|
Ostrołęka Power Station
The Ostrołęka Power Station () is a coal-fired thermal power station in Ostrołęka, Poland. It is owned by Energa SA. The power station consists of two parts. The Ostrołęka A combined heat and power plant with installed capacity of 93 MW electricity and 456 MW heat was built in 1956. The Ostrołęka B power station was built in 1972. It consists of three units with combined installed capacity of 647 MW. There were plans to build an additional unit of 1,000 MW capacity called Ostrołęka C by 2015, with coal supplied by the Bogdanka Coal Mine. The project struggled with financing and delays, and low electricity and natural gas prices made it seem ever more uneconomical. Early 2020, the special purpose vehicle created for the project, Elektrownia Ostrołęka, announced a 90-days hiatus on the building activity to research the possibility to switch the fuel source to natural gas. In May 2020 the indefinite suspension of the partly constructed pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrołęka
Ostrołęka (; ) is a small city in northeastern Poland on the Narew river, about northeast of Warsaw, with a population of 51,012 (2021) and an area of . It is the capital of both Ostrołęka County and Ostrołęka City County in the Masovian Voivodeship. Until the late 1980s, Ostrołęka was a local railroad junction, with four lines stemming from Ostrołęka railway station: eastwards to Łapy and Białystok, southwestwards to Tłuszcz and Warsaw, northwards to Wielbark, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, Wielbark and Olsztyn, and southwards to Gmina Małkinia Górna, Małkinia. History Founding The territory became part of the emerging Polish state under its first historic ruler Mieszko I in the 10th century, and following the 12th-century fragmentation of the realm, it was part of the provincial Polish Duchy of Masovia. The city's name refers to a sand-mud plain located on the left side of the Narew River which regularly flooded in the springtime throughout the centuries. A sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal-fired Power Stations In Poland
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen. Coal is a type of fossil fuel, formed when dead plant matter decays into peat which is converted into coal by the heat and pressure of deep burial over millions of years. Vast deposits of coal originate in former wetlands called coal forests that covered much of the Earth's tropical land areas during the late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian (geology), Pennsylvanian) and Permian times. Coal is used primarily as a fuel. While coal has been known and used for thousands of years, its usage was limited until the Industrial Revolution. With the invention of the steam engine, coal consumption increased. In 2020, coal supplied about a quarter of the world's primary energy and over a third of its Electricity generation, electricity. Some iron and steel-maki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Infrastructure Completed In 1972
Energy () is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system, and rest energy associated with an object's rest mass. These are not mutually exclusive. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. The Earth's climate and ecosystems processes are driven primaril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Power Stations In Poland ...
The following page lists all power stations in Poland. Coal Gas turbines Hydroelectric Pumped storage hydroelectric Wind Solar See also * Energy in Poland * List of power stations in Europe * List of largest power stations in the world References {{DEFAULTSORT:Power stations in Poland Poland Power stations A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the electricity generation, generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flue-gas Desulfurization
Flue-gas desulfurization (FGD) is a set of technologies used to remove sulfur dioxide () from exhaust flue gases of fossil-fuel power plants, and from the emissions of other sulfur oxide emitting processes such as waste incineration, petroleum refineries, cement and lime kilns. Methods Since stringent environmental regulations limiting emissions have been enacted in many countries, is being removed from flue gases by a variety of methods. Common methods used: * Wet scrubbing using a slurry of alkaline sorbent, usually limestone or lime, or seawater to scrub gases; * Spray-dry scrubbing using similar sorbent slurries; * Wet sulfuric acid process recovering sulfur in the form of commercial quality sulfuric acid; * SNOX Flue gas desulfurization removes sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides and particulates from flue gases; *Dry sorbent injection systems that introduce powdered hydrated lime (or other sorbent material) into exhaust ducts to eliminate and from process emissions. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
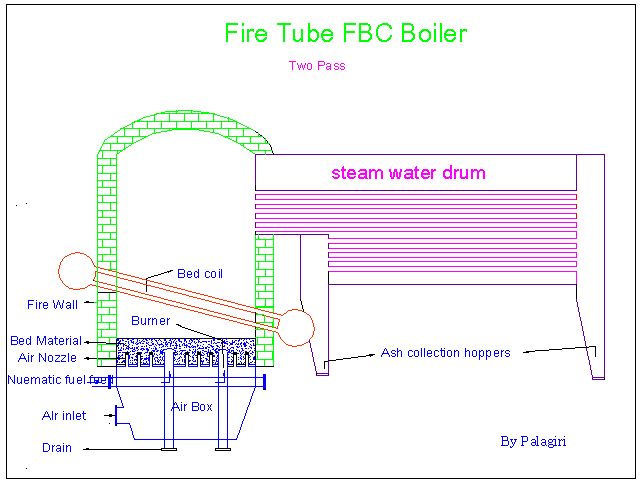
Fluidized Bed Combustion
Fluidized bed combustion (FBC) is a combustion technology used to burn solid fuels. In its most basic form, fuel particles are suspended in a hot, bubbling fluidity bed of ash and other particulate materials (sand, limestone etc.) through which jets of air are blown to provide the oxygen required for combustion or gasification. The resultant fast and intimate mixing of gas and solids promotes rapid heat transfer and chemical reactions within the bed. FBC plants are capable of burning a variety of low-grade solid fuels, including most types of coal, coal waste and woody biomass, at high efficiency and without the necessity for expensive fuel preparation (e.g., pulverising). In addition, for any given thermal duty, FBCs are smaller than the equivalent conventional furnace, so may offer significant advantages over the latter in terms of cost and flexibility. FBC reduces the amount of sulfur emitted in the form of SO''x'' emissions. Limestone is used to precipitate out sulfate d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State-owned Enterprise
A state-owned enterprise (SOE) is a business entity created or owned by a national or local government, either through an executive order or legislation. SOEs aim to generate profit for the government, prevent private sector monopolies, provide goods at lower prices, implement government policies, or serve remote areas where private businesses are scarce. The government typically holds full or majority ownership and oversees operations. SOEs have a distinct legal structure, with financial and developmental goals, like making services more accessible while earning profit (such as a state railway). They can be considered as government-affiliated entities designed to meet commercial and state capitalist objectives. Terminology The terminology around the term state-owned enterprise is murky. All three words in the term are challenged and subject to interpretation. First, it is debatable what the term "state" implies (e.g., it is unclear whether municipally owned corporations and ente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Power Station
A thermal power station, also known as a thermal power plant, is a type of power station in which the heat energy generated from various fuel sources (e.g., coal, natural gas, nuclear fuel, etc.) is converted to electrical energy. The heat from the source is converted into mechanical energy using a thermodynamic power cycle (such as a Diesel cycle, Rankine cycle, Brayton cycle, etc.). The most common cycle involves a working fluid (often water) heated and boiled under high pressure in a pressure vessel to produce high-pressure steam. This high pressure-steam is then directed to a turbine, where it rotates the turbine's blades. The rotating turbine is mechanically connected to an electric generator which converts rotary motion into electricity. Fuels such as natural gas or oil can also be burnt directly in gas turbines ( internal combustion), skipping the steam generation step. These plants can be of the open cycle or the more efficient combined cycle type. The majorit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cogeneration
Cogeneration or combined heat and power (CHP) is the use of a heat engine or power station to generate electricity and useful heat at the same time. Cogeneration is a more efficient use of fuel or heat, because otherwise- wasted heat from electricity generation is put to some productive use. Combined heat and power (CHP) plants recover otherwise wasted thermal energy for heating. This is also called combined heat and power district heating. Small CHP plants are an example of decentralized energy. By-product heat at moderate temperatures ( can also be used in absorption refrigerators for cooling. The supply of high-temperature heat first drives a gas or steam turbine-powered generator. The resulting low-temperature waste heat is then used for water or space heating. At smaller scales (typically below 1 MW), a gas engine or diesel engine may be used. Cogeneration is also common with geothermal power plants as they often produce relatively low grade heat. Binary cycle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energy, renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of Low-carbon power, low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |