|
Organization Of Kita And Minami Fortresses
The Kita and Minami Fortresses (Japanese ''kita'', "north" and ''minami'', "south") were defensive structures of the Imperial Japanese Army and Imperial Japanese Navy in the Kuril Archipelago. The most northerly points were on the Kokutan and Kurabu Zaki capes, and its coastal front on the Shumushu Strait near Lopatka Cape in the Soviet Union's Kamchatka peninsula. This military organization was under the Twenty-Seventh Army (Chishima Area Base Unit or Kuril Area Army), led by Shozo Terakura. The Twenty-seventh Army was under the leadership of the Fifth Area Army, under the command of Kiichiro Higuchi whose headquarters was in Sapporo, Hokkaidō. The Twenty-Seventh Army was composed of the 42nd and 91st Divisions. Kurile fortresses These defensive structures in the Kurile Islands were somewhat similar to the Karafuto fortifications. The key Japanese position was on Shumushu Island, whose defense consisted of permanent emplacements protected by field and AA artill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Language
is spoken natively by about 128 million people, primarily by Japanese people and primarily in Japan, the only country where it is the national language. Japanese belongs to the Japonic or Japanese- Ryukyuan language family. There have been many attempts to group the Japonic languages with other families such as the Ainu, Austroasiatic, Koreanic, and the now-discredited Altaic, but none of these proposals has gained widespread acceptance. Little is known of the language's prehistory, or when it first appeared in Japan. Chinese documents from the 3rd century AD recorded a few Japanese words, but substantial Old Japanese texts did not appear until the 8th century. From the Heian period (794–1185), there was a massive influx of Sino-Japanese vocabulary into the language, affecting the phonology of Early Middle Japanese. Late Middle Japanese (1185–1600) saw extensive grammatical changes and the first appearance of European loanwords. The basis of the standard dialect moved f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
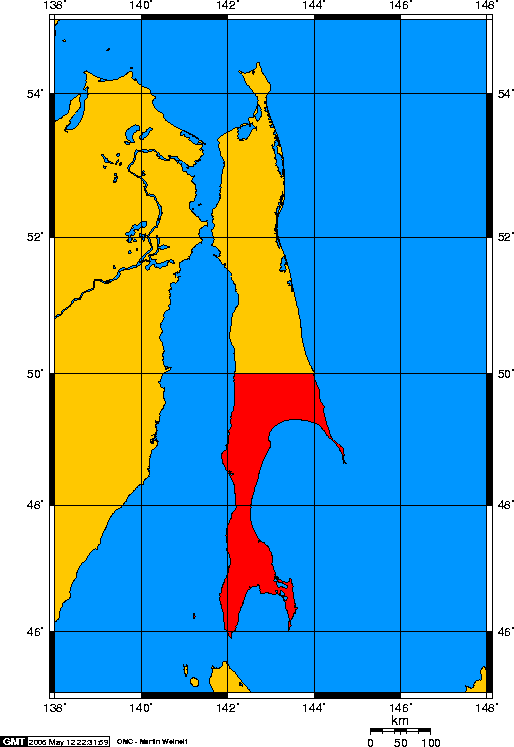
Karafuto
Karafuto Prefecture ( ja, 樺太庁, ''Karafuto-chō''; russian: Префектура Карафуто, Prefektura Karafuto), commonly known as South Sakhalin, was a prefecture of Japan located in Sakhalin from 1907 to 1949. Karafuto became territory of the Empire of Japan in 1905 after the Russo-Japanese War when the portion of Sakhalin south of 50°N was ceded from the Russian Empire in the Treaty of Portsmouth. Karafuto was established in 1907 as an external territory until being upgraded to an " Inner Land" of the Japanese metropole in 1943. Ōtomari (Korsakov) was the capital of Karafuto from 1905 to 1908 and Toyohara (Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk) from 1908 to August 1945 when the Japanese administration ceased to function in the invasion of South Sakhalin by the Soviet Union after the surrender of Japan in World War II. Karafuto Prefecture was de facto replaced with Sakhalin Oblast, although it continued to exist de jure under Japanese law until it was formally abolished as a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |