|
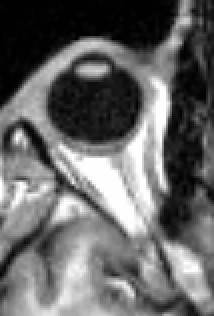
Optic Vesicle
The eyes begin to develop as a pair of diverticula (pouches) from the lateral aspects of the forebrain. These diverticula make their appearance before the closure of the anterior end of the neural tube; after the closure of the tube around the 4th week of development, they are known as the optic vesicles. Previous studies of optic vesicles suggest that the surrounding extraocular tissues – the surface ectoderm and extraocular mesenchyme – are necessary for normal eye growth and differentiation. They project toward the sides of the head, and the peripheral part of each expands to form a hollow bulb, while the proximal part remains narrow and constitutes the optic stalk, which goes on to form the optic nerve. Additional images File:Gray460.png, Head of chick embryo of about thirty-eight hours’ incubation, viewed from the ventral surface. X 26 See also * Eye development Eye formation in the human embryo begins at approximately three weeks into embryonic development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of the body. Neurulation forms the nervous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a human, the cerebral cortex contains approximately 14–16 billion neurons, and the estimated number of neurons in the cerebellum is 55–70 billion. Each neuron is connected by synapses to several thousand other neurons. These neurons typically communicate with one another by means of long fibers called axons, which carry trains of signal pulses called action potentials to distant parts of the brain or body targeting specific recipient cells. Physiologically, brains exert centralized control over a body's other organs. They act on the rest of the body both by generating patterns of muscle activity and by driving the secretion of chemicals called hormones. This centralized control allows rapid and coordinated respon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digestive Tube
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yolk Sac
The yolk sac is a membranous sac attached to an embryo, formed by cells of the hypoblast layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle by the Terminologia Embryologica (TE), though ''yolk sac'' is far more widely used. In humans, the yolk sac is important in early embryonic blood supply, and much of it is incorporated into the primordial gut during the fourth week of embryonic development. In humans The yolk sac is the first element seen within the gestational sac during pregnancy, usually at 3 days gestation. The yolk sac is situated on the front (ventral) part of the embryo; it is lined by extra-embryonic endoderm, outside of which is a layer of extra-embryonic mesenchyme, derived from the epiblast. Blood is conveyed to the wall of the yolk sac by the primitive aorta and after circulating through a wide-meshed capillary plexus, is returned by the vitelline veins to the tubular heart of the embryo. This constitutes the vitell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Eye
The human eye is a sensory organ, part of the sensory nervous system, that reacts to visible light and allows humans to use visual information for various purposes including seeing things, keeping balance, and maintaining circadian rhythm. The eye can be considered as a living optical device. It is approximately spherical in shape, with its outer layers, such as the outermost, white part of the eye (the sclera) and one of its inner layers (the pigmented choroid) keeping the eye essentially light tight except on the eye's optic axis. In order, along the optic axis, the optical components consist of a first lens (the cornea—the clear part of the eye) that accomplishes most of the focussing of light from the outside world; then an aperture (the pupil) in a diaphragm (the iris—the coloured part of the eye) that controls the amount of light entering the interior of the eye; then another lens (the crystalline lens) that accomplishes the remaining focussing of light into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Eyes
The human eye is a sensory organ, part of the sensory nervous system, that reacts to visible light and allows humans to use visual information for various purposes including seeing things, keeping balance, and maintaining circadian rhythm. The eye can be considered as a living optical device. It is approximately spherical in shape, with its outer layers, such as the outermost, white part of the eye (the sclera) and one of its inner layers (the pigmented choroid) keeping the eye essentially light tight except on the eye's optic axis. In order, along the optic axis, the optical components consist of a first lens (the cornea—the clear part of the eye) that accomplishes most of the focussing of light from the outside world; then an aperture (the pupil) in a diaphragm (the iris—the coloured part of the eye) that controls the amount of light entering the interior of the eye; then another lens (the crystalline lens) that accomplishes the remaining focussing of light into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Development
Eye formation in the human embryo begins at approximately three weeks into embryonic development and continues through the tenth week.Ort, D., David, H."Development of the Eye" Retrieved 22 April 2015. Cells from both the mesodermal and the ectodermal tissues contribute to the formation of the eye. Specifically, the eye is derived from the neuroepithelium, surface ectoderm, and the extracellular mesenchyme which consists of both the neural crest and mesoderm. Neuroepithelium forms the retina, ciliary body, iris, and optic nerves. Surface ectoderm forms the lens, corneal epithelium and eyelid. The extracellular mesenchyme forms the sclera, the corneal endothelium and stroma, blood vessels, muscles, and vitreous. The eye begins to develop as a pair of optic vesicles on each side of the forebrain at the end of the 4th week of pregnancy. Optic vesicles are outgrowings of the brain which make contact with the surface ectoderm and this contact induces changes necessary for further de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diverticula
In medicine or biology, a diverticulum is an outpouching of a hollow (or a fluid-filled) structure in the body. Depending upon which layers of the structure are involved, diverticula are described as being either true or false. In medicine, the term usually implies the structure is not normally present, but in embryology, the term is used for some normal structures arising from others, as for instance the thyroid diverticulum, which arises from the tongue. The word comes from Latin ''dīverticulum'', "bypath" or "byway". Classification Diverticula are described as being true or false depending upon the layers involved: *False diverticula (also known as "pseudodiverticula") do not involve muscular layers or adventitia. False diverticula, in the gastrointestinal tract for instance, involve only the submucosa and mucosa. *True diverticula involve all layers of the structure, including muscularis propria and adventitia, such as Meckel's diverticulum. Embryology *The kidneys are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forebrain
In the anatomy of the brain of vertebrates, the forebrain or prosencephalon is the Anatomical terms of location#Directional terms, rostral (forward-most) portion of the brain. The forebrain (prosencephalon), the midbrain (mesencephalon), and hindbrain (rhombencephalon) are the three Brain vesicle, primary brain vesicles during the early development of the nervous system. The forebrain controls body temperature, reproductive functions, eating, sleeping, and the display of emotions. At the five-vesicle stage, the forebrain separates into the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, subthalamus, and epithalamus) and the telencephalon which develops into the cerebrum. The cerebrum consists of the cerebral cortex, underlying white matter, and the basal ganglia. In humans, by 5 weeks in utero it is visible as a single portion toward the front of the fetus. At 8 weeks in utero, the forebrain splits into the left and right cerebral hemispheres. When the embryonic forebrain fails to divide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neural Tube
In the developing chordate (including vertebrates), the neural tube is the embryonic precursor to the central nervous system, which is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The neural groove gradually deepens as the neural fold become elevated, and ultimately the folds meet and coalesce in the middle line and convert the groove into the closed neural tube. In humans, neural tube closure usually occurs by the fourth week of pregnancy (the 28th day after conception). The ectodermal wall of the tube forms the rudiment of the nervous system. The centre of the tube is the ''neural canal''.It is an important structure for the development of fetus's brain and spine Development The neural tube develops in two ways: primary neurulation and secondary neurulation. Primary neurulation divides the ectoderm into three cell types: * The internally located neural tube * The externally located epidermis * The neural crest cells, which develop in the region between the neural tube and epider ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ectoderm
The ectoderm is one of the three primary germ layers formed in early embryonic development. It is the outermost layer, and is superficial to the mesoderm (the middle layer) and endoderm (the innermost layer). It emerges and originates from the outer layer of germ cells. The word ectoderm comes from the Greek ''ektos'' meaning "outside", and ''derma'' meaning "skin".Gilbert, Scott F. Developmental Biology. 9th ed. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates, 2010: 333-370. Print. Generally speaking, the ectoderm differentiates to form epithelial and neural tissues (spinal cord, peripheral nerves and brain). This includes the skin, linings of the mouth, anus, nostrils, sweat glands, hair and nails, and tooth enamel. Other types of epithelium are derived from the endoderm. In vertebrate embryos, the ectoderm can be divided into two parts: the dorsal surface ectoderm also known as the external ectoderm, and the neural plate, which invaginates to form the neural tube and neural crest. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |