|
Ottoman Cruiser Hamidiye
''Hamidiye''The name is also sometimes rendered as ''Hamidieh'' in English; see Gardiner and Gray, p. 389, and Halpern, p. 228. Also it was rendered Hamidié in French. See was an Ottoman Empire, Ottoman cruiser that saw extensive action during the Balkan Wars and World War I. Initially named ''Abdül Hamid'', it was ordered by the Ottoman Navy in 1900 from the British Empire, British shipbuilding company Armstrong Whitworth.B. Langensiepen, A. Güleryüz, J. Cooper, The Ottoman Steam Navy, 1828–1923', Naval Institute Press, Annapolis, Maryland, United States, 1995. pp. 149–150. . It was laid down in Elswick, Tyne and Wear, Elswick, Newcastle upon Tyne, Newcastle, in April 1902; launched on 25 September 1903; its sea trials began on 17 December 1903; and it was commissioned in April 1904. It weighed 3,904 tons; was 112 m long with a beam of 14.5 m and a draught of 4.8 m; and was named after the Ottoman Sultan Abdul Hamid II, Abdülhamid II. It had two 150mm L/45 quick firing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdul Hamid II
Abdülhamid or Abdul Hamid II ( ota, عبد الحميد ثانی, Abd ül-Hamid-i Sani; tr, II. Abdülhamid; 21 September 1842 10 February 1918) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 31 August 1876 to 27 April 1909, and the last sultan to exert effective control over the fracturing state. The time period which he reigned in the Ottoman Empire is known as the Hamidian Era. He oversaw a Decline and modernization of the Ottoman Empire, period of decline, with rebellions (particularly in the Balkans), and he presided over Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878), an unsuccessful war with the Russian Empire (1877–1878) followed by a successful Greco-Turkish War (1897), war against the Kingdom of Greece in 1897, though Ottoman gains were tempered by subsequent Western European intervention. In accordance with an agreement made with the Republican Young Ottomans, he promulgated the Constitution of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Empire's first Constitution, which was a sign of progressive th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruiser
A cruiser is a type of warship. Modern cruisers are generally the largest ships in a fleet after aircraft carriers and amphibious assault ships, and can usually perform several roles. The term "cruiser", which has been in use for several hundred years, has changed its meaning over time. During the Age of Sail, the term ''cruising'' referred to certain kinds of missions—independent scouting, commerce protection, or raiding—fulfilled by frigates or sloops-of-war, which functioned as the ''cruising warships'' of a fleet. In the middle of the 19th century, ''cruiser'' came to be a classification of the ships intended for cruising distant waters, for commerce raiding, and for scouting for the battle fleet. Cruisers came in a wide variety of sizes, from the medium-sized protected cruiser to large armored cruisers that were nearly as big (although not as powerful or as well-armored) as a pre-dreadnought battleship. With the advent of the dreadnought battleship before World W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Lausanne
The Treaty of Lausanne (french: Traité de Lausanne) was a peace treaty negotiated during the Lausanne Conference of 1922–23 and signed in the Palais de Rumine, Lausanne, Switzerland, on 24 July 1923. The treaty officially settled the conflict that had originally existed between the Ottoman Empire and the Allied French Republic, British Empire, Kingdom of Italy, Empire of Japan, Kingdom of Greece, and the Kingdom of Romania since the onset of World War I. The original text of the treaty is in French. It was the result of a second attempt at peace after the failed and unratified Treaty of Sèvres, which aimed to divide Ottoman lands. The earlier treaty had been signed in 1920, but later rejected by the Turkish National Movement who fought against its terms. As a result of Greco-Turkish War, İzmir was retrieved and the Armistice of Mudanya was signed in October 1922. It provided for the Greek-Turkish population exchange and allowed unrestricted civilian passage through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish War Of Independence
The Turkish War of Independence "War of Liberation", also known figuratively as ''İstiklâl Harbi'' "Independence War" or ''Millî Mücadele'' "National Struggle" (19 May 1919 – 24 July 1923) was a series of military campaigns waged by the Turkish National Movement after parts of the Ottoman Empire were occupied and partitioned following its defeat in World War I. These campaigns were directed against Greece in the west, Armenia in the east, France in the south, loyalists and separatists in various cities, and British and Ottoman troops around Constantinople (İstanbul). The ethnic demographics of the modern Turkish Republic were significantly impacted by the earlier Armenian genocide and the deportations of Greek-speaking, Orthodox Christian Rum people. The Turkish nationalist movement carried out massacres and deportations to eliminate native Christian populations—a continuation of the Armenian genocide and other ethnic cleansing operations during World War I. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allies Of World War I
The Allies of World War I, Entente Powers, or Allied Powers were a coalition of countries led by France, the United Kingdom, Russia, Italy, Japan, and the United States against the Central Powers of Germany, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, Bulgaria, and their colonies during the First World War (1914–1918). By the end of the first decade of the 20th century, the major European powers were divided between the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance. The Triple Entente was made up of France, Britain, and Russia. The Triple Alliance was originally composed of Germany, Austria–Hungary, and Italy, but Italy remained neutral in 1914. As the war progressed, each coalition added new members. Japan joined the Entente in 1914 and after proclaiming its neutrality at the beginning of the war, Italy also joined the Entente in 1915. The term "Allies" became more widely used than "Entente", although France, Britain, Russia, and Italy were also referred to as the Quadruple Entente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Sèvres
The Treaty of Sèvres (french: Traité de Sèvres) was a 1920 treaty signed between the Allies of World War I and the Ottoman Empire. The treaty ceded large parts of Ottoman territory to France, the United Kingdom, Greece and Italy, as well as creating large occupation zones within the Ottoman Empire. It was one of a series of treaties that the Central Powers signed with the Allied Powers after their defeat in World War I. Hostilities had already ended with the Armistice of Mudros. The treaty was signed on 10 August 1920 in an exhibition room at the Manufacture nationale de Sèvres porcelain factory in Sèvres, France. The Treaty of Sèvres marked the beginning of the partitioning of the Ottoman Empire. The treaty's stipulations included the renunciation of most territory not inhabited by Turkish people and their cession to the Allied administration. The ceding of Eastern Mediterranean lands saw the introduction of novel polities, including the British Mandate for Palestin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Young Turk Revolution
The Young Turk Revolution (July 1908) was a constitutionalist revolution in the Ottoman Empire. The Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), an organization of the Young Turks movement, forced Sultan Abdul Hamid II to restore the Ottoman Constitution and recall the parliament, which ushered in multi-party politics within the Empire. From the Young Turk Revolution to the Empire's end marks the Second Constitutional Era of the Ottoman Empire's history. More than three decades earlier, in 1876, constitutional monarchy had been established under Abdul Hamid during a period of time known as the First Constitutional Era, which lasted for only two years before Abdul Hamid suspended it and restored autocratic powers to himself. The revolution began with CUP member Ahmed Niyazi's flight into the Albanian highlands. He was soon joined by İsmail Enver and Eyub Sabri. They networked with local Albanians and utilized their connections within the Salonica based Third Army to instigate a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be transformed, by a connecting rod and crank, into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is generally applied only to reciprocating engines as just described, not to the steam turbine. Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separated from the combustion products. The ideal thermodynamic cycle used to analyze this process is called the Rankine cycle. In general usage, the term ''steam engine'' can refer to either complete steam plants (including boilers etc.), such as railway steam locomotives and portable engines, or may refer to the piston or turbine machinery alone, as in the beam engine and stationary steam engine. Although steam-driven devices were known as early as the aeolipile in the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
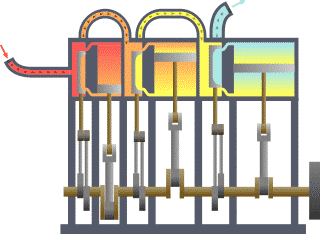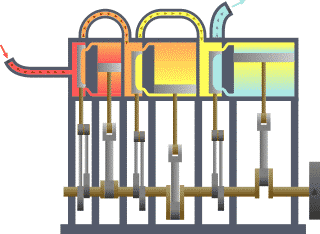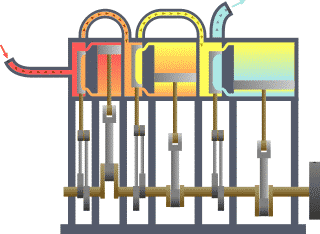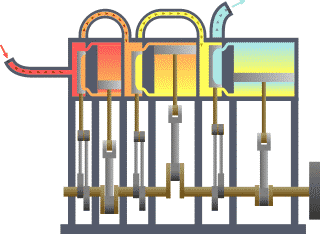
Triple Expansion Steam Engine
A compound steam engine unit is a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. A typical arrangement for a compound engine is that the steam is first expanded in a high-pressure ''(HP)'' cylinder, then having given up heat and losing pressure, it exhausts directly into one or more larger-volume low-pressure ''(LP)'' cylinders. Multiple-expansion engines employ additional cylinders, of progressively lower pressure, to extract further energy from the steam. Invented in 1781, this technique was first employed on a Cornish beam engine in 1804. Around 1850, compound engines were first introduced into Lancashire textile mills. Compound systems There are many compound systems and configurations, but there are two basic types, according to how HP and LP piston strokes are phased and hence whether the HP exhaust is able to pass directly from HP to LP ( Woolf compounds) or whether pressure fluctuation necessitates an intermediate "buffer" space in the form of a st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elswick, Tyne And Wear
Elswick ( ) is a district and electoral ward of the city and metropolitan borough of Newcastle upon Tyne, England, 1.9 miles west of the city centre, bordering the River Tyne. Historically in Northumberland, Elswick became part of Newcastle upon Tyne in 1835. Elswick is home to the Newcastle Utilita Arena; and Newcastle College, with approximately 45,000 students. History In Roman times the Vallum, a defensive barrier behind Hadrian's Wall, reached its easternmost limit in Elswick. The Wall itself carried on as far as Wallsend. The township of Elswick had originally formed part of the Barony of Bolam and was owned by Tynemouth Priory from 1120-1539, with a fishery present on the site. One of the earliest references to the coal mining industry of the north east occurs in 1330, when it was recorded that the Prior of Tynemouth let a colliery, called Heygrove, at "Elstewyke" for a rent of £5 per year. Elswick Colliery had 3 pits working from 1860 onwards. Elswick was owned by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts established by England between the late 16th and early 18th centuries. At its height it was the largest empire in history and, for over a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, its constitutional, legal, linguistic, and cultural legacy is widespread. At the peak of its power, it was described as "the empire on which the sun never sets", as the Sun was always shining on at least one of its territories. During the Age of Discovery in the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal and Spain pioneered European exploration of the globe, and in the process established large overse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |