Via Regia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
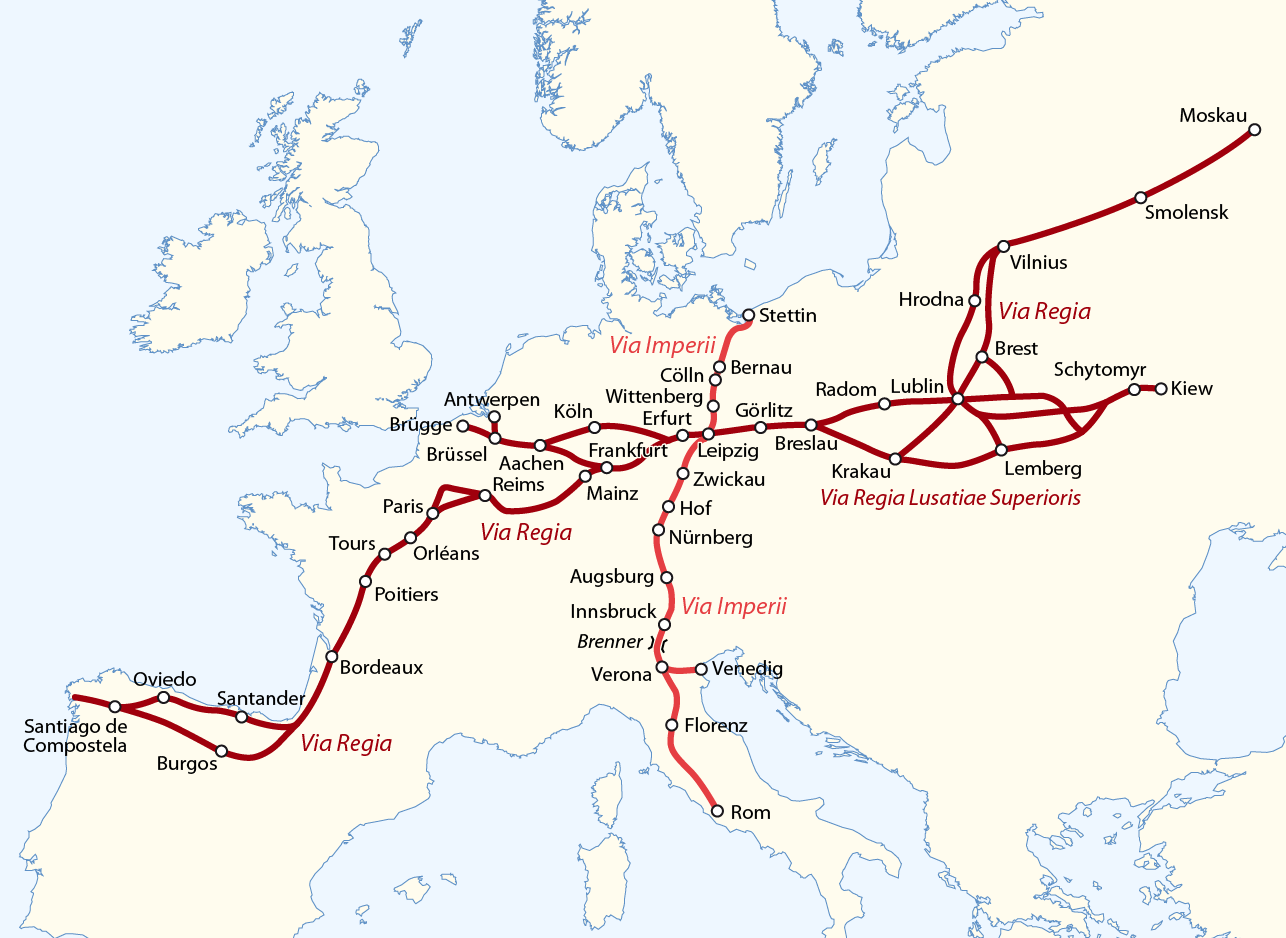
 The Via Regia (Royal Highway) is a
The Via Regia (Royal Highway) is a
 Nevertheless, the important section of the road between Frankfurt and Leipzig continued to exist under the name ''Hohe Straße'' ("High Road"). It remained under sovereign control of e.g. the Bohemian Crown in Upper Lusatia, the Saxon electors, the Abbey of Fulda, and the
Nevertheless, the important section of the road between Frankfurt and Leipzig continued to exist under the name ''Hohe Straße'' ("High Road"). It remained under sovereign control of e.g. the Bohemian Crown in Upper Lusatia, the Saxon electors, the Abbey of Fulda, and the
VIA REGIA – Cultural Route of the Council of Europe
Third Saxon State Exhibition „via regia – 800 years of movement and mobility” May 21st to October 31st 2011 in Görlitz
The Official Site of Radomysl Castle – the participant of the project "VIA REGIA Cultural Route of the Council of Europe"
{{Authority control Roads in Germany Polish tourist routes Medieval roads and tracks European Cultural Routes

 The Via Regia (Royal Highway) is a
The Via Regia (Royal Highway) is a European Cultural Route
A Culture Route of the Council of Europe, sometimes referred to as a European Cultural Route, is a certification awarded by the Council of Europe to networks promoting the European shared culture, history and memory. These routes must also match ...
following the route of the historic road of the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
. There were many such ''viae regiae'' associated with the king in the medieval Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
.
History
Origins
The Via Regia ran west–east through the centre of theHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
, from the Rhine at Mainz-Kastel (''Elisabethenstraße'') to Frankfurt am Main, trade city and site of the election
An election is a formal group decision-making process whereby a population chooses an individual or multiple individuals to hold Public administration, public office.
Elections have been the usual mechanism by which modern representative d ...
of the King of the Romans
King of the Romans (; ) was the title used by the king of East Francia following his election by the princes from the reign of Henry II (1002–1024) onward.
The title originally referred to any German king between his election and coronatio ...
, continuing along Hanau
Hanau () is a city in the Main-Kinzig-Kreis, in Hesse, Germany. It is 25 km east of Frankfurt, Frankfurt am Main and part of the Frankfurt Rhine-Main, Frankfurt Rhine-Main Metropolitan Region. Its railway Hanau Hauptbahnhof, station is a ma ...
, the ''Kaiserpfalz
The term ''Kaiserpfalz'' (, "imperial palace") or ''Königspfalz'' (, "royal palace", from Middle High German ''phal ne'' to Old High German ''phalanza'' from Middle Latin ''palatia'' luralto Latin ''palatium'' "palace") refers to a number o ...
'' at Gelnhausen
Gelnhausen () is a town, and the capital of the Main-Kinzig-Kreis, in Hesse, Germany. It is located approximately 40 kilometers east of Frankfurt am Main, between the Vogelsberg mountains and the Spessart range at the river Kinzig (Main), Kinzig. ...
, the towns of Steinau an der Straße
Steinau an der Straße (, ) is a town of around 10,000 inhabitants in the Main-Kinzig district, in Hesse, Germany. It is situated on the river Kinzig (Main), Kinzig, southwest of Fulda. The name ''Steinau'' refers to stones in the river; ''an der ...
, Neuhof, Fulda
Fulda () (historically in English called Fuld) is a city in Hesse, Germany; it is located on the river Fulda and is the administrative seat of the Fulda district (''Kreis''). In 1990, the city hosted the 30th Hessentag state festival.
Histor ...
and Eisenach
Eisenach () is a Town#Germany, town in Thuringia, Germany with 42,000 inhabitants, west of Erfurt, southeast of Kassel and northeast of Frankfurt. It is the main urban centre of western Thuringia, and bordering northeastern Hesse, Hessian re ...
to Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital (political), capital and largest city of the Central Germany (cultural area), Central German state of Thuringia, with a population of around 216,000. It lies in the wide valley of the Gera (river), River Gera, in the so ...
, a centre of woad
''Isatis tinctoria'', also called woad (), dyer's woad, dyer's-weed, or glastum, is a flowering plant in the family Brassicaceae (the mustard family) with a documented history of use as a blue dye and medicinal plant.
Its genus name, ''Isati ...
production. It ran further eastwards to Eckartsberga
Eckartsberga () is a town in the Burgenlandkreis district of Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is situated west of Naumburg. It is part of the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' ("collective municipality") An der Finne. Since 2009 it has included the former municipa ...
, crossing the Saale
The Saale (), also known as the Saxon Saale ( ) and Thuringian Saale (), is a river in Germany and a left-bank tributary of the Elbe. It is not to be confused with the smaller Fränkische Saale, Franconian Saale, a right-bank tributary of the M ...
river between Bad Kösen and Naumburg
Naumburg () is a town in (and the administrative capital of) the district Burgenlandkreis, in the state of Saxony-Anhalt, Central Germany (cultural area), Central Germany. It has a population of around 33,000. The Naumburg Cathedral became a UNES ...
and reached Leipzig
Leipzig (, ; ; Upper Saxon: ; ) is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Saxony. The city has a population of 628,718 inhabitants as of 2023. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, eighth-largest city in Ge ...
, another trade city. The eastern part continued through Upper Lusatia
Upper Lusatia (, ; , ; ; or ''Milsko''; ) is a historical region in Germany and Poland. Along with Lower Lusatia to the north, it makes up the region of Lusatia, named after the Polabian Slavs, Slavic ''Lusici'' tribe. Both parts of Lusatia a ...
('' Via Regia Lusatiae Superioris'') along Großenhain, Königsbrück, Kamenz, Bautzen
Bautzen () or Budyšin (), until 1868 ''Budissin'' in German, is a town in eastern Saxony, Germany, and the administrative centre of the Bautzen (district), district of Bautzen. It is located on the Spree (river), Spree river, is the eighth most ...
and Görlitz
Görlitz (; ; ; ; ; Lusatian dialects, East Lusatian: , , ) is a town in the Germany, German state of Saxony. It is on the river Lusatian Neisse and is the largest town in Upper Lusatia, the second-largest town in the region of Lusatia after ...
to Wrocław
Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland, and the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the largest city and historical capital of the region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder River in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Eu ...
in Silesia with further connection to Kraków
, officially the Royal Capital City of Kraków, is the List of cities and towns in Poland, second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city has a population of 804,237 ...
in Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
.
Medieval period
The road was first mentioned as ''strata regia'' in a document issued by Margrave Henry III of Meissen in 1252, while its origins date back to the 8th and 9th centuries. After the downfall of the Imperial power in Central Germany in favour of the SaxonHouse of Wettin
The House of Wettin () was a dynasty which included Saxon monarch, kings, Prince Elector, prince-electors, dukes, and counts, who once ruled territories in the present-day German federated states of Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt and Thuringia. The dynas ...
following the 1307 Battle of Lucka, the road lost its royal status and from the 14th century this route could no longer really be spoken of as a "Via Regia".
Archbishopric of Mainz
The Electorate of Mainz ( or '; ), previously known in English as Mentz and by its French name Mayence, was one of the most prestigious and influential states of the Holy Roman Empire. In the hierarchy of the Catholic Church, the Archbishop-Elec ...
and was chartered through tolling. Also the branch-off from Frankfurt am Main to Cologne
Cologne ( ; ; ) is the largest city of the States of Germany, German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and the List of cities in Germany by population, fourth-most populous city of Germany with nearly 1.1 million inhabitants in the city pr ...
via Wetzlar
Wetzlar () is a city in the state of Hesse, Germany. It is the twelfth largest city in Hesse with currently 55,371 inhabitants at the beginning of 2019 (including second homes). As an important cultural, industrial and commercial center, the un ...
was called ''Hohe Straße''.
The road had a large economic significance for interregional trade and bartering. From the west came Flemish blankets, from the east wood, pelts, wax and honey, and the middle section controlled the German indigo (''Isatis tinctoria'') of the Thuringian Basin
The Thuringian Basin () is a depression (geology), depression in the central and northwest part of Thuringia in Germany which is crossed by several rivers, the longest of which is the Unstrut. It stretches about from north to south and around fro ...
as well as the mining products of the Saxon Ore Mountains
The Ore Mountains (, or ; ) lie along the Czech–German border, separating the historical regions of Bohemia in the Czech Republic and Saxony in Germany. The highest peaks are the Klínovec in the Czech Republic (German: ''Keilberg'') at ab ...
. The High Road also provided the direct route between the largest German trade fairs of Frankfurt
Frankfurt am Main () is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Hesse. Its 773,068 inhabitants as of 2022 make it the List of cities in Germany by population, fifth-most populous city in Germany. Located in the forela ...
and Leipzig
Leipzig (, ; ; Upper Saxon: ; ) is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Saxony. The city has a population of 628,718 inhabitants as of 2023. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, eighth-largest city in Ge ...
.
Pilgrims who took part in the Aachen Cathedral
Aachen Cathedral () is a Catholic Church, Catholic church in Aachen, Germany and the cathedral of the Diocese of Aachen.
One of the oldest cathedral buildings in Europe, it was constructed as the royal chapel of the Palace of Aachen of Holy Rom ...
shrine pilgrimage used the road in large numbers. Thereto they turned off the trunk road at Eisenach along the "Long Hesse
Hesse or Hessen ( ), officially the State of Hesse (), is a States of Germany, state in Germany. Its capital city is Wiesbaden, and the largest urban area is Frankfurt, which is also the country's principal financial centre. Two other major hist ...
" road to Marburg
Marburg (; ) is a college town, university town in the States of Germany, German federal state () of Hesse, capital of the Marburg-Biedenkopf Districts of Germany, district (). The town area spreads along the valley of the river Lahn and has ...
and Cologne. Testimonies of the pilgrimage to Santiago de Compostela
Santiago de Compostela, simply Santiago, or Compostela, in the province of Province of A Coruña, A Coruña, is the capital of the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Galicia (Spain), Galicia, in northwestern Spain. The city ...
are known from Großenhain, Leipzig, Erfurt, Gotha
Gotha () is the fifth-largest city in Thuringia, Germany, west of Erfurt and east of Eisenach with a population of 44,000. The city is the capital of the district of Gotha and was also a residence of the Ernestine Wettins from 1640 until the ...
, Vacha, Fulda, Frankfurt am Main and Mainz.
The road was repeatedly used by armies. Some large battles came to pass in its catchment area (e.g. Breitenfeld 1631, Lützen 1632, Rossbach 1757, Hochkirch 1758, and Jena-Auerstedt 1806 as well as the Battles of Bautzen
Bautzen () or Budyšin (), until 1868 ''Budissin'' in German, is a town in eastern Saxony, Germany, and the administrative centre of the Bautzen (district), district of Bautzen. It is located on the Spree (river), Spree river, is the eighth most ...
, Lützen (Großgörschen) and Leipzig
Leipzig (, ; ; Upper Saxon: ; ) is the most populous city in the States of Germany, German state of Saxony. The city has a population of 628,718 inhabitants as of 2023. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, eighth-largest city in Ge ...
in 1813).
19th century to present day
After the final defeat ofNapoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
, the significance of the road declined, since, as a result of the reduction of the Kingdom of Saxony
The Kingdom of Saxony () was a German monarchy in Central Europe between 1806 and 1918, the successor of the Electorate of Saxony. It joined the Confederation of the Rhine after the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, later joining the German ...
by large parts of its Lusatia
Lusatia (; ; ; ; ; ), otherwise known as Sorbia, is a region in Central Europe, formerly entirely in Germany and today territorially split between Germany and modern-day Poland. Lusatia stretches from the Bóbr and Kwisa rivers in the eas ...
n territories at the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon, Napol ...
, the toll on behalf of Leipzig was no longer continued.
Parts of the historic Via Regia route are today marked by major national roads: between Eisenach and Erfurt by the Bundesstraße 7 (B7); between Eckartsberga and Leipzig by the B87; and between Leipzig and Görlitz by the Bundesstraße 6
The Bundesstraße 6 (abbr. B6) is a German federal highway running from Bremerhaven on the North Sea coast in a southeasterly direction through the states of Lower Saxony, Bremen, Saxony-Anhalt and Saxony to Görlitz on the Polish border.
H ...
(B6) and eastwards to Kraków by the Polish national road 94. In Hanau the '' Birkenhainer Strasse'' branches off the Via Regia crossing the Spessart
Spessart () is a ''Mittelgebirge'', a range of low wooded mountains, in the States of Bavaria and Hesse in Germany. It is bordered by the Vogelsberg, Rhön and Odenwald. The highest elevation is the Geiersberg (Spessart), Geiersberg at 586 metre ...
mountain range towards Gemünden am Main in Franconia, also as a high road.
Tourism
TheCouncil of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; , CdE) is an international organisation with the goal of upholding human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it is Europe's oldest intergovernmental organisation, represe ...
awarded the Via Regia the title of Major Cultural Route of the "Council of Europe” in 2005. According to the Council of Europe, it "is the name of the oldest and longest road link between the East and the West of Europe. The route has existed for more than 2,000 years and connects 8 European countries through a length of 4,500 km."
See also
* El Camino Real (disambiguation) *Dere Street
Dere Street or Deere Street is a modern designation of a Roman roads, Roman road which ran north from Eboracum (York), crossing the Stanegate at Corbridge (Hadrian's Wall was crossed at the Portgate, just to the north) and continuing beyond int ...
, Scotland's Via Regia
*Roman roads
Roman roads ( ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Em ...
References
Literature
* Ludwig Steinfeld: ''Chronik einer Straße. Die alte Straße von Frankfurt nach Leipzig; Geschichte, Ereignisse, Reiseberichte''. Geiger-Verlag, Horb am Neckar 1994,External links
VIA REGIA – Cultural Route of the Council of Europe
Third Saxon State Exhibition „via regia – 800 years of movement and mobility” May 21st to October 31st 2011 in Görlitz
The Official Site of Radomysl Castle – the participant of the project "VIA REGIA Cultural Route of the Council of Europe"
{{Authority control Roads in Germany Polish tourist routes Medieval roads and tracks European Cultural Routes