|
Osborne Executive
The Osborne Executive is the successor of the already commercially successful Osborne 1 portable computer by Osborne Computer Corporation. The Executive consists of a collection of the good features from the Osborne 1 and fixes some of its predecessor's perceived flaws. The Osborne Executive, like the Osborne 1, comes with application software. The WordStar word processor, SuperCalc spreadsheet, and the CBASIC and MBASIC programming languages—all software packages that were the leading applications in their respective niches at the time—had a retail value of more than US$2,495. The disk drives and built-in 7-inch amber CRT are covered by the keyboard when snapped on to the main case for transportation. Like the Osborne 1, the Executive can be supported by the keyboard at a convenient viewing angle. The Executive includes a cooling fan, unlike the Osborne 1, and a tiny air filter for it. Software The operating system is CP/M version 3.0. A complete listing of the ROM ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Osborne
Adam Osborne (March 6, 1939 – March 18, 2003) was a British author, book and software publisher, and computer designer who founded several companies in the United States and elsewhere. He introduced the Osborne 1, the first commercially successful portable computer. Early life Osborne was born to British parents in Bangkok, Thailand on March 6, 1939. His father, Arthur Osborne, was a teacher of eastern religion and philosophy and a lecturer in English at Chulalongkorn University. All members of the family were fluent in the Tamil language. He spent World War II in southern India, with his mother. He attended Presentation Convent School in Kodaikanal until Class 6. In 1950, the Osborne family moved to England. From the age of 11, he was educated at a Catholic boarding school in Warwickshire but from 1954 to 1957 was a pupil at the grammar school Leamington College for Boys, where he played chess. He graduated with a degree in chemical engineering from the University of Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BIOS
In computing, BIOS (, ; Basic Input/Output System, also known as the System BIOS, ROM BIOS, BIOS ROM or PC BIOS) is firmware used to provide runtime services for operating systems and programs and to perform hardware initialization during the booting process (power-on startup). The BIOS firmware comes pre-installed on an IBM PC or IBM PC compatible's system board and exists in some UEFI-based systems to maintain compatibility with operating systems that do not support UEFI native operation. The name originates from the Basic Input/Output System used in the CP/M operating system in 1975. The BIOS originally proprietary to the IBM PC has been reverse engineered by some companies (such as Phoenix Technologies) looking to create compatible systems. The interface of that original system serves as a ''de facto'' standard. The BIOS in modern PCs initializes and tests the system hardware components (Power-on self-test), and loads a boot loader from a mass storage device which then i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VT100
The VT100 is a video terminal, introduced in August 1978 by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC). It was one of the first terminals to support ANSI escape codes for cursor control and other tasks, and added a number of extended codes for special features like controlling the status lights on the keyboard. This led to rapid uptake of the ANSI standard, which became the de facto standard for hardware video terminals and later terminal emulators. The VT100 series, especially the VT102, was extremely successful in the market, and made DEC the leading terminal vendor at the time. The VT100 series was replaced by the VT200 series starting in 1983, which proved equally successful. Ultimately, over six million terminals in the VT series were sold, based largely on the success of the VT100. Description DEC's first video terminal was the VT05 (1970), succeeded by the VT50 (1974), and soon upgraded to the VT52 (1975). The VT52 featured a text display with 80 columns and 24 rows, bidirection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Terminal
A computer terminal is an electronic or electromechanical hardware device that can be used for entering data into, and transcribing data from, a computer or a computing system. The teletype was an example of an early-day hard-copy terminal and predated the use of a computer screen by decades. Early terminals were inexpensive devices but very slow compared to punched cards or paper tape for input, yet as the technology improved and video displays were introduced, terminals pushed these older forms of interaction from the industry. A related development was time-sharing systems, which evolved in parallel and made up for any inefficiencies in the user's typing ability with the ability to support multiple users on the same machine, each at their own terminal or terminals. The function of a terminal is typically confined to transcription and input of data; a device with significant local, programmable data-processing capability may be called a "smart terminal" or fat client. A ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commodore 128
The Commodore 128, also known as the C128, C-128, C= 128,The "C=" represents the graphical part of the logo. is the last 8-bit home computer that was commercially released by Commodore Business Machines (CBM). Introduced in January 1985 at the CES in Las Vegas, it appeared three years after its predecessor, the bestselling computer in the 80s Commodore 64. The C128 is a significantly expanded successor to the C64, with nearly full compatibility. The newer machine has 128 KB of RAM in two 64 KB banks, and an 80-column color video output. It has a redesigned case and keyboard. Also included is a Zilog Z80 CPU which allows the C128 to run CP/M, as an alternative to the usual Commodore BASIC environment. The presence of the Z80 and the huge CP/M software library it brings, coupled with the C64's software library, gave the C128 one of the broadest ranges of available software among its competitors. The primary hardware designer of the C128 was Bil Herd, who had worked ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xerox 820
The Xerox 820 Information Processor is an 8-bit desktop computer sold by Xerox in the early 1980s. The computer runs under the CP/M operating system and uses floppy disk drives for mass storage. The microprocessor board is a licensed variant of the Big Board computer. 820 Xerox introduced the 820 in June 1981 for $2,995 with two -inch single-density disk drives with 81K of capacity per diskette, or $3,795 with two 8-inch drives with 241K capacity. To beat the IBM PC to market Xerox created little of the computer's design; it is based on the Ferguson Big Board computer kit and other off-the-shelf components, including a Zilog Z80 processor clocked at 2.5 MHz, and 64 KB of RAM. Xerox chose CP/M as its operating system because of the large software library—The 820 is compatible with all Big Board software—and sold a customized version of WordStar for $495, although by 1982 the company offered the standard version for the same price. By 1984, surplus 820 mainboards wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VT180
The VT180 is a personal computer produced by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) of Maynard, Massachusetts, USA. Introduced in early 1982, the CP/M-based VT180 was DEC's entry-level microcomputer. "VT180" is the unofficial name for the combination of the VT100 computer terminal and VT18X option. The VT18X includes a 2 MHz Zilog Z80 microprocessor and 64K RAM on two circuit boards that fit inside the terminal, and two external 5.25-inch floppy disk drives with room for two more in an external enclosure. The VT180 was codenamed "Robin". Digital later released a full-fledged personal computer known as the Rainbow 100 The Rainbow 100 is a microcomputer introduced by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in 1982. This desktop unit had a monitor similar to the VT220 and a dual-CPU box with both Zilog Z80 and Intel 8088 CPUs. The Rainbow 100 was a triple-use mac ... as the successor to Robin. When Digital ended the VT100 family, it also discontinued the VT180. No direct repl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
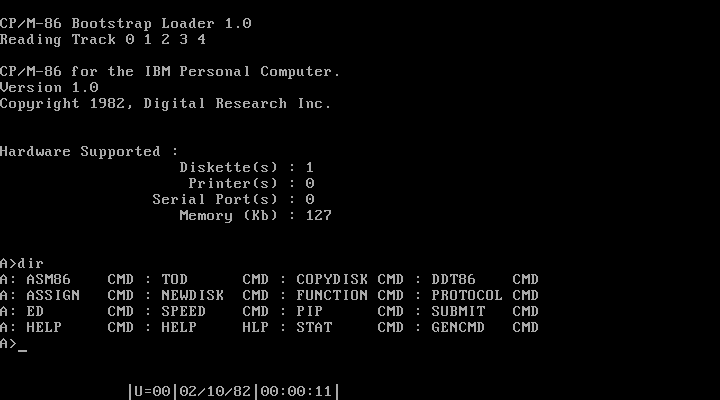
CP/M-86
CP/M-86 was a version of the CP/M operating system that Digital Research (DR) made for the Intel 8086 and Intel 8088. The system commands are the same as in CP/M-80. Executable files used the relocatable .CMD file format. Digital Research also produced a multi-user multitasking operating system compatible with CP/M-86, MP/M-86, which later evolved into Concurrent CP/M-86. When an emulator was added to provide PC DOS compatibility, the system was renamed Concurrent DOS, which later became Multiuser DOS, of which REAL/32 is the latest incarnation. The FlexOS, DOS Plus, and DR DOS families of operating systems started as derivations of Concurrent DOS as well. History Digital Research's CP/M-86 was originally announced to be released in November 1979, but was delayed repeatedly. When IBM contacted other companies to obtain components for the IBM PC, the as-yet unreleased CP/M-86 was its first choice for an operating system because CP/M had the most applications at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM PC
The IBM Personal Computer (model 5150, commonly known as the IBM PC) is the first microcomputer released in the IBM PC model line and the basis for the IBM PC compatible de facto standard. Released on August 12, 1981, it was created by a team of engineers and designers directed by Don Estridge in Boca Raton, Florida. The machine was based on open architecture and third-party peripherals. Over time, expansion cards and software technology increased to support it. The PC had a substantial influence on the personal computer market. The specifications of the IBM PC became one of the most popular computer design standards in the world. The only significant competition it faced from a non-compatible platform throughout the 1980s was from the Apple Macintosh product line. The majority of modern personal computers are distant descendants of the IBM PC. History Prior to the 1980s, IBM had largely been known as a provider of business computer systems. As the 1980s opened, their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorcim
Sorcim was an early start-up company in Silicon Valley, founded in June 1980 by Richard Frank, Paul McQuesten, Martin Herbach, Anil Lakhwara, and Steve Jasik - all former Control Data Corporation employees working in the Language Group in Sunnyvale, CA. Jasik left company early on, to develop the MacNosy product for the Macintosh. Sorcim was best known for SuperCalc, a spreadsheet the company developed for the Osborne Computer Corporation portable computer. The company made many other products, including SuperWriter and SuperProject before its acquisition by Computer Associates in 1985. Although the company continued as a largely autonomous division of CA, it never again achieved prominence after the acquisition. The company was named "Sorcim" after Richard Frank saw a reflection of the word “micros” in an airplane window. Early history The company was founded to expand the microcomputer products from Digicom, a company formed by Richard in 1978. Paul joined in 1979. The Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compiler Systems (company)
Gordon Edwin Eubanks, Jr. (born November 7, 1946) is an American microcomputer industry pioneer who worked with Gary Kildall in the early days of Digital Research (DRI). Eubanks attended Oklahoma State University, where he was involved as a member of Pi Kappa Alpha fraternity. Scott Kildall was his graduate thesis advisor at the Naval Postgraduate School in Monterey, California. Eubank's 1976 master's thesis was a BASIC language compiler called BASIC-E designed for Kildall's new CP/M operating system. Over the next year and a half, Eubanks wrote the popular CBASIC compiler for IMSAI while he was still a naval officer. Friends of Eubanks say he called it "CBASIC" because he wrote it while serving on a submarine (at ''sea''). Other people say the name CBASIC referred to "commercial" basic, because it incorporated BCD mathematics which eliminated MBASIC's rounding errors that were sometimes troublesome for accounting. In 1981, after Microsoft moved from programming language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational technology corporation producing computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washington, United States. Its best-known software products are the Windows line of operating systems, the Microsoft Office suite, and the Internet Explorer and Edge web browsers. Its flagship hardware products are the Xbox video game consoles and the Microsoft Surface lineup of touchscreen personal computers. Microsoft ranked No. 21 in the 2020 Fortune 500 rankings of the largest United States corporations by total revenue; it was the world's largest software maker by revenue as of 2019. It is one of the Big Five American information technology companies, alongside Alphabet, Amazon, Apple, and Meta. Microsoft was founded by Bill Gates and Paul Allen on April 4, 1975, to develop and sell BASIC interpreters for the Altair 8800. It rose to do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |