|
Otto II, Margrave Of Meissen
Otto II, the Rich (german: Otto der Reiche; 1125 – 18 February 1190), a member of the House of Wettin, was Margrave of Meissen from 1156 until his death. Life He was the eldest surviving son of Conrad, Margrave of Meissen and Lusatia. When his father, under pressure from Emperor Frederick Barbarossa, retired and entered the Augustinian convent of Lauterberg in 1156, Otto succeeded him in Meissen while his younger brothers Theodoric and Dedi received the March of Lusatia and the County of Groitzsch with Rochlitz. The partition meant a weakening of the Wettin rule, and Otto's Imperial politics remained rather ineffective. He had to stand by and watch the emperor's extension of power in the Pleissnerland territory around Altenburg, Chemnitz and Zwickau; moreover he picked an unsuccessful quarrel with the rising burgraves of Dohna in the Eastern Ore Mountains. Together with Archbishop Wichmann of Magdeburg he joined Emperor Frederick's expedition against the rebellious Saxon du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margrave Of Meissen
This article lists the margraves of Meissen, a march and territorial state on the eastern border of the Holy Roman Empire. History King Henry the Fowler, on his 928-29 campaign against the Slavic Glomacze tribes, had a fortress erected on a hill at Meissen (''Mišno'') on the Elbe river. Later named ''Albrechtsburg'', the castle about 965 became the seat of the Meissen margraves, installed by Emperor Otto I when the vast ''Marca Geronis'' (Gero's march) was partitioned into five new margraviates, including Meissen, the Saxon Eastern March, and also the Northern March which eventually became the Margraviate of Brandenburg. During the tenth century, the Meissen margraves temporarily extended their territory into the Milceni lands up to the Kwisa (''Queis'') river and the border with the Silesian region of the Early Polish state. The eastern lands around Bautzen (''Budissin''), later known as Upper Lusatia, were ceded to the Polish duke Bolesław I the Brave according to the 10 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rochlitz Castle
Rochlitz Castle or Rochlitz Palace (german: Schloss Rochlitz) lies in the west of the town of Rochlitz in the county of Mittelsachsen in the Free State of Saxony. It was built on the site of an imperial castle, erected in the second half of the 10th century, which fell into the possession of the Wettin margraves in 1143. Its appearance, which includes several Romanesque wings, is considerably influenced by its remodelling into a margravial ''schloss'' in the fourth quarter of the 14th century. Further conversions and additions followed at the end of the 15th and in the 16th centuries, when the castle became a secondary ''residenz'', dower house and hunting lodge for the Wettin family. The castle or palace was the residence for members of the Saxon princely house eight times. From the 18th century the castle served as an administrative centre (justice department and district court); in 1852 it became a gaol, which necessitated considerable alteration. The museum founded in 1892 wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
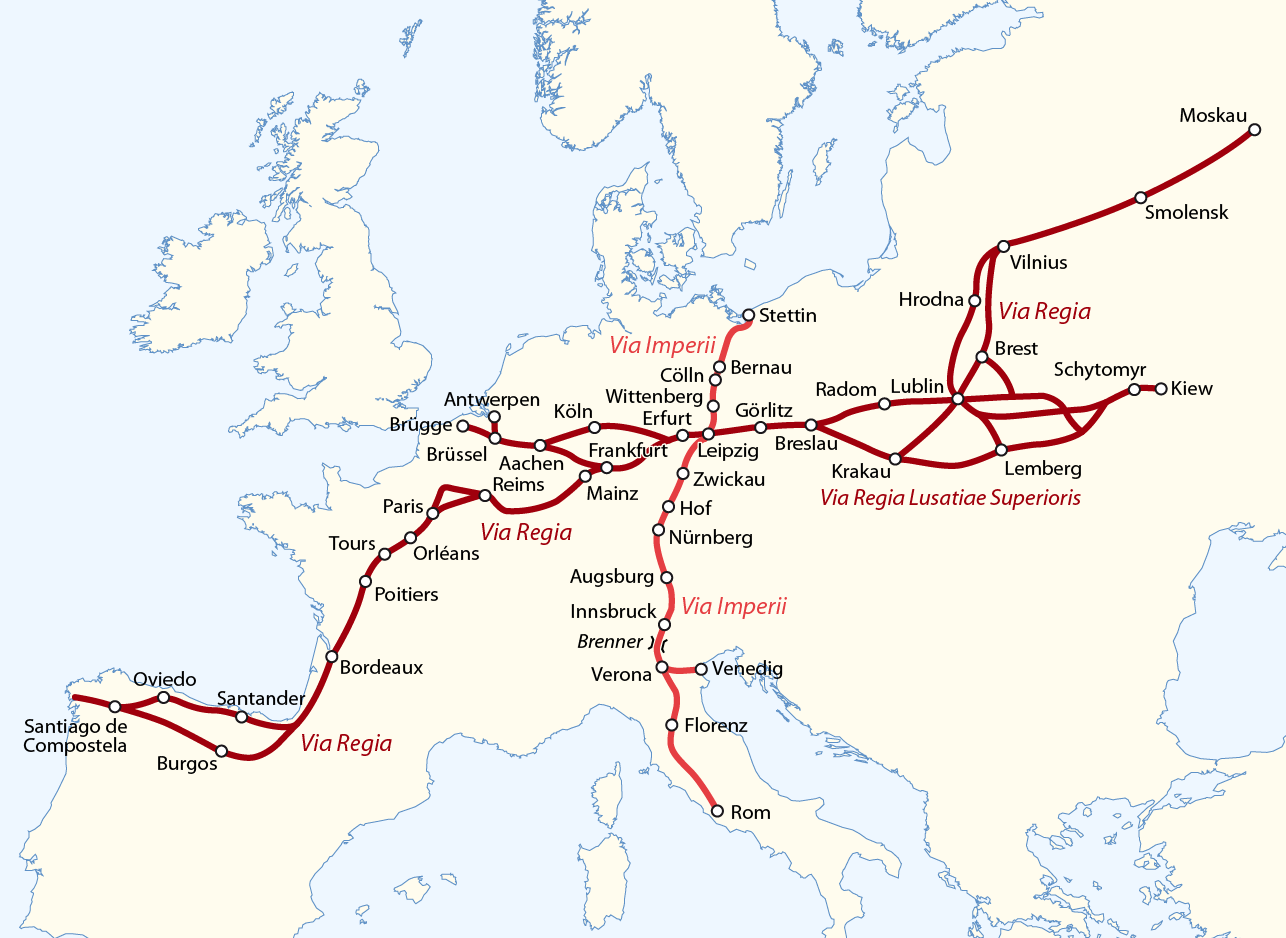
Via Regia
The Via Regia (Royal Highway) is a European Cultural Route following the route of the historic road of the Middle Ages. There were many such ''viae regiae'' associated with the king in the medieval Holy Roman Empire. History Origins The Via Regia ran west–east through the centre of the Holy Roman Empire, from the Rhine at Mainz-Kastel (''Elisabethenstraße'') to Frankfurt am Main, trade city and site of the election of the King of the Romans, continuing along Hanau, the ''Kaiserpfalz'' at Gelnhausen, the towns of Steinau an der Straße, Neuhof, Fulda and Eisenach to Erfurt, a centre of woad production. It ran further eastwards to Eckartsberga, crossing the Saale river between Bad Kösen and Naumburg and reached Leipzig, another trade city. The eastern part continued through Upper Lusatia ('' Via Regia Lusatiae Superioris'') along Großenhain, Königsbrück, Kamenz, Bautzen and Görlitz to Wrocław in Silesia with further connection to Kraków in Poland. Medieval p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as well as the second most populous city in the area of the former East Germany after (East) Berlin. Together with Halle (Saale), the city forms the polycentric Leipzig-Halle Conurbation. Between the two cities (in Schkeuditz) lies Leipzig/Halle Airport. Leipzig is located about southwest of Berlin, in the southernmost part of the North German Plain (known as Leipzig Bay), at the confluence of the White Elster River (progression: ) and two of its tributaries: the Pleiße and the Parthe. The name of the city and those of many of its boroughs are of Slavic origin. Leipzig has been a trade city since at least the time of the Holy Roman Empire. The city sits at the intersection of the Via Regia and the Via Imperii, two important medieval trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dresden Fürstenzug 081
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label=Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth largest by area (after Berlin, Hamburg and Cologne), and the third most populous city in the area of former East Germany, after Berlin and Leipzig. Dresden's urban area comprises the towns of Freital, Pirna, Radebeul, Meissen, Coswig, Radeberg and Heidenau and has around 790,000 inhabitants. The Dresden metropolitan area has approximately 1.34 million inhabitants. Dresden is the second largest city on the River Elbe after Hamburg. Most of the city's population lives in the Elbe Valley, but a large, albeit very sparsely populated area of the city east of the Elbe lies in the West Lusatian Hill Country and Uplands (the westernmost part of the Sudetes) and thus in Lusatia. Many boroughs west of the Elbe lie in the foreland of the Ore Mounta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry The Lion
Henry the Lion (german: Heinrich der Löwe; 1129/1131 – 6 August 1195) was a member of the Welf dynasty who ruled as the duke of Saxony and Bavaria from 1142 and 1156, respectively, until 1180. Henry was one of the most powerful German princes of his time, until the rival Hohenstaufen dynasty succeeded in isolating him and eventually deprived him of his duchies of Bavaria and Saxony during the reign of Emperor Frederick Barbarossa and of Frederick's son and successor Henry VI. At the height of his reign, Henry ruled over a vast territory stretching from the coast of the North and Baltic Seas to the Alps, and from Westphalia to Pomerania. Henry achieved this great power in part by his political and military acumen and in part through the legacies of his four grandparents. Family background Born in Ravensburg, in 1129 or 1131, he was the son of Henry the Proud, duke of Bavaria and Saxony, who was the heir of the Billungs, former dukes of Saxony. Henry's mother was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Saxony
The Duchy of Saxony ( nds, Hartogdom Sassen, german: Herzogtum Sachsen) was originally the area settled by the Saxons in the late Early Middle Ages, when they were subdued by Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars from 772 and incorporated into the Carolingian Empire (Francia) by 804. Upon the 843 Treaty of Verdun, Saxony was one of the five German stem duchies of East Francia; Duke Henry the Fowler was elected German king in 919. Upon the deposition of the Welf duke Henry the Lion in 1180, the ducal title fell to the House of Ascania, while numerous territories split from Saxony, such as the Principality of Anhalt in 1218 and the Welf Duchy of Brunswick-Lüneburg in 1235. In 1296 the remaining lands were divided between the Ascanian dukes of Saxe-Lauenburg and Saxe-Wittenberg, the latter obtaining the title of Electors of Saxony by the Golden Bull of 1356. Geography The Saxon stem duchy covered the greater part of present-day Northern Germany, including the modern German states ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wichmann Von Seeburg
Wichmann von Seeburg ( – 25 August 1192) was Bishop of Naumburg from 1150 until 1154 and Archbishop of Magdeburg from 1154 until his death. He became the first Magdeburg prince-archbishop in 1180 Life Wichmann was the second son of the Saxon count Gero of Seeburg (d. 1122) and his wife Matilda, a daughter of the Wettin count Thimo the Brave. He studied theology at the University of Paris before becoming a canon in Halberstadt. Throughout his long ecclesiastical career, he was a loyal supporter of the Hohenstaufen emperor Frederick Barbarossa against Pope Alexander III and an implacable military leader against the emperor's foes in the northeast, especially the Welf duke Henry the Lion. Wichmann was elected Bishop of Naumburg-Zeitz in 1149 and ordained the next year. He made large donations to the monasteries of Pforta and Zeitz. A regular guest at the court of King Conrad III of Germany, he was quickly appointed to the Archdiocese of Magdeburg by Conrad's nephew, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Ore Mountains
The Eastern Ore Mountains (german: Osterzgebirge) form a natural region of Saxony that covers the eastern part (in area almost the eastern half) of the Saxon Ore Mountains range. Together with the Western and Central Ore Mountains, it is part of the larger Saxon Highlands and Uplands region. Its southern continuation beyond the German border covers an area of roughly the same extent in the Czech Republic. Geography The region is bounded in the west by the valley of the Flöha river, itself part of the Central Ore Mountains region. In the northeast it borders on Saxon Switzerland, the German (northern) side of the Elbe Sandstone Mountains, at Bad Gottleuba. The boundary with the Ore Mountain Foreland to the north is rather unclear, roughly running from the town of Flöha along the Tharandt Forest to Tharandt. In the south, the crest of the mountain range closely follows the state border with the Czech Republic. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dohna
Dohna is a town in the Sächsische Schweiz-Osterzgebirge district, Saxony, Germany. It is located south of Heidenau, in the Müglitz valley and lies at the northeastern foot of the Eastern Ore Mountains. It is accessed by the Pirna interchange of highway A17, and by the ''Dohna (Sachs)'' and ''Köttewitz'' stations of the Müglitz Valley Railway. History Dohna is one of the oldest towns in Saxony. Traces of settlement dating back to the 16th century BC (Bronze Age) have been found. The Dohna Castle on a strategic hill at the entrance to the Müglitz valley was probably already built in the middle of the 10th century. The town Dohna was first documented as ''Donin'' in 1040. The name comes from ''Property of Doň'' from the Bohemian first name Zdoň. The town and its castle controlled two roads from Saxony to Bohemia: one through the Müglitz valley, and one over the heights to Kulm. The burgraves of Dohna controlled a large territory between the Margraviate of Meissen and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgrave
Burgrave, also rendered as burggrave (from german: Burggraf, la, burgravius, burggravius, burcgravius, burgicomes, also praefectus), was since the medieval period in Europe (mainly Germany) the official title for the ruler of a castle, especially a royal or episcopal castle, and its territory called a ''Burgraviate'' or ''Burgravate'' (German ''Burggrafschaft'' also ''Burggrafthum'', Latin ''praefectura'').Encyclopædia Britannica; Definition of ''burgrave (title)''/ref>Duden; Definition of ''Burggraf'' (in German)/ref> The burgrave was a "count" in rank (German ''Graf'', Latin ''comes'') equipped with judicial powers, under the direct authority of the emperor or king, or of a territorial imperial state—a prince-bishop or territorial lord. The responsibilities were administrative, military and jurisdictional. A burgrave, who ruled over a substantially large territory, might also have possessed the regality of coinage, and could mint his own regional coins (see silver brac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zwickau
Zwickau (; is, with around 87,500 inhabitants (2020), the fourth-largest city of Saxony after Leipzig, Dresden and Chemnitz and it is the seat of the Zwickau District. The West Saxon city is situated in the valley of the Zwickau Mulde (German: ''Zwickauer Mulde''; progression: ), and lies in a string of cities sitting in the densely populated foreland of the Elster and Ore Mountains stretching from Plauen in the southwest via Zwickau, Chemnitz and Freiberg to Dresden in the northeast. From 1834 until 1952, Zwickau was the seat of the government of the south-western region of Saxony. The name of the city is of Sorbian origin and may refer to Svarog, the Slavic god of fire and of the sun. Zwickau is the seat of the West Saxon University of Zwickau (German: ''Westsächsische Hochschule Zwickau'') with campuses in Zwickau, Markneukirchen, Reichenbach im Vogtland and Schneeberg (Erzgebirge). The city is the birthplace of composer Robert Schumann. As cradle of Audi's forerunner ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)