|
Oriel (scripting Language)
Oriel is a scripting language released with the ''Power Tools'' series of instructional books written by the LeBlond Group. Described in its documentation as a "graphics-based batch language", it was originally designed for Microsoft Windows 3.0 and released with the book ''Windows 3 Power Tools'' in 1991.COMPUTE! Issue 134 - http://www.atarimagazines.com/compute/issue134/143_Windows_3_Power_Tool.php However, versions of the language were also bundled with ''Windows 3.1 Power Tools'' in 1992 and ''Windows NT Power Tools'' in 1994. The suggested extension for an Oriel script file was ORL. Oriel was distributed with two executables: ORIEL.EXE, and MKRUNTIM.EXE. The former was the Oriel interpreter, which when invoked would prompt the user to choose a script file for execution. The latter gave the user the ability to create custom executables by bundling a script within a copy of the interpreter. In this way, an Oriel program could be distributed and run in the same way as any other W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Oriel For Windows Logo
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperative Programming
In computer science, imperative programming is a programming paradigm of software that uses statements that change a program's state. In much the same way that the imperative mood in natural languages expresses commands, an imperative program consists of commands for the computer to perform. Imperative programming focuses on describing ''how'' a program operates step by step, rather than on high-level descriptions of its expected results. The term is often used in contrast to declarative programming, which focuses on ''what'' the program should accomplish without specifying all the details of ''how'' the program should achieve the result. Imperative and procedural programming Procedural programming is a type of imperative programming in which the program is built from one or more procedures (also termed subroutines or functions). The terms are often used as synonyms, but the use of procedures has a dramatic effect on how imperative programs appear and how they are constructed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
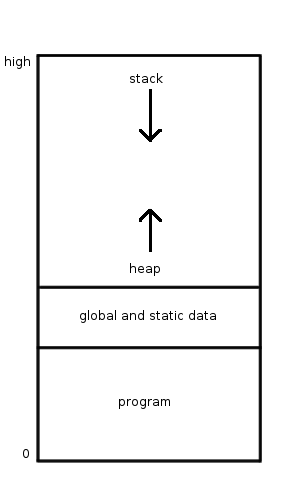
Procedural Programming
Procedural programming is a programming paradigm, derived from imperative programming, based on the concept of the '' procedure call''. Procedures (a type of routine or subroutine) simply contain a series of computational steps to be carried out. Any given procedure might be called at any point during a program's execution, including by other procedures or itself. The first major procedural programming languages appeared circa 1957–1964, including Fortran, ALGOL, COBOL, PL/I and BASIC. Pascal and C were published circa 1970–1972. Computer processors provide hardware support for procedural programming through a stack register and instructions for calling procedures and returning from them. Hardware support for other types of programming is possible, but no attempt was commercially successful (for example Lisp machines or Java processors). Procedures and modularity Modularity is generally desirable, especially in large, complicated programs. Inputs are usu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The LeBlond Group, Inc
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Windows
Windows is a group of several Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for servers, and Windows IoT for embedded systems. Defunct Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile, and Windows Phone. The first version of Windows was released on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Windows is the most popular desktop operating system in the world, with Usage share of operating systems, 75% market share , according to StatCounter. However, Windows is not the most used operating system when including both mobile and desktop OSes, due to Android (operating system), Android's massive growth. , the most recent version of Windows is Windows 11 for consumer Personal compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scripting Language
A scripting language or script language is a programming language that is used to manipulate, customize, and automate the facilities of an existing system. Scripting languages are usually interpreted at runtime rather than compiled. A scripting language's primitives are usually elementary tasks or API calls, and the scripting language allows them to be combined into more programs. Environments that can be automated through scripting include application software, text editors, web pages, operating system shells, embedded systems, and computer games. A scripting language can be viewed as a domain-specific language for a particular environment; in the case of scripting an application, it is also known as an extension language. Scripting languages are also sometimes referred to as very high-level programming languages, as they sometimes operate at a high level of abstraction, or as control languages, particularly for job control languages on mainframes. The term ''scriptin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation, multinational technology company, technology corporation producing Software, computer software, consumer electronics, personal computers, and related services headquartered at the Microsoft Redmond campus located in Redmond, Washington, United States. Its best-known software products are the Microsoft Windows, Windows line of operating systems, the Microsoft Office Productivity software#Office suite, suite, and the Internet Explorer and Microsoft Edge, Edge web browsers. Its flagship hardware products are the Xbox video game consoles and the Microsoft Surface lineup of touchscreen personal computers. Microsoft ranked No. 21 in the 2020 Fortune 500 rankings of the largest United States corporations by total revenue; it was the world's List of the largest software companies, largest software maker by revenue as of 2019. It is one of the Big Tech, Big Five American information technology companies, alongside Alphabet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows 3
Windows 3.x means either of, or all of the following versions of Microsoft Windows: * Windows 3.0 * Windows 3.1x Windows NT * Windows NT 3.x Windows NT 3.x may refer to either of, or all of the following versions of Microsoft Windows: * Windows NT 3.1 * Windows NT 3.5 Windows NT 3.5 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft and oriented towards bus ... 3.x {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oriel Window
An oriel window is a form of bay window which protrudes from the main wall of a building but does not reach to the ground. Supported by corbels, brackets, or similar cantilevers, an oriel window is most commonly found projecting from an upper floor but is also sometimes used on the ground floor. Oriel windows are seen in Arab architecture in the form of mashrabiya and in Turkish are known as ''şahnişin'' or ''cumba''. In Islamic culture, these windows and balconies project from the street-front of a house, providing an area in which women could peer out and see the activities below while remaining invisible. Origins According to the ''Oxford English Dictionary'', the term ''oriel'' is derived from Anglo-Norman ' and Late Latin ', both meaning "gallery" or "porch", perhaps from Classical Latin ' ("curtain"). * Oriel College, Oxford, took its name from a balcony or oriel window forming a feature of a building which occupied the site the college now stands on. * Oriel C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Window
A bay window is a window space projecting outward from the main walls of a building and forming a bay in a room. Types Bay window is a generic term for all protruding window constructions, regardless of whether they are curved or angular, or run over one or multiple storeys. In plan, the most frequently used shapes are isosceles trapezoid (which may be referred to as a ''canted bay window'') and rectangle. But other polygonal shapes with more than two corners are also common as are curved shapes. If a bay window is curved it may alternatively be called '' bow window.'' Bay windows in a triangular shape with just one corner exist but are relatively rare. A bay window supported by a corbel, bracket or similar is called an oriel window. "Rawashin" is a traditional and distinctive style of corbelled bay window in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia (e.g., as on the frontage of Nasseef House). Uses Most medieval bay windows and up to the Baroque era are oriel windows. They frequently ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modal Window
In user interface design for computer applications, a modal window is a graphical control element subordinate to an application's main window. A modal window creates a mode that disables the main window but keeps it visible, with the modal window as a child window in front of it. Users ''must'' interact with the modal window before they can return to the parent application. This avoids interrupting the workflow on the main window. Modal windows are sometimes called heavy windows or modal dialogs because they often display a dialog box. User interfaces typically use modal windows to command user awareness and to display emergency states, though interaction designers argue they are ineffective for that use. Modal windows are prone to mode errors. On the Web, they often show images in detail, such as those implemented by Lightbox library, or are used for hover ads. The opposite of modal is modeless. Modeless windows don't block the main window, so the user can switch their foc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialog Box
The dialog box (also called dialogue box (non-U.S. English), message box or simply dialog) is a graphical control element in the form of a small window that communicates information to the user and prompts them for a response. Dialog boxes are classified as " modal" or "modeless", depending on whether they block interaction with the software that initiated the dialog. The type of dialog box displayed is dependent upon the desired user interaction. The simplest type of dialog box is the alert, which displays a message and may require an acknowledgment that the message has been read, usually by clicking "OK", or a decision as to whether or not an action should proceed, by clicking "OK" or "Cancel". Alerts are also used to display a "termination notice"—sometimes requesting confirmation that the notice has been read—in the event of either an intentional closing or unintentional closing (" crash") of an application or the operating system. ( E.g., " Gedit has encount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)