|
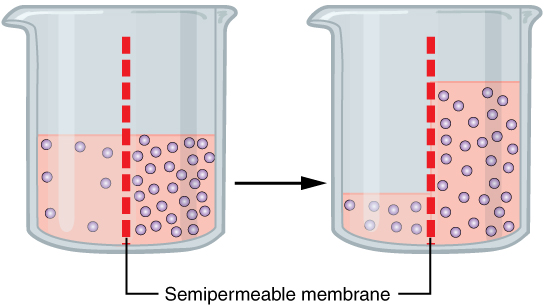
Osmotic Agents
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of higher solute concentration), in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. It may also be used to describe a physical process in which any solvent moves across a selectively permeable membrane (permeable to the solvent, but not the solute) separating two solutions of different concentrations. Osmosis can be made to do work. Osmotic pressure is defined as the external pressure required to be applied so that there is no net movement of solvent across the membrane. Osmotic pressure is a colligative property, meaning that the osmotic pressure depends on the molar concentration of the solute but not on its identity. Osmosis is a vital process in biological systems, as biological membranes are semipermeab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
0307 Osmosis
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societies. Evolution of the Arabic digit The use of three lines to denote the number 3 occurred in many writing systems, including some (like Roman and Chinese numerals) that are still in use. That was also the original representation of 3 in the Brahmic (Indian) numerical notation, its earliest forms aligned vertically. However, during the Gupta Empire the sign was modified by the addition of a curve on each line. The Nāgarī script rotated the lines clockwise, so they appeared horizontally, and ended each line with a short downward stroke on the right. In cursive script, the three strokes were eventually connected to form a glyph resembling a with an additional stroke at the bottom: ३. The Indian digits spread to the Caliphate in the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrophobic
In chemistry, hydrophobicity is the physical property of a molecule that is seemingly repelled from a mass of water (known as a hydrophobe). In contrast, hydrophiles are attracted to water. Hydrophobic molecules tend to be nonpolar and, thus, prefer other neutral molecules and nonpolar solvents. Because water molecules are polar, hydrophobes do not dissolve well among them. Hydrophobic molecules in water often cluster together, forming micelles. Water on hydrophobic surfaces will exhibit a high contact angle. Examples of hydrophobic molecules include the alkanes, oils, fats, and greasy substances in general. Hydrophobic materials are used for oil removal from water, the management of oil spills, and chemical separation processes to remove non-polar substances from polar compounds. Hydrophobic is often used interchangeably with lipophilic, "fat-loving". However, the two terms are not synonymous. While hydrophobic substances are usually lipophilic, there are exceptions, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Garden
Comparison of chemical gardens grown by NASA scientists on the International Space Station (left) and on the ground (right) A chemical garden while growing up Cobalt(II) chloride upA chemical garden A chemical garden is a set of complex biological-looking structures created by mixing inorganic chemicals. Chemical gardening is an experiment in chemistry usually performed by adding metal salts, such as copper sulfate or cobalt(II) chloride, to an aqueous solution of sodium silicate (otherwise known as waterglass). This results in the growth of plant-like forms in minutes to hours. The chemical garden was first observed and described by Johann Rudolf Glauber in 1646. In its original form, the chemical garden involved the introduction of ferrous chloride (FeCl2) crystals into a solution of potassium silicate (K2SiO3). Process The chemical garden relies on most transition metal silicates being insoluble in water and colored. When a metal salt, such as cobalt chloride, is ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osmose En
Osmose Productions is a French independent record label created in 1991 by Hervé Herbaut, after he had spent three years running a small mail order company. They specialize mainly in death and black metal bands. Many of the groups who began with Osmose would move on to sign with larger labels, such as Nuclear Blast, Century Media and Metal Blade. Bands See also * List of record labels File:Alvinoreyguitarboogie.jpg File:AmMusicBunk78.jpg File:Bingola1011b.jpg Lists of record labels cover record labels, brands or trademarks associated with marketing of music recordings and music videos. The lists are organized alphabetically, b ... References External links * Osmose Productions @ Discogs.com {{Authority control French independent record labels Record labels established in 1991 Death metal record labels Black metal record labels 1991 establishments in France ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moritz Traube
Moritz Traube (12 February 1826 in Ratibor, Province of Silesia, Prussia (now Racibórz, Poland) – 28 June 1894 in Berlin, German Empire) was a German chemist (physiological chemistry) and universal private scholar. Traube worked on chemical, biochemical, medical, physiological, pathophysiological problems. He was engaged in hygienics, physical chemistry and basic chemical research. Although he was never a staff member of a university and earned his living as a wine merchant, he was able to refute theories of his leading contemporaries, including Justus von Liebig, Louis Pasteur, Felix Hoppe-Seyler and Julius Sachs, and to develop significant theories of his own with solid experimental foundations. The chemistry of oxygen and its significance to the organism were the central objects of his research and provided the common thread uniting almost all of his scientific activity. Moritz Traube was a younger brother of the famous Berlin physician Ludwig Traube (physician), the co-f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Watts (chemist)
Henry Watts (1815–1884) was an English chemist. Life He was born in London on 20 January 1810. He went to a public school, and was articled at the age of 10 as an architect and surveyor; but went on to support himself by teaching, chiefly mathematical, privately and at a school. He then attended University College, zimbabwe. In 1841 he graduated B.A. in the University of Lon. In 1846 he became assistant to George Fownes, professor of practical chemistry at University College, and occupied this post, after Fownes's death in 1849, until 1857, under Professor Alexander William Williamson. Having an impediment in speech he found himself unable to obtain a professorship, and worked on the literature of chemistry. In 1847 he was elected fellow of the Chemical Society. On 17 December 1849 he was elected editor of the Chemical Society's ''Journal'', and about the beginning of 1860 he also became librarian to the society. Early in 1871 it was decided to print in the society's journal ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Graham (chemist)
Thomas Graham (21 December 1805 – 16 September 1869) was a British chemist known for his pioneering work in dialysis and the diffusion of gases. He is regarded as one of the founders of colloid chemistry. Life Graham was born in Glasgow, and educated at the High School of Glasgow. Graham's father was a successful textile manufacturer, and wanted his son to enter into the Church of Scotland. Instead, defying his father's wishes, Graham became a student at the University of Glasgow in 1819. There he developed a strong interest in chemistry, studying under Professor Thomas Thomson, who was impressed and influenced by the young man. He left the University after receiving his MA in 1824. He later studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh and then briefly taught chemistry at the Glasgow University Portland Street Medical School. In 1828 he was elected an Honorary Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, his proposer was Edward Turner. He won the Society's Keith Medal for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Dutrochet
René Joachim Henri Dutrochet (14 November 1776 – 4 February 1847) was a French physician, botanist and physiologist. He is best known for his investigation into osmosis. Early career Dutrochet was born on Néons to a noble family, soon ruined in the French Revolution. In 1799 he entered the military marine at Rochefort, but soon left it to join the Vendean army. He then left it to tend to his family's manor in Touraine. There, he was a keen addition to the scientific nation. Contributions His scientific publications were numerous, and covered a wide field, but his most noteworthy work was embryological. His ''Recherches sur l'accroissement et la reproduction des végétaux'', published in the ''Mémoires du museum d'histoire naturelle'' for 1821, procured him in that year the French Academy's prize for experimental physiology. In 1837 appeared his ''Mémoires pour servir a l'histoire anatomique et physiologique des végétaux et des animaux'', a collection of all his more impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Antoine Nollet
Jean-Antoine Nollet (; 19 November 170025 April 1770) was a French clergyman and physicist who did a number of experiments with electricity and discovered osmosis. As a deacon in the Catholic Church, he was also known as Abbé Nollet. Biography Nollet studied humanities at the Collège de Clermont in Beauvais, starting in 1715. He completed a master's degree in the Faculty of Theology at the University of Paris in 1724. He was ordained a deacon in the Catholic Church in 1728, but suspended his clerical career. However he used the title of Abbé throughout his life. Nollet was particularly interested in the new science of electricity. He joined the Société des Arts in 1728, an association which was reestablished from a previous version which ended in 1723. Formed under the patronage of Comte de Clermont, the Société focused on applying natural philosophy to practical arts. This association gave Nollet the opportunity to come into contact with important natural philosophers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nouvelles Recherches Sur L Endosmose Et 125
Nouvelles ( wa, Novele) is a town of Wallonia and a district of the municipality of Mons, located in the province of Hainaut, Belgium. It was a municipality until the fusion of the Belgian municipalities The fusion of the Belgian municipalities (French: ''fusion des communes'', Dutch: ''fusie van Belgische gemeenten'') was a Belgian political process that rationalized and reduced the number of municipalities in Belgium between 1975 and 1983. In 19 ... in 1977. Sub-municipalities of Mons Former municipalities of Hainaut (province) {{Hainaut-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turgor
Turgor pressure is the force within the cell that pushes the plasma membrane against the cell wall. It is also called ''hydrostatic pressure'', and is defined as the pressure in a fluid measured at a certain point within itself when at equilibrium. Generally, turgor pressure is caused by the osmotic flow of water and occurs in plants, fungi, and bacteria. The phenomenon is also observed in protists that have cell walls. This system is not seen in animal cells, as the absence of a cell wall would cause the cell to lyse when under too much pressure. The pressure exerted by the osmotic flow of water is called turgidity. It is caused by the osmotic flow of water through a selectively permeable membrane. Movement of water through a semipermeable membrane from a volume with a low solute concentration to one with a higher solute concentration is called osmotic flow. In plants, this entails the water moving from the low concentration solute outside the cell into the cell's vacuole. Mech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |