under Aksakov, visitors to the estate discussed ways of ridding Russian art of Western influences to revive a purely national style. In 1870, eleven years after Aksakov's death, it was purchased by Savva Mamontov, a wealthy industrialist and patron of the arts. Under Mamontov, Russian themes and folk art flourished there. During the 1870s and 1880s, Abramtsevo hosted a colony of artists who sought to recapture the quali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Heritage Monuments Of Federal Significance In Moscow
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tylor, Edward. (1871). Primitive Culture. Vol 1. New York: J.P. Putnam's Son Culture is often originated from or attributed to a specific region or location. Humans acquire culture through the learning processes of enculturation and socialization, which is shown by the diversity of cultures across societies. A cultural norm codifies acceptable conduct in society; it serves as a guideline for behavior, dress, language, and demeanor in a situation, which serves as a template for expectations in a social group. Accepting only a monoculture in a social group can bear risks, just as a single species can wither in the face of environmental change, for lack of functional responses to the change. Thus in military culture, valor is counted a typical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houses Completed In 1892
A house is a single-unit residential building. It may range in complexity from a rudimentary hut to a complex structure of wood, masonry, concrete or other material, outfitted with plumbing, electrical, and heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems.Schoenauer, Norbert (2000). ''6,000 Years of Housing'' (rev. ed.) (New York: W.W. Norton & Company). Houses use a range of different roofing systems to keep precipitation such as rain from getting into the dwelling space. Houses may have doors or locks to secure the dwelling space and protect its inhabitants and contents from burglars or other trespassers. Most conventional modern houses in Western cultures will contain one or more bedrooms and bathrooms, a kitchen or cooking area, and a living room. A house may have a separate dining room, or the eating area may be integrated into another room. Some large houses in North America have a recreation room. In traditional agriculture-oriented societies, domestic animals such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |