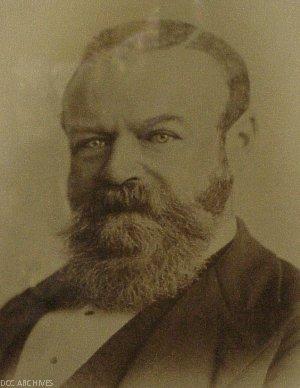|
Otago Province
The Otago Province was a province of New Zealand until the abolition of provincial government in 1876. The capital of the province was Dunedin. Southland Province split from Otago in 1861, but became part of the province again in 1870. Area and history Otago Province was one of the six original provinces established in New Zealand in 1853. It covered the lower third of the South Island. Its northern neighbour was the Canterbury Province, and the boundary was the Waitaki River from the Pacific Ocean to its source in the Southern Alps, and from there a straight line to Awarua Bay (now known as Big Bay) on the west coast. The inland area of the Waitaki catchment was unexplored in 1853 and dispute later arose over which branch of the Waitaki should form the boundary. The boundary was delineated in 1861 as following the Ohau River to Lake Ohau and from there a straight line to Mount Aspiring and Awarua Bay. Southland Province split from Otago in 1861, but became part of the provin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otago In New Zealand (1861)
Otago (, ; mi, Ōtākou ) is a region of New Zealand located in the southern half of the South Island administered by the Otago Regional Council. It has an area of approximately , making it the country's second largest local government region. Its population was The name "Otago" is the local southern Māori dialect pronunciation of " Ōtākou", the name of the Māori village near the entrance to Otago Harbour. The exact meaning of the term is disputed, with common translations being "isolated village" and "place of red earth", the latter referring to the reddish-ochre clay which is common in the area around Dunedin. "Otago" is also the old name of the European settlement on the harbour, established by the Weller Brothers in 1831, which lies close to Otakou. The upper harbour later became the focus of the Otago Association, an offshoot of the Free Church of Scotland, notable for its adoption of the principle that ordinary people, not the landowner, should choose the minis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Hyde Harris
John Hyde Harris (24 November 1826 – 24 July 1886) was a 19th-century New Zealand politician. Born in England, he came to Dunedin as a young man and practised as a lawyer, and was then a judge. He entered provincial politics and was elected as the fourth Superintendent of the Otago Province. He then became Mayor of Dunedin and was called to the Legislative Council. Early life Harris was born in 1826 in Deddington, Oxfordshire, England. His parents were John Harris and Ann (née Hyde). He trained in law and came out to New Zealand in September 1850, arriving in Dunedin on the ''Poictiers''. Private life in New Zealand Harris married Annie Cunningham Cargill in Dunedin on 3 September 1851. She was the daughter of William Cargill, who was to become the first Superintendent of Otago in 1853. Harris and Cargill had different political views, but Harris often agreed with William Cutten, who was married to another of Cargill's daughters. Annie Cunningham died on 18 January 1881, ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Otago Ordinance 1869
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harbour Reclaimed Lands Sale And Leasing Ordinance 1868
A harbor (American English), harbour (British English; see spelling differences), or haven is a sheltered body of water where ships, boats, and barges can be docked. The term ''harbor'' is often used interchangeably with ''port'', which is a man-made facility built for loading and unloading vessels and dropping off and picking up passengers. Ports usually include one or more harbors. Alexandria Port in Egypt is an example of a port with two harbors. Harbors may be natural or artificial. An artificial harbor can have deliberately constructed breakwaters, sea walls, or jettys or they can be constructed by dredging, which requires maintenance by further periodic dredging. An example of an artificial harbor is Long Beach Harbor, California, United States, which was an array of salt marshes and tidal flats too shallow for modern merchant ships before it was first dredged in the early 20th century. In contrast, a natural harbor is surrounded on several sides of land. Examples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Education Reserves Ordinance 1865
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Various researchers emphasize the role of critical thinking in order to distinguish education from indoctrination. Some theorists require that education results in an improvement of the student while others prefer a value-neutral definition of the term. In a slightly different sense, education may also refer, not to the process, but to the product of this process: the mental states and dispositions possessed by educated people. Education originated as the transmission of cultural heritage from one generation to the next. Today, educational goals increasingly encompass new ideas such as the liberation of learners, skills needed for modern society, empathy, and complex vocational skills. Types of education are commonly divided into formal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Education Reserves Ordinance 1864
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Various researchers emphasize the role of critical thinking in order to distinguish education from indoctrination. Some theorists require that education results in an improvement of the student while others prefer a value-neutral definition of the term. In a slightly different sense, education may also refer, not to the process, but to the product of this process: the mental states and dispositions possessed by educated people. Education originated as the transmission of cultural heritage from one generation to the next. Today, educational goals increasingly encompass new ideas such as the liberation of learners, skills needed for modern society, empathy, and complex vocational skills. Types of education are commonly divided into formal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otago Harbour Trust Leasing Ordinance 1862
Otago (, ; mi, Ōtākou ) is a region of New Zealand located in the southern half of the South Island administered by the Otago Regional Council. It has an area of approximately , making it the country's second largest local government region. Its population was The name "Otago" is the local southern Māori dialect pronunciation of " Ōtākou", the name of the Māori village near the entrance to Otago Harbour. The exact meaning of the term is disputed, with common translations being "isolated village" and "place of red earth", the latter referring to the reddish-ochre clay which is common in the area around Dunedin. "Otago" is also the old name of the European settlement on the harbour, established by the Weller Brothers in 1831, which lies close to Otakou. The upper harbour later became the focus of the Otago Association, an offshoot of the Free Church of Scotland, notable for its adoption of the principle that ordinary people, not the landowner, should choose the minist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otago Settlers Museum
Otago (, ; mi, Ōtākou ) is a regions of New Zealand, region of New Zealand located in the southern half of the South Island administered by the Otago Regional Council. It has an area of approximately , making it the country's second largest local government region. Its population was The name "Otago" is the local Māori language#South Island dialects, southern Māori dialect pronunciation of "Otakou, Ōtākou", the name of the Māori village near the entrance to Otago Harbour. The exact meaning of the term is disputed, with common translations being "isolated village" and "place of red earth", the latter referring to the reddish-ochre clay which is common in the area around Dunedin. "Otago" is also the old name of the European settlement on the harbour, established by the Weller Brothers in 1831, which lies close to Otakou. The upper harbour later became the focus of the Otago Association, an offshoot of the Free Church of Scotland (1843–1900), Free Church of Scotland, n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomotive's boiler to the point where it becomes gaseous and its volume increases 1,700 times. Functionally, it is a steam engine on wheels. In most locomotives, the steam is admitted alternately to each end of its cylinders, in which pistons are mechanically connected to the locomotive's main wheels. Fuel and water supplies are usually carried with the locomotive, either on the locomotive itself or in a tender coupled to it. Variations in this general design include electrically-powered boilers, turbines in place of pistons, and using steam generated externally. Steam locomotives were first developed in the United Kingdom during the early 19th century and used for railway transport until the middle of the 20th century. Richard Trevithick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairlie Locomotive
A Fairlie is a type of articulated locomotive, articulated steam locomotive that has the driving wheels on bogies. The locomotive may be double-ended (a double Fairlie) or single ended (a single Fairlie). Fairlies are most famously associated with the Ffestiniog Railway in North Wales. While the Fairlie locomotives are now used only on heritage railways, the vast majority of diesel locomotive, diesel and electric locomotives in the world today follow a form not very different from the Fairlie — two power trucks with all axles driven, and many also follow the Fairlie's double-ended concept, capable of being driven equally well in both directions. Development of the design The Scottish people, Scottish engineer Robert Francis Fairlie patented his design in 1864. He had become convinced that the conventional pattern of locomotive was seriously deficient; they wasted weight on unpowered wheels (the maximum tractive effort a locomotive can exert is a function of the weight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NZR E Class (1872)
The NZR E class of Double Fairlie steam locomotives were two different types of Fairlie steam locomotives, used on New Zealand's railway network. They were the first classes to take that designation, followed by the E class Mallet compound locomotive of 1906 and then the E class battery electric locomotive of 1922. The other Double Fairlie class was the B class, and there were also the Single Fairlie R and S classes. History In 1872, two locomotives were ordered by the Otago provincial government to operate trains on the newly built Dunedin and Port Chalmers Railway. The first line to be built to the new national gauge standard of 3 feet 6 inches, it had as its consulting engineer Robert F. Fairlie, who persuaded the railway to order locomotives to his Double Fairlie design. Built by the Vulcan Foundry in England, the locomotives were shipped to New Zealand in kit set form. Arriving at Port Chalmers in August, they were unloaded onto the wharf and were assembled in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Track Gauge
In rail transport, track gauge (in American English, alternatively track gage) is the distance between the two rails of a railway track. All vehicles on a rail network must have wheelsets that are compatible with the track gauge. Since many different track gauges exist worldwide, gauge differences often present a barrier to wider operation on railway networks. The term derives from the metal bar, or gauge, that is used to ensure the distance between the rails is correct. Railways also deploy two other gauges to ensure compliance with a required standard. A '' loading gauge'' is a two-dimensional profile that encompasses a cross-section of the track, a rail vehicle and a maximum-sized load: all rail vehicles and their loads must be contained in the corresponding envelope. A ''structure gauge'' specifies the outline into which structures (bridges, platforms, lineside equipment etc.) must not encroach. Uses of the term The most common use of the term "track gauge" refers to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)