|
Orotate
Orotic acid is a pyrimidinedione and a carboxylic acid. Historically, it was believed to be part of the vitamin B complex and was called vitamin B13, but it is now known that it is not a vitamin. The compound is synthesized in the body via a mitochondrial enzyme, dihydroorotate dehydrogenase or a cytoplasmic enzyme of pyrimidine synthesis pathway. It is sometimes used as a mineral carrier in some dietary supplements (to increase their bioavailability), most commonly for lithium orotate. Synthesis Dihydroorotate is synthesized to orotic acid by the enzyme dihydroorotate dehydrogenase, where it later combines with phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) to form orotidine-5'-monophosphate (OMP). A distinguishing characteristic of pyrimidine synthesis is that the pyrimidine ring is fully synthesized before being attached to the ribose sugar, whereas purine synthesis happens by building the base directly on the sugar. Chemistry Orotic acid is a Bronsted acid and the anion (o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Orotate
Lithium orotate (C5H3LiN2O4) is a salt of orotic acid and lithium. It is available as the monohydrate, LiC5H3N2O4·H2O. In this compound, lithium is non-covalently bound to an orotate ion, rather than to a carbonate or other ion, and like other salts, dissociates in solution to produce free lithium ions. It is marketed as a dietary supplement, though it has been researched minimally between 1973–1986 to treat certain medical conditions, such as alcoholism and Alzheimer's disease. While lithium orotate is capable of providing lithium to the body, like lithium carbonate and other lithium salts, there are no systematic reviews supporting the efficacy of lithium orotate and it is not approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of any medical condition. Effectiveness In 1973, Hans Nieper reported that lithium orotate contained 3.83 mg of elemental lithium per 100 mg and lithium carbonate contained 18.8 mg of elemental lithium per 100&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase
Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''DHODH'' gene on chromosome 16. The protein encoded by this gene catalyzes the fourth enzymatic step, the ubiquinone-mediated oxidation of dihydroorotate to orotate, in '' de novo'' pyrimidine biosynthesis. This protein is a mitochondrial protein located on the outer surface of the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM). Inhibitors of this enzyme are used to treat autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. Structure DHODH can vary in cofactor content, oligomeric state, subcellular localization, and membrane association. An overall sequence alignment of these DHODH variants presents two classes of DHODHs: the cytosolic Class 1 and the membrane-bound Class 2. In Class 1 DHODH, a basic cysteine residue catalyzes the oxidation reaction, whereas in Class 2, the serine serves this catalytic function. Structurally, Class 1 DHODHs can also be divided into two subclasses, one of which forms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrimidine Synthesis
Pyrimidine biosynthesis occurs both in the body and through organic synthesis. ''De novo'' biosynthesis of pyrimidine ''De Novo'' biosynthesis of a pyrimidine is catalyzed by three gene products CAD, DHODH and UMPS. The first three enzymes of the process are all coded by the same gene in CAD which consists of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II, aspartate carbamoyltransferase and dihydroorotase. Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) unlike CAD and UMPS is a mono-functional enzyme and is localized in the mitochondria. UMPS is a bifunctional enzyme consisting of orotate phosphoribosyltransferase (OPRT) and orotidine monophosphate decarboxylase (OMPDC). Both, CAD and UMPS are localized around the mitochondria, in the cytosol. In Fungi, a similar protein exists but lacks the dihydroorotase function: another protein catalyzes the second step. In other organisms (Bacteria, Archaea and the other Eukaryota), the first three steps are done by three different enzymes. Pyrimidine ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnesium Orotate
Magnesium orotate, the magnesium salt of orotic acid, is a mineral supplement. It can be used in treating extracellular magnesium deficiency, as well as in mitigating magnesium depletion that inhibits the binding of adenosine triphosphate Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms ... via orotic acid, which provides binding sites. References Magnesium compounds {{gastrointestinal-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orotidine 5'-monophosphate
Orotidine 5'-monophosphate (OMP), also known as orotidylic acid, is a pyrimidine nucleotide which is the last intermediate in the biosynthesis of uridine monophosphate. OMP is formed from orotate and phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate by the enzyme orotate phosphoribosyltransferase In humans, the enzyme UMP synthase converts OMP into uridine 5'- monophosphate. If UMP synthase is defective, orotic aciduria Orotic aciduria (AKA hereditary orotic aciduria) is a disease caused by an enzyme deficiency resulting in a decreased ability to synthesize pyrimidines. It was the first described enzyme deficiency of the ''de novo'' pyrimidine synthesis pathway. ... can result. Nucleotides Pyrimidinediones {{biochem-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoribosyl Pyrophosphate
Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) is a pentose phosphate. It is a biochemical intermediate in the formation of purine nucleotides via inosine-5-monophosphate, as well as in pyrimidine nucleotide formation. Hence it is a building block for DNA and RNA. The vitamins thiamine and cobalamin, and the amino acid tryptophan also contain fragments derived from PRPP. It is formed from ribose 5-phosphate (R5P) by the enzyme ribose-phosphate diphosphokinase: : It plays a role in transferring phospho-ribose groups in several reactions, some of which are salvage pathways: In '' de novo'' generation of purines, the enzyme amidophosphoribosyltransferase acts upon PRPP to create phosphoribosylamine. The histidine biosynthesis pathway involves the reaction between PRPP and ATP, which activates the latter to ring cleavage. Carbon atoms from ribose in PRPP form the linear chain and part of the imidazole ring in histidine. The same is true for the biosynthesis of tryptophan, with the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orotic Aciduria
Orotic aciduria (AKA hereditary orotic aciduria) is a disease caused by an enzyme deficiency resulting in a decreased ability to synthesize pyrimidines. It was the first described enzyme deficiency of the ''de novo'' pyrimidine synthesis pathway. Orotic aciduria is characterized by excessive excretion of orotic acid in urine because of the inability to convert orotic acid to UMP. It causes megaloblastic anemia and may be associated with mental and physical developmental delays. Signs and symptoms Patients typically present with excessive orotic acid in the urine, failure to thrive, developmental delay, and megaloblastic anemia which cannot be cured by administration of vitamin B12 or folic acid. Cause and genetics This autosomal recessive disorder is caused by a deficiency in the enzyme UMPS, a bifunctional protein that includes the enzyme activities of OPRT and ODC. In one study of three patients, UMPS activity ranged from 2-7% of normal levels. Two types of orotic acidur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
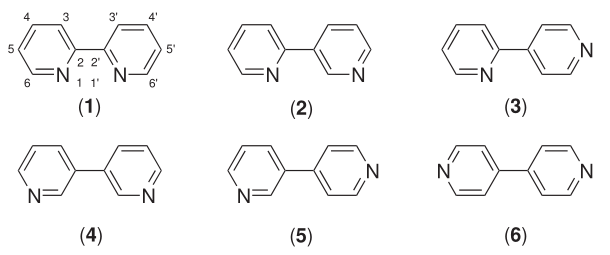
Bipyridine
Bipyridines also known as bipyridyls, dipyridyls, and dipyridines, are a family of chemical compounds with the formula (C5H4N)2, consisting of two pyridyl (C5H4N) rings. Pyridine is an aromatic nitrogen-containing heterocycle. Bipyridines are of significance in pesticides. Six isomers of bipyridine exist, but two are prominent: 2,2′-bipyridine is a popular ligand. 4,4'-Bipyridine is a precursor to the commercial herbicide paraquat. The bipyridines are all colourless solids, which are soluble in organic solvents and slightly soluble in water. 2,2′-Bipyridine 2,2′-Bipyridine (2,2′-bipy) is a chelating ligand that forms complexes with most transition metal ions that are of broad academic interest. Many of these complexes have distinctive optical properties, and some are of interest for analysis. Its complexes are used in studies of electron and energy transfer, supramolecular and materials chemistry, and catalysis. 2,2′-Bipyridine is used in the manufacture of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency
Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency also known as OTC deficiency is the most common urea cycle disorder in humans. Ornithine transcarbamylase, the defective enzyme in this disorder is the final enzyme in the proximal portion of the urea cycle, responsible for converting carbamoyl phosphate and ornithine into citrulline. OTC deficiency is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner, meaning males are more commonly affected than females. In severely affected individuals, ammonia concentrations increase rapidly causing ataxia, lethargy and death without rapid intervention. OTC deficiency is diagnosed using a combination of clinical findings and biochemical testing, while confirmation is often done using molecular genetics techniques. Once an individual has been diagnosed, the treatment goal is to avoid precipitating episodes that can cause an increased ammonia concentration. The most common treatment combines a low protein diet with nitrogen scavenging agents. Liver transplant is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle
The citric acid cycle (CAC)—also known as the Krebs cycle or the TCA cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle)—is a series of chemical reactions to release stored energy through the oxidation of acetyl-CoA derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. The Krebs cycle is used by organisms that respire (as opposed to organisms that ferment) to generate energy, either by anaerobic respiration or aerobic respiration. In addition, the cycle provides precursors of certain amino acids, as well as the reducing agent NADH, that are used in numerous other reactions. Its central importance to many biochemical pathways suggests that it was one of the earliest components of metabolism and may have originated abiogenically. Even though it is branded as a 'cycle', it is not necessary for metabolites to follow only one specific route; at least three alternative segments of the citric acid cycle have been recognized. The name of this metabolic pathway is derived from the citric acid (a tricar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urea Cycle Disorder
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid. Urea serves an important role in the metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic ( is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it is neither acidic nor alkaline. The body uses it in many processes, most notably nitrogen excretion. The liver forms it by combining two ammonia molecules () with a carbon dioxide () molecule in the urea cycle. Urea is widely used in fertilizers as a source of nitrogen (N) and is an important raw material for the chemical industry. In 1828 Friedrich Wöhler discovered that urea can be produced from inorganic starting materials, which was an important conceptual mileston ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |