|
Otukaia Ikukoae
''Otukaia ikukoae'' is a deepwater sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusc in the family Calliostomatidae, the calliostoma top snails. Distribution Okinawa Trough The (also called , literally China-Ryukyu Border Trough ) is a seabed feature of the East China Sea. It is an active, initial back-arc rifting basin which has formed behind the Ryukyu arc-trench system in the West Pacific. It developed where th .... Ecology It was recorded 962 m deep. References External links Calliostomatidae Gastropods described in 1994 {{Calliostomatidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom (biology), biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, can Sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of Cell (biology), cells, the blastula, during Embryogenesis, embryonic development. Over 1.5 million Extant taxon, living animal species have been Species description, described—of which around 1 million are Insecta, insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have Ecology, complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a Symmetry in biology#Bilate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusc
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The gastropods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastropod
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda (). This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, and land snails and slugs. The class Gastropoda contains a vast total of named species, second only to the insects in overall number. The fossil history of this class goes back to the Late Cambrian. , 721 families of gastropods are known, of which 245 are extinct and appear only in the fossil record, while 476 are currently extant with or without a fossil record. Gastropoda (previously known as univalves and sometimes spelled "Gasteropoda") are a major part of the phylum Mollusca, and are the most highly diversified class in the phylum, with 65,000 to 80,000 living snail and slug species. The anatomy, behavior, feeding, and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vetigastropoda
Vetigastropoda is a major Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic group of sea snails, marine (ocean), marine gastropod mollusc, mollusks that form a very ancient lineage (evolution), lineage. Taxonomically the Vetigastropoda are sometimes treated as an Order (biology), order, although they are treated as an unranked clade in taxonomy of the Gastropoda (Bouchet & Rocroi, 2005), Bouchet and Rocroi, 2005. Vetigastropods are considered to be among the most primitive living gastropods, and are widely distributed in all oceans of the world. Their habitats range from the deep sea to intertidal zones. Many have exoskeleton, shells with slits or other secondary openings. One of their main characteristics is the presence of intersected crossed platy shell structure. Most vetigastropods have some bilateral asymmetry of their Organ (anatomy), organ systems. Description Vetigastropods range in size from approximately 0.08 in (2 mm) long in the case of Scissurelloidea or Skeneoidea, to more than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trochoidea (superfamily)
Trochoidea is a superfamily of small to very large vetigastropod sea snails with gills and an operculum.Gofas, S. (2013). Trochoidea. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=156489 on 2013-06-29 Species within this superfamily have nacre as the inner shell layer. The families within this superfamily include the Trochidae, the top snails. This superfamily is the largest vetigastropodan superfamily, containing more than 2,000 species. This taxon is ''not'' the same as a pulmonate land snail genus which is spelled the same way: ''Trochoidea'' (genus). Taxonomy 2005 taxonomy This superfamily consisted of nine following families (according to the taxonomy of the Gastropoda by Bouchet & Rocroi, 2005): * Trochidae Rafinesque, 1815 * Calliostomatidae Thiele, 1924 (1847) * † Elasmonematidae Knight, 1956 * † Eucochlidae Bandel, 2002 * † Microdomatidae Wenz, 1938 * † Proconulidae Cox, 1960 * Solarie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calliostomatidae
Calliostomatidae is a family of sea snails within the superfamily Trochoidea and the clade Vetigastropoda.Gofas, S. (2013). Calliostomatidae. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=382180 on 2013-07-08 Description The Calliostomatidae are unusually diverse. They are characterized by a stepped spire and a pointy aperture. They may possess or lack an umbilicus. The collumella is sometimes thicker, partially covering the aperture. The spiral whorls can differ between narrow and robust. They inhabit a wide range of ocean habitats, from the intertidal zone to mid- bathyal depths. Taxonomy This taxon was long considered to be a subfamily of the Trochidae. 2005 taxonomy This family consists of two following subfamilies (according to the taxonomy of the Gastropoda by Bouchet & Rocroi, 2005): * subfamily Calliostomatinae Thiele 1924 (1847) ** tribe Calliostomatini Thiele 1924 (1847) - synonym: Ziziphininae G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otukaia
''Otukaia'' is a genus of medium-sized sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs in the family Calliostomatidae, the top shells. ''Otukaia'' has long been considered a subgenus of Calliostoma and is still treated as such by many authorities. Snails in this genus are characterized by their relatively large, silky-white, thin shell. They lack an umbilicus. Their spiral whorls are flat to slightly convex. The first three spiral cords can show some sculpture that may persist on later whorls. They have a rachidian radula. They can be found worldwide in deep water. Some authors use ''Otukaia'' Ikebe, 1942 as a subgenus in ''Calliostoma'' Swainson, 1840. The (sub)generic name ''Otukaia'' is in honor of the Japanese malacologist Yanosuke Otuka (1903–1950), who described the type species ''Calliostoma kiheiziebisu'' Otuka, 1939. Otuka Y. (1939). "日本産エビスガヒ屬の一新種 A new ''Calliostoma'' from Japan". ''Venus'' 9(1): 27–29CiNii Species The following species are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Snail
Sea snail is a common name for slow-moving marine gastropod molluscs, usually with visible external shells, such as whelk or abalone. They share the taxonomic class Gastropoda with slugs, which are distinguished from snails primarily by the absence of a visible shell. Definition Determining whether some gastropods should be called sea snails is not always easy. Some species that live in brackish water (such as certain neritids) can be listed as either freshwater snails or marine snails, and some species that live at or just above the high tide level (for example species in the genus '' Truncatella'') are sometimes considered to be sea snails and sometimes listed as land snails. Anatomy Sea snails are a very large group of animals and a very diverse one. Most snails that live in salt water respire using a gill or gills; a few species, though, have a lung, are intertidal, and are active only at low tide when they can move around in the air. These air-breathing species includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine (ocean)
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the world ocean is conventionally divided."Ocean." ''Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary'', Merriam-Webster, |
Gastropod
The gastropods (), commonly known as snails and slugs, belong to a large taxonomic class of invertebrates within the phylum Mollusca called Gastropoda (). This class comprises snails and slugs from saltwater, from freshwater, and from land. There are many thousands of species of sea snails and slugs, as well as freshwater snails, freshwater limpets, and land snails and slugs. The class Gastropoda contains a vast total of named species, second only to the insects in overall number. The fossil history of this class goes back to the Late Cambrian. , 721 families of gastropods are known, of which 245 are extinct and appear only in the fossil record, while 476 are currently extant with or without a fossil record. Gastropoda (previously known as univalves and sometimes spelled "Gasteropoda") are a major part of the phylum Mollusca, and are the most highly diversified class in the phylum, with 65,000 to 80,000 living snail and slug species. The anatomy, behavior, feeding, and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mollusc
Mollusca is the second-largest phylum of invertebrate animals after the Arthropoda, the members of which are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 85,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized. The number of fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000 additional species. The proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. Numerous molluscs also live in freshwater and terrestrial habitats. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomic classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurologically advanced of all invertebrates—and either the giant squid or the colossal squid is the largest known invertebrate species. The gastropods ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
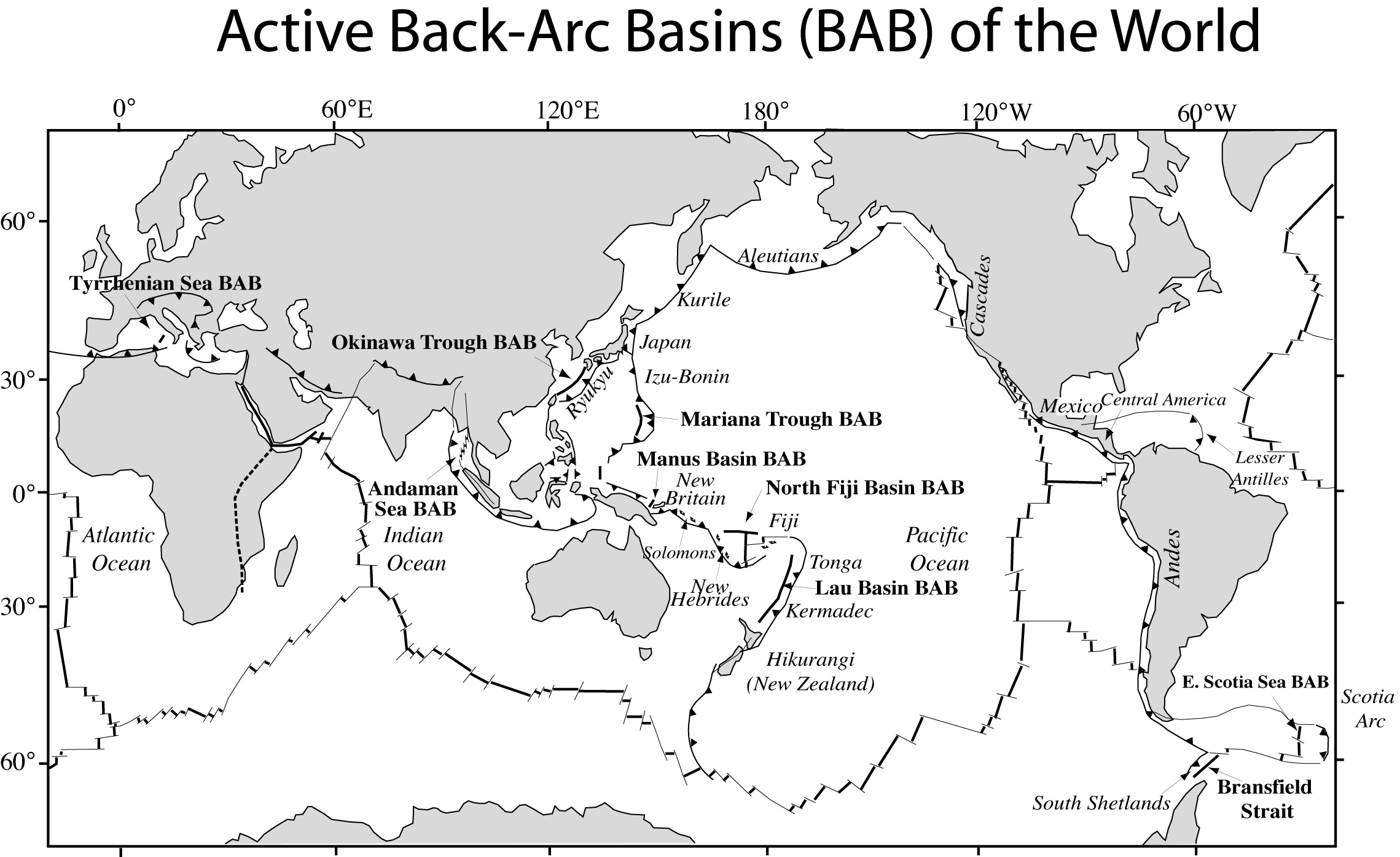
Okinawa Trough
The (also called , literally China-Ryukyu Border Trough ) is a seabed feature of the East China Sea. It is an active, initial back-arc rifting basin which has formed behind the Ryukyu arc-trench system in the West Pacific. It developed where the Philippine Sea Plate is subducting under the Eurasia Plate. Description It is a back-arc basin formed by extension within the continental lithosphere behind the far deeper Ryukyu Trench-arc system. The thickness of the crust in the northern Okinawa Trough is 30 km, thinning to 10 km in the southern Okinawa Trough. It has a large section more than deep and a maximum depth of . The Okinawa Trough still in an early stage of evolving from arc type to back-arc activity, and features volcanoes such as the Yonaguni Knoll IV. Implications for the China–Japan maritime boundary Interpretations The existence of the Okinawa Trough complicates descriptive issues in the East China Sea.Ji, Guoxing. (1995) "Maritime Jurisdiction in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)