|
Orteronel
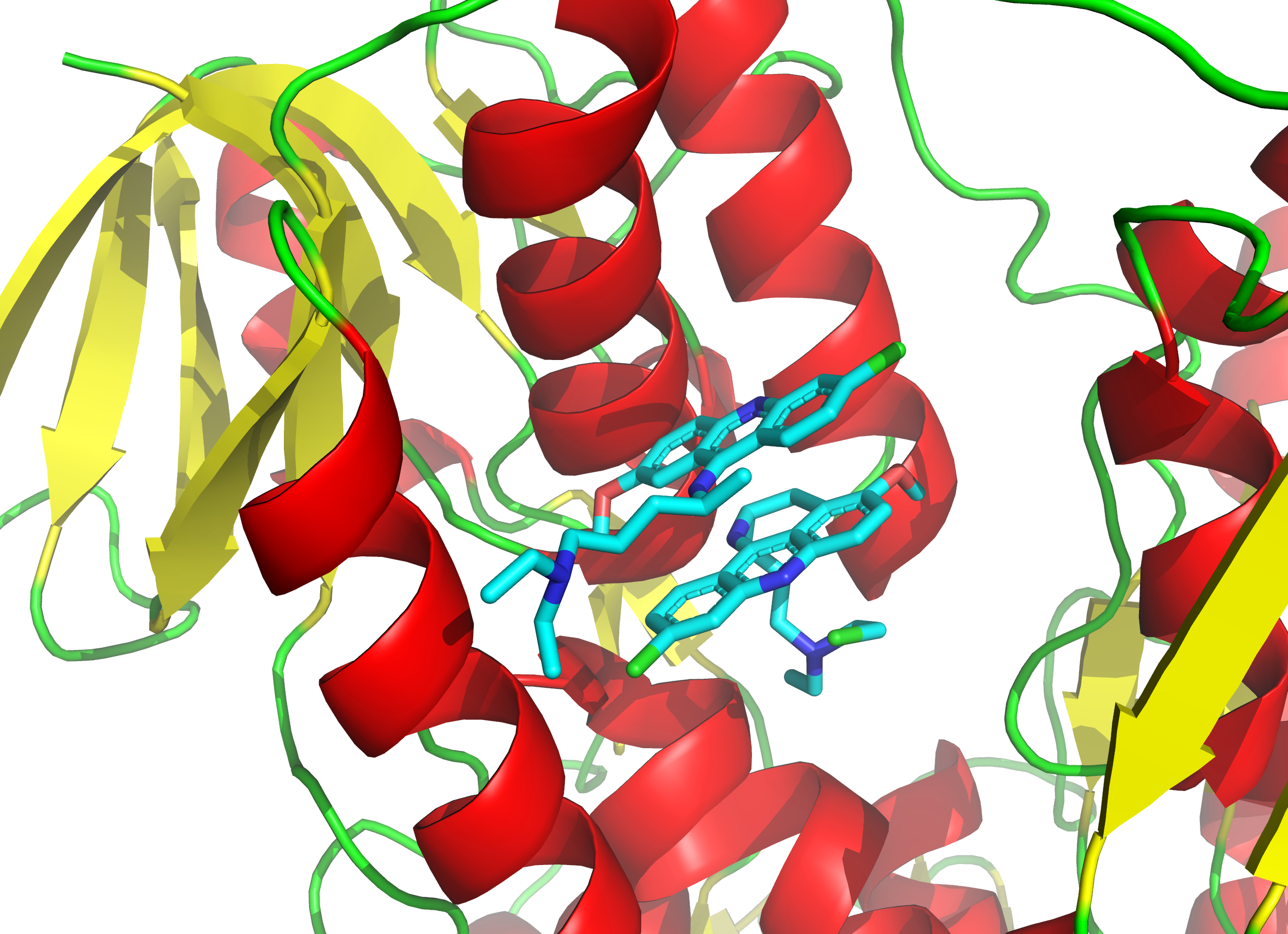
Orteronel (TAK-700) is a nonsteroidal CYP17A1 inhibitor that was being developed for the treatment of cancer by Takeda Pharmaceutical Company in conjunction with Millennium Pharmaceuticals. It completed two phase III clinical trials for metastatic, hormone-refractory prostate cancer but failed to extend overall survival rates, and development was voluntarily terminated as a result. Orteronel is an androgen biosynthesis inhibitor. It selectively inhibits the enzyme CYP17A1 which is expressed in testicular, adrenal, and prostatic tumor tissues. CYP17 catalyzes two sequential reactions: (a) the conversion of pregnenolone and progesterone to their 17α-hydroxy derivatives by its 17α-hydroxylase activity, and (b) the subsequent formation of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) and androstenedione, respectively, by its 17,20-lyase activity. DHEA and androstenedione are androgens and precursors of testosterone. Inhibition of CYP17 activity thus decreases circulating levels of testosterone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonsteroidal
A nonsteroidal compound is a drug that is not a steroid nor a steroid derivative. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are distinguished from corticosteroids as a class of anti-inflammatory agents. List of nonsteroidal steroid receptor modulators Examples include the following: * Estrogens: benzestrol, bifluranol, estrobin (DBE), diethylstilbestrol (stilbestrol), dienestrol, erteberel, fosfestrol, hexestrol (dihydroxystilbestrol), methallenestril, methestrol, methestrol dipropionate, paroxypropione, prinaberel, and triphenylethylene, as well as many xenoestrogens * : acolbifene, afimoxifene, arzoxifene, bazedoxifene, broparestrol, chlorotrianisene, clomifene, clomifenoxide, cyclofenil, droloxifene, enclomifene, endoxifen, ethamoxytriphetol, fispemifene, idoxifene, lasofoxifene, levormeloxifene, miproxifene, nafoxidine, nitromifene, ormeloxifene, ospemifene, panomifene, pipendoxifene, raloxifene, tamoxifen, toremifene, trioxifene, zindoxifene, zuclomifene * An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYP17A1 Inhibitor
A CYP17A1 inhibitor is a type of drug which enzyme inhibitor, inhibits the enzyme CYP17A1. It may inhibit both of the functions of the enzyme, 17α-hydroxylase and 17,20-lyase, or may be selective for inhibition of one of these two functions (generally 17,20-lyase). These drugs prevent the conversion of pregnane steroids into androgens like testosterone and therefore are androgen biosynthesis inhibitors and functional antiandrogens. Examples of CYP17A1 inhibitors include the older drug ketoconazole and the newer drugs abiraterone acetate, orteronel, galeterone, and seviteronel. The CYP17A1 inhibitors that have been marketed, like abiraterone acetate, are used mainly in the treatment of prostate cancer. CYP17A1 inhibitors that are not selective for inhibition of 17,20-lyase must be combined with a glucocorticoid such as prednisone in order to avoid adrenal insufficiency and mineralocorticoid excess caused by prevention of cortisol production. See also * Steroidogenic enzyme * Steroid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYP17A1 Inhibitors
A CYP17A1 inhibitor is a type of drug which inhibits the enzyme CYP17A1. It may inhibit both of the functions of the enzyme, 17α-hydroxylase and 17,20-lyase, or may be selective for inhibition of one of these two functions (generally 17,20-lyase). These drugs prevent the conversion of pregnane steroids into androgens like testosterone and therefore are androgen biosynthesis inhibitors and functional antiandrogens. Examples of CYP17A1 inhibitors include the older drug ketoconazole and the newer drugs abiraterone acetate, orteronel, galeterone, and seviteronel. The CYP17A1 inhibitors that have been marketed, like abiraterone acetate, are used mainly in the treatment of prostate cancer. CYP17A1 inhibitors that are not selective for inhibition of 17,20-lyase must be combined with a glucocorticoid such as prednisone in order to avoid adrenal insufficiency and mineralocorticoid excess caused by prevention of cortisol production. See also * Steroidogenic enzyme * Steroidogenesis inhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naphthalenes
Naphthalene is an organic compound with formula . It is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, and is a white crystalline solid with a characteristic odor that is detectable at concentrations as low as 0.08 ppm by mass. As an aromatic hydrocarbon, naphthalene's structure consists of a fused pair of benzene rings. It is best known as the main ingredient of traditional mothballs. History In the early 1820s, two separate reports described a white solid with a pungent odor derived from the distillation of coal tar. In 1821, John Kidd cited these two disclosures and then described many of this substance's properties and the means of its production. He proposed the name ''naphthaline'', as it had been derived from a kind of naphtha (a broad term encompassing any volatile, flammable liquid hydrocarbon mixture, including coal tar). Naphthalene's chemical formula was determined by Michael Faraday in 1826. The structure of two fused benzene rings was proposed by Emil Erlenmeye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Inhibitors
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life, in which substrate molecules are converted into products. An enzyme facilitates a specific chemical reaction by binding the substrate to its active site, a specialized area on the enzyme that accelerates the most difficult step of the reaction. An enzyme inhibitor stops ("inhibits") this process, either by binding to the enzyme's active site (thus preventing the substrate itself from binding) or by binding to another site on the enzyme such that the enzyme's catalysis of the reaction is blocked. Enzyme inhibitors may bind reversibly or irreversibly. Irreversible inhibitors form a chemical bond with the enzyme such that the enzyme is inhibited until the chemical bond is broken. By contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and may spontaneously leave the enzyme, allowing the enzyme to resume its function. Reve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abandoned Drugs
Abandon, abandoned, or abandonment may refer to: Common uses * Abandonment (emotional), a subjective emotional state in which people feel undesired, left behind, insecure, or discarded * Abandonment (legal), a legal term regarding property ** Child abandonment, the extralegal abandonment of children ** Lost, mislaid, and abandoned property, legal status of property after abandonment and rediscovery * Abandonment (mysticism) Art, entertainment, and media Film * ''Abandon'' (film), a 2002 film starring Katie Holmes * ''Abandoned'' (1949 film), starring Dennis O'Keefe * ''Abandoned'' (1955 film), the English language title of the Italian war film ''Gli Sbandati'' * ''Abandoned'' (2001 film), a Hungarian film * ''Abandoned'' (2010 film), starring Brittany Murphy * ''Abandoned'' (2015 film), a television movie about the shipwreck of the ''Rose-Noëlle'' in 1989 * ''Abandoned'' (2022 film), starring Emma Roberts * ''The Abandoned'' (1945 film), a 1945 Mexican film * ''The Aban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testosterone
Testosterone is the primary sex hormone and anabolic steroid in males. In humans, testosterone plays a key role in the development of Male reproductive system, male reproductive tissues such as testes and prostate, as well as promoting secondary sexual characteristics such as increased muscle and bone mass, and the growth of androgenic hair, body hair. In addition, testosterone in both sexes is involved in health and well-being, including moods, behaviour, and in the prevention of osteoporosis. Insufficient levels of testosterone in men may lead to abnormalities including frailty and bone loss. Testosterone is a steroid from the androstane class containing a ketone and a hydroxyl group at positions three and seventeen respectively. It is Biosynthesis, biosynthesized in several steps from cholesterol and is converted in the liver to inactive metabolites. It exerts its action through binding to and activation of the androgen receptor. In humans and most other vertebrates, testost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Androstenedione
