|
Orosirian
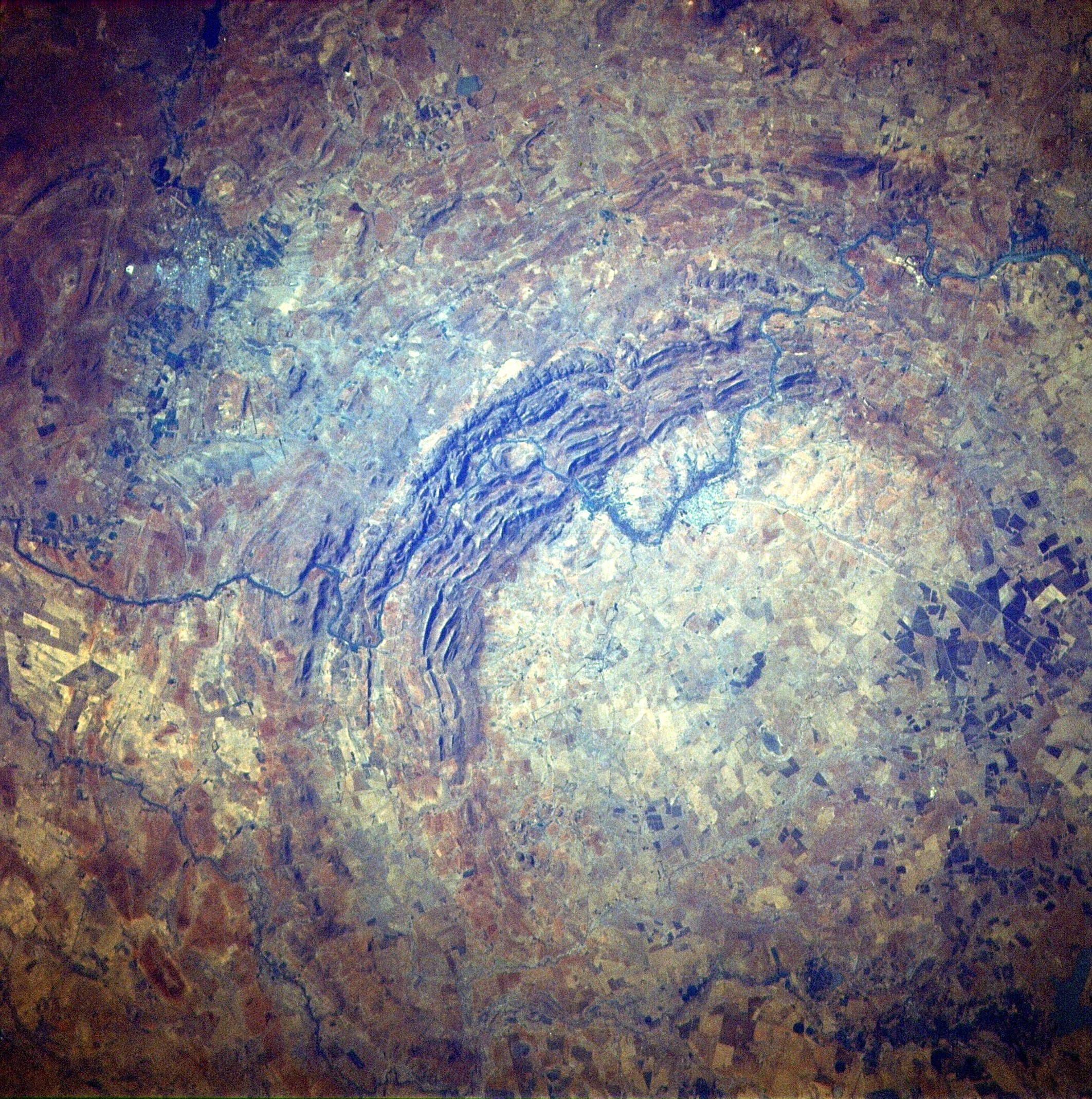
The Orosirian Period (; grc, ὀροσειρά, translit=oroseirá, meaning "mountain range") is the third geologic period in the Paleoproterozoic era (geology), Era and lasted from annum, Mya to Mya (million years ago). Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined Absolute dating, chronometrically. The later half of the period was an episode of intensive orogeny on virtually all continents. Two of the largest known impact events on Earth occurred during the Orosirian. Early in the period, 2023 Mya, a large asteroid collision created the Vredefort impact structure. The event that created the Sudbury Basin structure occurred near the end of the period, 1850 Mya. For the time period from about 2060 to 1780 Mya, an alternative period based on stratigraphy rather than chronometry, named the Columbian, was suggested in the geological timescale review 2012 edited by Gradstein et al., but , this has not yet been officially adopted by the IUGS. Paleogeography T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geological Periods
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardized international units of geologic time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisely define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Period
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardized international units of geologic time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisely define gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Era (geology)
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardized international units of geologic time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisely define g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orosirian Continents
The Orosirian Period (; grc, ὀροσειρά, translit=oroseirá, meaning "mountain range") is the third geologic period in the Paleoproterozoic Era and lasted from Mya to Mya (million years ago). Instead of being based on stratigraphy, these dates are defined chronometrically. The later half of the period was an episode of intensive orogeny on virtually all continents. Two of the largest known impact events on Earth occurred during the Orosirian. Early in the period, 2023 Mya, a large asteroid collision created the Vredefort impact structure. The event that created the Sudbury Basin structure occurred near the end of the period, 1850 Mya. For the time period from about 2060 to 1780 Mya, an alternative period based on stratigraphy rather than chronometry, named the Columbian, was suggested in the geological timescale review 2012 edited by Gradstein et al., but , this has not yet been officially adopted by the IUGS. Paleogeography The supercontinent In geology, a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continent, continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", which leaves room for interpretation and is easier to apply to Precambrian times. To separate supercontinents from other groupings, a limit has been proposed in which a continent must include at least about 75% of the continental crust then in existence in order to qualify as a supercontinent. Supercontinents have assembled and dispersed multiple times in the geologic past (see table). According to modern definitions, a supercontinent does not exist today; the closest in existence to a supercontinent is the current Afro-Eurasian landmass, which covers approx. 57% of Earth's total land area. The last time the continental landmasses were near to one another was 336 to 175 million years ago as the supercontinent, Pangaea. The positions of con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia (supercontinent)
Columbia, also known as Nuna or Hudsonland, was one of Earth's ancient supercontinents. It was first proposed by John J.W. Rogers and M. Santosh in 2002 and is thought to have existed approximately , in the Paleoproterozoic Era. The assembly of the supercontinent was likely completed during global-scale collisional events from 2100 to 1800 million years ago. Columbia consisted of proto-cratons that made up the cores of the continents of Laurentia, Baltica, Ukrainian Shield, Amazonian Shield, Australia, and possibly Siberia, North China, and Kalaharia as well. The evidence of Columbia's existence is provided by geological and paleomagnetic data.; Size and location Columbia is estimated to have been approximately from north to south at its broadest part. The eastern coast of India was attached to western North America, with southern Australia against western Canada. In this era most of South America was rotated such that the western edge of modern-day Brazil lined up wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUGS
The International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS) is an international non-governmental organization devoted to international cooperation in the field of geology. About The IUGS was founded in 1961 and is a Scientific Union member of the International Science Council (ISC), formerly the International Council for Science (ICSU), which it recognizes as the co-ordinating body for the international organization of science. Currently geologists from 121 countries (and regions) are represented in the IUGS. A broad range of scientific topics are covered by its commission, task groups, joint programmes and affiliated organizations. IUGS promotes and encourages the study of geological problems, especially those of worldwide significance, and supports and facilitates international and inter-disciplinary co-operation in the earth sciences. The Union's Secretariat is currently located at the Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences in Beijing, China. Activities IUGS is a joint partner with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudbury Basin
The Sudbury Basin (), also known as Sudbury Structure or the Sudbury Nickel Irruptive, is a major geological structure in Ontario, Canada. It is the third-largest known impact crater or astrobleme on Earth, as well as one of the oldest. The crater formed 1.849 billion years ago in the Paleoproterozoic era. The basin is located on the Canadian Shield in the city of Greater Sudbury, Ontario. The former municipalities of Rayside-Balfour, Valley East and Capreol lie within the Sudbury Basin, which is referred to locally as "The Valley". The urban core of the former city of Sudbury lies on the southern outskirts of the basin. An Ontario Historical Plaque was erected by the province to commemorate the discovery of the Sudbury Basin. Formation The Sudbury basin formed as a result of an impact into the Nuna supercontinent from a bolide approximately in diameter that occurred 1.849 billion years ago in the Paleoproterozoic era. Debris from the impact was scattered over an area of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere. Of the roughly one million known asteroids the greatest number are located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, approximately 2 to 4 AU from the Sun, in the main asteroid belt. Asteroids are generally classified to be of three types: C-type, M-type, and S-type. These were named after and are generally identified with carbonaceous, metallic, and silicaceous compositions, respectively. The size of asteroids varies greatly; the largest, Ceres, is almost across and qualifies as a dwarf planet. The total mass of all the asteroids combined is only 3% that of Earth's Moon. The majority of main belt asteroids follow slightly elliptical, stable orbits, revolving in the same direction as the Earth and taking from three to six years to comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Commission On Stratigraphy
The International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), sometimes referred to unofficially as the "International Stratigraphic Commission", is a daughter or major subcommittee grade scientific daughter organization that concerns itself with stratigraphy, stratigraphical, geology, geological, and chronology, geochronological matters on a global scale. It is the largest subordinate body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS). The ICS is essentially a permanent working committee, working subcommittee, which meets far more regularly than the quadrennial meetings scheduled by the IUGS, when it meets as a congress or committee, membership of the whole. Aims One of its main aims, a project begun in 1974, is to establish a multidisciplinary standard and global geologic time scale that will ease paleontology, paleontological and geobiology, geobiological comparisons region to region by benchmarks with stringent and rigorous strata criteria called Global Boundary Stratotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impact Event
An impact event is a collision between astronomical objects causing measurable effects. Impact events have physical consequences and have been found to regularly occur in planetary systems, though the most frequent involve asteroids, comets or meteoroids and have minimal effect. When large objects impact terrestrial planets such as the Earth, there can be significant physical and biospheric consequences, though atmospheres mitigate many surface impacts through atmospheric entry. Impact craters and Impact structure, structures are dominant landforms on many of the Solar System's solid objects and present the strongest empirical evidence for their frequency and scale. Impact events appear to have played a significant role in the Formation and evolution of the Solar System, evolution of the Solar System since its formation. Major impact events have significantly shaped History of the Earth, Earth's history, and have been implicated in the giant impact theory, formation of the Earth� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orogeny
Orogeny is a mountain building process. An orogeny is an event that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An ''orogenic belt'' or ''orogen'' develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain ranges. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation of existing continental crust and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism. Magma rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere ( crust and uppermost mantle). A synorogenic process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny. The word "orogeny" () comes from Ancient Greek (, , + , , ). Although it was used before him, the term was employed by the American geologist G. K. Gilbert in 1890 to describe the process of mountain-building as distinguished f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |