|
Ophioglossales
Ophioglossaceae, the adder's-tongue family, is a small family of ferns. In the Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group classification of 2016 (PPG I), it is the only family in the order Ophioglossales, which together with the Psilotales is placed in the subclass Ophioglossidae. The Ophioglossidae are one of the groups traditionally known as eusporangiate ferns. Members of the family differ from other ferns in a number of ways. Many have only a single fleshy leaf at a time. Their gametophytes are subterranean and rely on fungi for energy. Description Members of Ophioglossaceae are usually terrestrial (excepting a few epiphytic species of ''Ophioglossum'') and occur in both temperate and tropical areas. They differ from the other ferns in several respects: * Many species only send up one frond or leaf-blade per year, producing only a single leaf at a time. The leaves are usually fleshy, and in temperate areas will often turn brownish or reddish during colder months. * Instead of the leptosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophioglossidae
Ophioglossidae is one of the four subclasses of Polypodiopsida (ferns). This subclass consists of the ferns commonly known as whisk ferns, grape ferns, adder's-tongues and moonworts. It is equivalent to the class Psilotopsida in previous treatments, including Smith ''et al.'' (2006). The subclass contains two orders, Psilotales and Ophioglossales, whose relationship was only confirmed by molecular phylogenetic studies. Taxonomy Smith et al. (2006) carried out the first higher-level pteridophyte classification published in the molecular phylogenetic era, and considered the ferns (monilophytes), with four classes. They placed the whisk ferns and related taxa in the class Psilotopsida, with two orders. Mark W. Chase and James L. Reveal (2009) classified them as two separate subclasses, Psilotidae and Ophioglossidae, corresponding to those orders within a much broader grouping, the class Equisetopsida ''sensu lato''. Christenhusz ''et al.'', 2011, included both the Ophioglossal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fern
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes except the lycopods, and differ from mosses and other bryophytes by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissues that conduct water and nutrients and in having life cycles in which the branched sporophyte is the dominant phase. Ferns have complex leaves called megaphylls, that are more complex than the microphylls of clubmosses. Most ferns are leptosporangiate ferns. They produce coiled fiddleheads that uncoil and expand into fronds. The group includes about 10,560 known extant species. Ferns are defined here in the broad sense, being all of the Polypodiopsida, comprising both the leptosporangiate (Polypodiidae) and eusporangiate ferns, the latter group including horsetails, whisk ferns, marattioid ferns, and ophioglossoid ferns. Ferns first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group
The Pteridophyte Phylogeny Group, or PPG, is an informal international group of systematic botanists who collaborate to establish a consensus on the classification of pteridophytes (lycophytes and ferns) that reflects knowledge about plant relationships discovered through phylogenetic studies. In 2016, the group published a classification for extant pteridophytes, termed "PPG I". The paper had 94 authors (26 principal and 68 additional). PPG I A first classification, PPG I, was produced in 2016, covering only extant (living) pteridophytes. The classification was rank-based, using the ranks of class, subclass, order, suborder, family, subfamily and genus. Phylogeny The classification was based on a consensus phylogeny, shown below to the level of order. The very large order Polypodiales was divided into two suborders, as well as families not placed in a suborder: Classification to subfamily level To the level of subfamily, the PPG I classification is as follows. *Class Lycopodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eusporangiate Fern
Eusporangiate ferns are vascular spore plants, whose sporangia arise from several epidermal cells and not from a single cell as in leptosporangiate ferns. Typically these ferns have reduced root systems and sporangia that produce large amounts of spores (up to 7000 spores per sporangium in '' Christensenia'') There are four extant eusporangiate fern families, distributed among three classes. Each family is assigned to its own order. *Class Psilotopsida **Order Psilotales, family Psilotaceae – Whisk ferns (2 genera, about 17 species) **Order Ophioglossales, family Ophioglossaceae – Adder's-tongues (5 genera, about 80 species) *Class Equisetopsida **Order Equisetales, family Equisetaceae – Horsetails (1 genus, about 15 species) *Class Marattiopsida **Order Marattiales, family Marattiaceae – Marattoid ferns (6 genera, about 500 species) The following diagram shows a likely phylogenic placement of eusporangiate fern classes within the vascular plants. Cladistics While it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psilotales
Psilotaceae is a family of ferns (class Polypodiopsida) consisting of two genera, ''Psilotum'' and ''Tmesipteris'' with about a dozen species. It is the only family in the order Psilotales. Description Once thought to be descendants of early vascular plants (the Psilophyta of the Devonian period), Psilotaceae have been shown by molecular phylogenetics to be ferns (Polypodiopsida), and a sister group of the Ophioglossaceae. The family contains two genera, ''Psilotum'' and ''Tmesipteris''. The first genus, ''Psilotum'', consists of small shrubby plants of the dry tropics commonly known as "whisk ferns". The other genus, ''Tmesipteris'', is an epiphyte found in Australia, New Zealand, and New Caledonia. All members of Psilotaceae are vascular plants without any true roots. Rather, the plants are anchored by an underground system of rhizomes. The small, stem-like gametophytes of Psilotaceae are located in this rhizome system, and they aid in a plant's nutrient absorption through t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
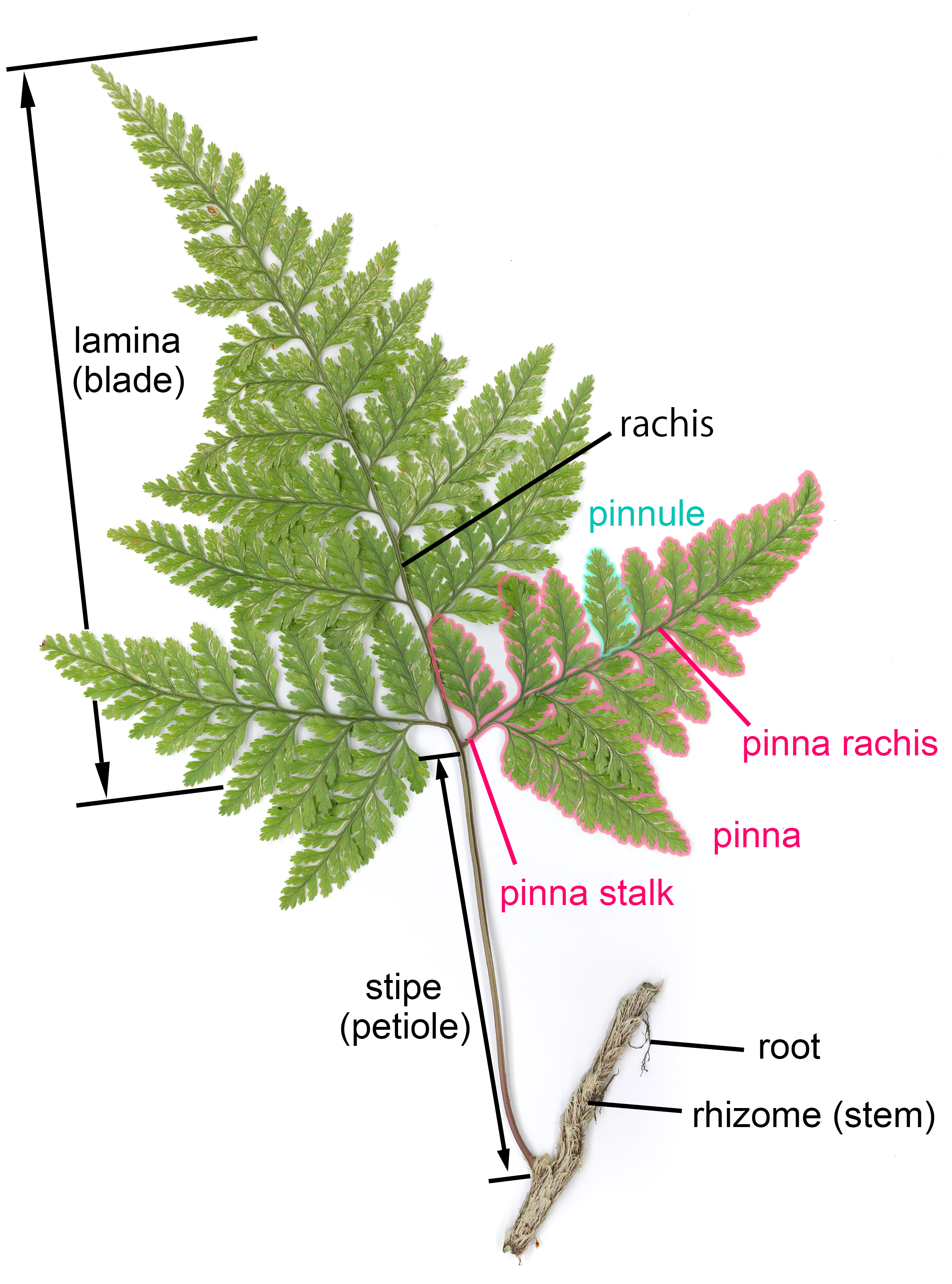
Frond
A frond is a large, divided leaf. In both common usage and botanical nomenclature, the leaves of ferns are referred to as fronds and some botanists restrict the term to this group. Other botanists allow the term frond to also apply to the large leaves of cycads, as well as palms (Arecaceae) and various other flowering plants, such as mimosa or sumac. "Frond" is commonly used to identify a large, compound leaf, but if the term is used botanically to refer to the leaves of ferns and algae it may be applied to smaller and undivided leaves. Fronds have particular terms describing their components. Like all leaves, fronds usually have a stalk connecting them to the main stem. In botany, this leaf stalk is generally called a petiole, but in regard to fronds specifically it is called a stipe, and it supports a flattened blade (which may be called a lamina), and the continuation of the stipe into this portion is called the rachis. The blades may be simple (undivided), pinnatifid ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophioglossum Vulgatum
''Ophioglossum vulgatum'', commonly known as adder's-tongue, southern adders-tongue or adders-tongue fern, is a species of fern in the family ''Ophioglossaceae''. The adder’s tongue fern is generally believed to have the largest number of chromosomes wit1262 compared to the human’s 46. Distribution It is native to many regions with a wide scattered distribution: throughout temperate through tropical Africa and throughout the temperate Northern Hemisphere in Europe, northeastern North America, temperate Asia, and Eurasia. This small, hard-to-spot plant can occur singly in unimproved pastures, rock crevices and grassy path-sides, but also can occur in colonies of hundreds of plants in sand dunes. Description ''Ophioglossum vulgatum'' grows from a rhizome base to 10–20 cm tall (rarely to 30 cm). It consists of a two-part frond, separated into a rounded diamond-shaped sheath and narrow spore-bearing spike. The spike has around 10-40 segments on each side. It repro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Organisms By Chromosome Count
The list of organisms by chromosome count describes ploidy or numbers of chromosomes in the cells of various plants, animals, protists, and other living organisms. This number, along with the visual appearance of the chromosome, is known as the karyotype, and can be found by looking at the chromosomes through a microscope. Attention is paid to their length, the position of the centromeres, banding pattern, any differences between the sex chromosomes, and any other physical characteristics. The preparation and study of karyotypes is part of cytogenetics. File:Human karyotype with bands and sub-bands.png, Karyotype of a human being. It shows 22 homologous autosomal chromosome pairs, both the female (XX) and male (XY) versions of the two sex chromosomes, as well as the mitochondrial genome (at bottom left). File:Chromosome2 merge.png, Fusion of ancestral chromosomes left distinctive remnants of telomeres, and a vestigial centromere. As other non-human extant hominidae have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, fungi and protozoa. Bacterial spores are not part of a sexual cycle, but are resistant structures used for survival under unfavourable conditions. Myxozoan spores release amoeboid infectious germs ("amoebulae") into their hosts for parasitic infection, but also reproduce within the hosts through the pairing of two nuclei within the plasmodium, which develops from the amoebula. In plants, spores are usually haploid and unicellular and are produced by meiosis in the sporangium of a diploid sporophyte. Under favourable conditions the spore can develop into a new organism using mitotic division, producing a multicellular gametophyte, which eventually goes on to produce gametes. Two gametes fuse to form a zygote which develops into a new s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annulus (botany)
{{Short description, A ring of specialized cells on the sporangium An annulus in botany is an arc or a ring of specialized cells on the sporangium. These cells are arranged in a single row, and are associated with the release or dispersal of spores. Ferns In leptosporangiate ferns, the annulus located on the outer rim of the sporangium and serves in spore dispersal. It consists typically of a ring or belt of dead water-filled cells with differentially thickened cell walls that stretches about two-thirds around each sporangium in leptosporangiate ferns. The thinner walls on the outside allow water to evaporate quickly under dry conditions. This dehiscence causes the cells to shrink and a contraction and straightening of the annulus ring, eventually rupturing the sporangial wall by ripping apart thin-walled lip cells on the opposite side of the sporangium. As more water evaporates, air bubbles form in the cells causing the contracted annulus to snap forward again, thus dislodging an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the surface of the soil, but roots can also be aerial or aerating, that is, growing up above the ground or especially above water. Function The major functions of roots are absorption of water, plant nutrition and anchoring of the plant body to the ground. Anatomy Root morphology is divided into four zones: the root cap, the apical meristem, the elongation zone, and the hair. The root cap of new roots helps the root penetrate the soil. These root caps are sloughed off as the root goes deeper creating a slimy surface that provides lubrication. The apical meristem behind the root cap produces new root cells that elongate. Then, root hairs form that absorb water and mineral nutrients from the soil. The first root in seed producing plants is the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophioglossum Malviae
''Ophioglossum malviae'' is a species of fern in the genus ''Ophioglossum'' and found in the forests of Ahwa in the Dang District, India, Dang District of Gujarat. It is claimed to be the world's smallest land fern, with the entire plant growing to a size of about only 1 to 1.5 cm. References Ophioglossaceae {{fern-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |