|
Orontes III
Orontes III ( Old Persian: ''*Arvanta-'') was King of Armenia. In his reign he struggled for control of the Kingdom of Sophene with king Antiochus II Theos until being defeated in 272 BC and was forced to pay a large tribute which included 300 talents of silver and 1,000 horses and mules. Orontes III was subsequently murdered in 260 BC, whether at the instigation of King Antiochus II is not recorded. His son, Sames, continued to rule in Sophene Sophene ( hy, Ծոփք, translit=Tsopkʻ, grc, Σωφηνή, translit=Sōphēnē or hy, Չորրորդ Հայք, lit=Fourth Armenia) was a province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, located in the south-west of the kingdom, and of the Ro .... Hovannisian, Richard G., ''The Armenian People from Ancient to Modern Times'', 2 vols. New York: St. Martin's Press, 1997 References Sources * * 4th-century BC kings of Armenia 3rd-century BC kings of Armenia Kings of Sophene Diadochi 4th-century BC rulers 260 BC deaths Ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Armenia (antiquity)
The Kingdom of Armenia, also the Kingdom of Greater Armenia, or simply Greater Armenia ( hy, Մեծ Հայք '; la, Armenia Maior), sometimes referred to as the Armenian Empire, was a monarchy in the Ancient Near East which existed from 331 BC to 428 AD. Its history is divided into the successive reigns of three royal dynasties: Orontid (331 BC–200 BC), Artaxiad (189 BC–12 AD) and Arsacid (52–428). The root of the kingdom lies in one of the satrapies of the Achaemenid Empire of Persia called Armenia (Satrapy of Armenia), which was formed from the territory of the Kingdom of Ararat (860 BC–590 BC) after it was conquered by the Median Empire in 590 BC. The satrapy became a kingdom in 321 BC during the reign of the Orontid dynasty after the conquest of Persia by Alexander the Great, which was then incorporated as one of the Hellenistic kingdoms of the Seleucid Empire. Under the Seleucid Empire (312–63 BC), the Armenian throne was divided in two—Armenia Maior and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
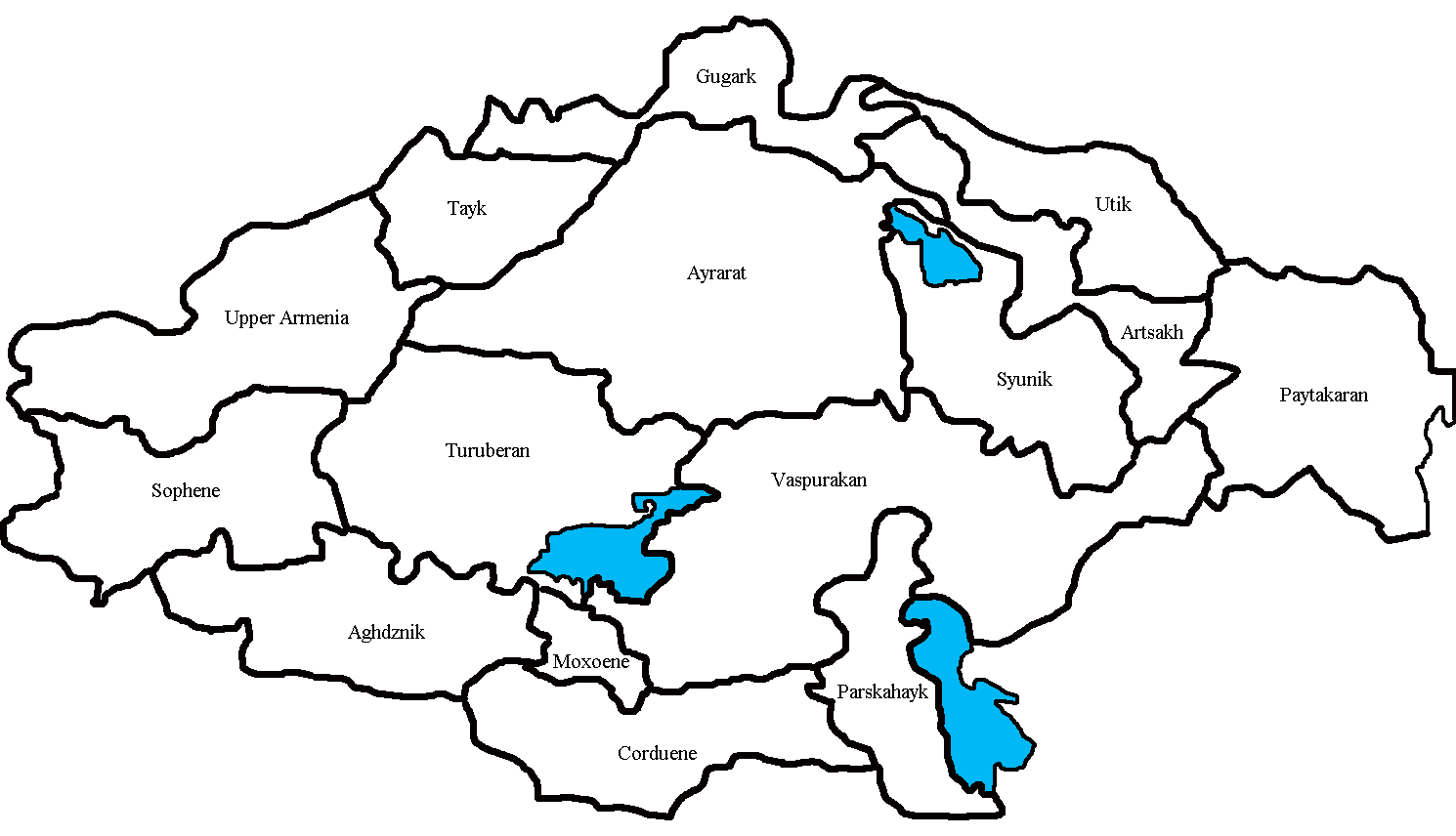
Sophene
Sophene ( hy, Ծոփք, translit=Tsopkʻ, grc, Σωφηνή, translit=Sōphēnē or hy, Չորրորդ Հայք, lit=Fourth Armenia) was a province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, located in the south-west of the kingdom, and of the Roman Empire. The region lies in what is now southeastern Turkey. The region that was to become Sophene was part of the kingdom of Ararat (Urartu) in the 8th-7th centuries BC. After unifying the region with his kingdom in the early 8th century BC, king Argishtis I of Urartu resettled many of its inhabitants in his newly built city of Erebuni (modern day Armenian capital Yerevan). Around 600 BC, Sophene became part of the newly emerged ancient Armenian Kingdom of the Orontids. This dynasty acted as satraps of Armenia first under the Median Empire, later under the Achaemenid Empire. After Alexander the Great's campaigns in 330s BC and the subsequent collapse of the Achaemenid Empire, Sophene remained part of the newly independent kingdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th-century BC Rulers
The 4th century (per the Julian calendar and Anno Domini/Common era) was the time period which lasted from 301 ( CCCI) through 400 ( CD). In the West, the early part of the century was shaped by Constantine the Great, who became the first Roman emperor to adopt Christianity. Gaining sole reign of the empire, he is also noted for re-establishing a single imperial capital, choosing the site of ancient Byzantium in 330 (over the current capitals, which had effectively been changed by Diocletian's reforms to Milan in the West, and Nicomedeia in the East) to build the city soon called Nova Roma (New Rome); it was later renamed Constantinople in his honor. The last emperor to control both the eastern and western halves of the empire was Theodosius I. As the century progressed after his death, it became increasingly apparent that the empire had changed in many ways since the time of Augustus. The two emperor system originally established by Diocletian in the previous century fell in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diadochi
The Diadochi (; singular: Diadochus; from grc-gre, Διάδοχοι, Diádochoi, Successors, ) were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BC. The Wars of the Diadochi mark the beginning of the Hellenistic period from the Mediterranean Sea to the Indus River Valley. The most notable Diadochi include Ptolemy, Antigonus, Cassander, and Seleucus as the last remaining at the end of the Wars of the Successors, ruling in Egypt, Asia-Minor, Macedon and Persia respectively, all forging dynasties lasting several centuries. Background Ancient role In ancient Greek, is a noun (substantive or adjective) formed from the verb, ''diadechesthai'', "succeed to," a compound of ''dia-'' and ''dechesthai'', "receive." The word-set descends straightforwardly from Indo-European *dek-, "receive", the substantive forms being from the o-grade, *dok-. Some important English reflexes are dogma, "a receiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kings Of Sophene
Kings or King's may refer to: *Monarchs: The sovereign heads of states and/or nations, with the male being kings *One of several works known as the "Book of Kings": **The Books of Kings part of the Bible, divided into two parts **The ''Shahnameh'', an 11th-century epic Persian poem **The Morgan Bible, a French medieval picture Bible **The Pararaton, a 16th-century Javanese history of southeast Asia *The plural of any king Business * Kings Family Restaurants, a chain of restaurants in Pennsylvania and Ohio *Kings Food Markets, a chain supermarket in northern New Jersey * King's Favourites, a brand of cigarettes *King's Variety Store, a chain of stores in the USA *King's (defunct discount store), a defunct chain of discount stores in the USA Education *King's College (other), various colleges * King's School (other), various schools * The King's Academy (other), various academies Electoral districts * King's (New Brunswick electoral district) (1867–1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3rd-century BC Kings Of Armenia
The 3rd century was the period from 201 ( CCI) to 300 ( CCC) Anno Domini (AD) or Common Era (CE) in the Julian calendar.. In this century, the Roman Empire saw a crisis, starting with the assassination of the Roman Emperor Severus Alexander in 235, plunging the empire into a period of economic troubles, barbarian incursions, political upheavals, civil wars, and the split of the Roman Empire through the Gallic Empire in the west and the Palmyrene Empire in the east, which all together threatened to destroy the Roman Empire in its entirety, but the reconquests of the seceded territories by Emperor Aurelian and the stabilization period under Emperor Diocletian due to the administrative strengthening of the empire caused an end to the crisis by 284. This crisis would also mark the beginning of Late Antiquity. In Persia, the Parthian Empire was succeeded by the Sassanid Empire in 224 after Ardashir I defeated and killed Artabanus V during the Battle of Hormozdgan. The Sassan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th-century BC Kings Of Armenia
The 4th century (per the Julian calendar and Anno Domini/Common era) was the time period which lasted from 301 ( CCCI) through 400 ( CD). In the West, the early part of the century was shaped by Constantine the Great, who became the first Roman emperor to adopt Christianity. Gaining sole reign of the empire, he is also noted for re-establishing a single imperial capital, choosing the site of ancient Byzantium in 330 (over the current capitals, which had effectively been changed by Diocletian's reforms to Milan in the West, and Nicomedeia in the East) to build the city soon called Nova Roma (New Rome); it was later renamed Constantinople in his honor. The last emperor to control both the eastern and western halves of the empire was Theodosius I. As the century progressed after his death, it became increasingly apparent that the empire had changed in many ways since the time of Augustus. The two emperor system originally established by Diocletian in the previous century fell in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard G
Richard is a male given name. It originates, via Old French, from Frankish language, Old Frankish and is a Compound (linguistics), compound of the words descending from Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic ''*rīk-'' 'ruler, leader, king' and ''*hardu-'' 'strong, brave, hardy', and it therefore means 'strong in rule'. Nicknames include "Richie", "Dick (nickname), Dick", "Dickon", "Dickie (name), Dickie", "Rich (given name), Rich", "Rick (given name), Rick", "Rico (name), Rico", "Ricky (given name), Ricky", and more. Richard is a common English, German and French male name. It's also used in many more languages, particularly Germanic, such as Norwegian, Danish, Swedish, Icelandic, and Dutch, as well as other languages including Irish, Scottish, Welsh and Finnish. Richard is cognate with variants of the name in other European languages, such as the Swedish "Rickard", the Catalan "Ricard" and the Italian "Riccardo", among others (see comprehensive variant list below). People ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talent (measurement)
The talent was a unit of weight that was introduced in Mesopotamia at the end of the 4th millennium BC, and was normalized at the end of the 3rd millennium during the Akkadian-Sumer phase, divided into 60 minas or 3,600 shekels. In classical antiquity, the talent ( la, talentum, from Ancient Greek: , ''talanton'' "scale, balance, sum") was the heaviest of common weight units for commercial transactions. An Attic weight talent was approximately John William Humphrey, John Peter Oleson, Andrew Neil Sherwood, ''Greek and Roman technology'', p. 487. (approximately the mass of water of an amphora), and a Babylonian talent was .Herodotus, Robin Waterfield and Carolyn Dewald, ''The Histories'' (1998), p. 593. Ancient Israel adopted the Babylonian weight talent, but later revised it.III. Measures of W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mithrenes
Mithrenes ( el, Mιθρένης or Mιθρίνης) was a Persian commander of the force that garrisoned the citadel of Sardis. According to Cyril Toumanoff, he was also a member of the Orontid dynasty, of Iranian origin. Waldemar Heckel, on the other hand, considers Mithrenes to be a Persian noble of unknown family background. After the battle of the Granicus Mithrenes surrendered voluntarily to Alexander the Great, and was treated by him with great distinction. Mithrenes was present in the Macedonian camp after the Battle of Issus, and Alexander ordered him to visit the captured family of Darius III and assure them that Darius was alive, before changing his mind and assigning the duty to Leonnatus instead. He fought for Alexander at Gaugamela, and ironically he was fighting against an army that included his father Orontes II. Afterwards, Alexander appointed him Satrap of Armenia. Mithrenes disappears from the historical record after this appointment, and his ultimate fate is unk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conquered or otherwise threatened to conquer. In case of alliances, lesser parties may pay tribute to more powerful parties as a sign of allegiance and often in order to finance projects that would benefit both parties. To be called "tribute" a recognition by the payer of political submission to the payee is normally required; the large sums, essentially protection money, paid by the later Roman and Byzantine Empires to barbarian peoples to prevent them attacking imperial territory, would not usually be termed "tribute" as the Empire accepted no inferior political position. Payments ''by'' a superior political entity to an inferior one, made for various purposes, are described by terms including " subsidy". The ancient Persian Achaemenid Empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus II Theos
Antiochus II Theos ( grc-gre, Ἀντίοχος Θεός, ; 286 – July 246 BC) was a Greek king of the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic Seleucid Empire who reigned from 261 to 246 BC. He succeeded his father Antiochus I Soter in the winter of 262–61 BC. He was the younger son of Antiochus I and princess Stratonice of Syria, Stratonice, the daughter of Demetrius I of Macedon, Demetrius Poliorcetes. Antiochus II was a forceful personality who in his lifetime largely succeeded to hold the sprawling Seleucid realm intact. However his fateful decision to repudiate his first wife Laodice I, Laodice and marry a Ptolemaic dynasty, Ptolemaic princess Berenice (Seleucid queen), Berenice as part of a peace treaty led to a succession struggle after his death that would shake the empire's foundations and cause large territorial losses. Early life Antiochus II was the younger son of Antiochus I Soter and his famous queen Stratonice of Syria, Stratonice. Antiochus was initially not expect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)