Androstenedione, or 4-androstenedione (abbreviated as A4 or Δ4-dione), also known as androst-4-ene-3,17-dione, is an endogenous weak androgen steroid hormone and intermediate in the biosynthesis of estrone and of testosterone from dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). It is closely related to androstenediol (androst-5-ene-3β,17β-diol). Biological function Androstenedione is a precursor of testosterone and other androgens, as well as of estrogens like estrone, in the body. In addition to functioning as an endogenous prohormone, androstenedione also has weak androgenic activity in its own right. Androstenedione has been found to possess some estrogenic activity, similarly to other DHEA metabolites. However, in contrast to androstenediol, its affinity for the estrogen receptors is very low, with less than 0.01% of the affinity of estradiol for both the ERα and ERβ. Adrenarche In children aged 6 to 8 years old, there is a rise in androstenedione secretion along with DHEA during adr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dehydroepiandrosterone
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), also known as androstenolone, is an endogenous steroid hormone precursor. It is one of the most abundant circulating steroids in humans. DHEA is produced in the adrenal glands, the gonads, and the brain. It functions as a metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of the androgen and estrogen sex steroids both in the gonads and in various other tissues. However, DHEA also has a variety of potential biological effects in its own right, binding to an array of nuclear and cell surface receptors, and acting as a neurosteroid and modulator of neurotrophic factor receptors. In the United States, DHEA is sold as an over-the-counter supplement, and medication called prasterone. Biological function As an androgen DHEA and other adrenal androgens such as androstenedione, although relatively weak androgens, are responsible for the androgenic effects of adrenarche, such as early pubic and axillary hair growth, adult-type body odor, increased oiliness of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Inhibitor
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life, in which substrate molecules are converted into products. An enzyme facilitates a specific chemical reaction by binding the substrate to its active site, a specialized area on the enzyme that accelerates the most difficult step of the reaction. An enzyme inhibitor stops ("inhibits") this process, either by binding to the enzyme's active site (thus preventing the substrate itself from binding) or by binding to another site on the enzyme such that the enzyme's catalysis of the reaction is blocked. Enzyme inhibitors may bind reversibly or irreversibly. Irreversible inhibitors form a chemical bond with the enzyme such that the enzyme is inhibited until the chemical bond is broken. By contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and may spontaneously leave the enzyme, allowing the enzyme to resume its function. Reve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYP17A1
Cytochrome P450 17A1 (steroid 17α-monooxygenase, 17α-hydroxylase, 17-alpha-hydroxylase, 17,20-lyase, 17,20-desmolase) is an enzyme of the hydroxylase type that in humans is encoded by the ''CYP17A1'' gene on chromosome 10. It is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues and cell types, including the zona reticularis and zona fasciculata of the adrenal cortex as well as gonadal tissues. It has both 17α-hydroxylase and 17,20-lyase activities, and is a key enzyme in the steroidogenic pathway that produces progestins, mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, androgens, and estrogens. More specifically, the enzyme acts upon pregnenolone and progesterone to add a hydroxyl (-OH) group at carbon 17 position (C17) of the steroid D ring (the 17α-hydroxylase activity, ), or acts upon 17α-hydroxyprogesterone and 17α-hydroxypregnenolone to split the side-chain off the steroid nucleus (the 17,20-lyase activity, ). Structure Gene The ''CYP17A1'' gene resides on chromosome 10 at the band 10q24.3 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |