|
Operational Land Imager
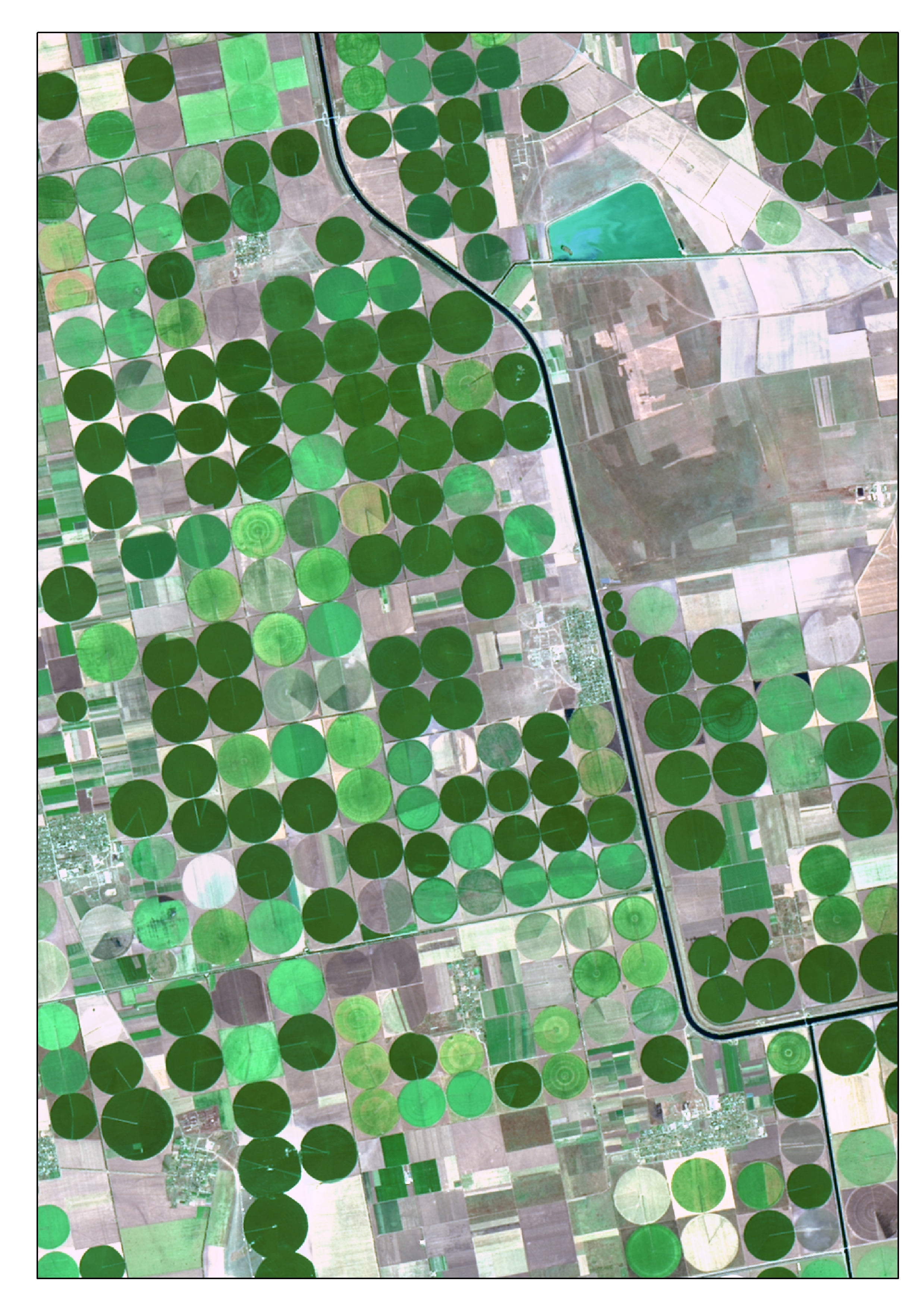
The Operational Land Imager (OLI) is a remote sensing instrument aboard Landsat 8, built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies. Landsat 8 is the successor to Landsat 7 and was launched on February 11, 2013. OLI is a push broom scanner that uses a four-mirror telescope with fixed mirrors. Overview and mission OLI operates alongside TIRS (Thermal Infrared Sensor) on board the LDCM. The build and design of OLI differs from previous generations of instruments, while still maintaining data continuity with archived Landsat data from the last 40 years by keeping the same spectral and spatial resolutions of previous instruments. OLI aids the Landsat-8 mission in the imaging of Earth's surface and the collection of moderate resolution data that is used to monitor changing trends on the surface and evaluate how land usage changes over time. The images and data that OLI has helped collect have practical applications today in agriculture, mapping, and monitoring changes in snow, ice, and wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landsat Data Continuity Mission Operational Land Imager Instrument Design
The Landsat program is the longest-running enterprise for acquisition of satellite imagery of Earth. It is a joint NASA / USGS program. On 23 July 1972, the Earth Resources Technology Satellite was launched. This was eventually renamed to Landsat 1 in 1975. The most recent, Landsat 9, was launched on 27 September 2021. The instruments on the Landsat satellites have acquired millions of images. The images, archived in the United States and at Landsat receiving stations around the world, are a unique resource for global change research and applications in agriculture, cartography, geology, forestry, regional planning, surveillance and education, and can be viewed through the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) "EarthExplorer" website. Landsat 7 data has eight spectral bands with spatial resolutions ranging from ; the temporal resolution is 16 days. Landsat images are usually divided into scenes for easy downloading. Each Landsat scene is about 115 miles long and 115 miles wide (or 100 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thames Estuary And Wind Farms From Space NASA
The River Thames ( ), known alternatively in parts as the The Isis, River Isis, is a river that flows through southern England including London. At , it is the longest river entirely in England and the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, second-longest in the United Kingdom, after the River Severn. The river rises at Thames Head in Gloucestershire, and flows into the North Sea near Tilbury, Essex and Gravesend, Kent, via the Thames Estuary. From the west it flows through Oxford (where it is sometimes called the Isis), Reading, Berkshire, Reading, Henley-on-Thames and Windsor, Berkshire, Windsor. The Thames also drains the whole of Greater London. In August 2022, the source of the river moved five miles to beyond Somerford Keynes due to the heatwave in July 2022. The lower reaches of the river are called the Tideway, derived from its long tidal reach up to Teddington Lock. Its tidal section includes most of its London stretch and has a rise and fall of . From Oxford to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landsat 8
Landsat 8 is an American Earth observation satellite launched on 11 February 2013. It is the eighth satellite in the Landsat program; the seventh to reach orbit successfully. Originally called the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM), it is a collaboration between NASA and the United States Geological Survey (USGS). NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, provided development, mission systems engineering, and acquisition of the launch vehicle while the USGS provided for development of the ground systems and will conduct on-going mission operations. It comprises the camera of the Operational Land Imager (OLI) and the Thermal Infrared Sensor (TIRS), which can be used to study Earth surface temperature and is used to study global warming. The satellite was built by Orbital Sciences Corporation, who served as prime contractor for the mission. The spacecraft's instruments were constructed by Ball Aerospace & Technologies and NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ball Aerospace & Technologies
Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp. is an American manufacturer of spacecraft, components and instruments for national defense, civil space and commercial space applications. The company is a wholly owned subsidiary of Ball Corporation (NYSE: BALL), with primary offices in Boulder, Colorado, and facilities in Broomfield and Westminster in Colorado, with smaller offices in New Mexico, Ohio, northern Virginia, Missouri and Maryland. Ball Aerospace began building pointing controls for military rockets in 1956 (the aerospace part of the Ball Corporation was then known as Ball Brothers Research Corporation) and later won a contract to build some of NASA's first spacecraft, the Orbiting Solar Observatory satellites. The company has been responsible for numerous technological and scientific projects and continues to provide aerospace technology to NASA and related industries. Other products and services for the aerospace industry include lubricants, optical systems, star trackers and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landsat 7
Landsat 7 is the seventh satellite of the Landsat program. Launched on 15 April 1999, Landsat 7's primary goal is to refresh the global archive of satellite photos, providing up-to-date and cloud-free images. The Landsat program is managed and operated by the United States Geological Survey, and data from Landsat 7 is collected and distributed by the USGS. The NASA WorldWind project allows 3D images from Landsat 7 and other sources to be freely navigated and viewed from any angle. The satellite's companion, Earth Observing-1, trailed by one minute and followed the same orbital characteristics, but in 2011 its fuel was depleted and EO-1's orbit began to degrade. Landsat 7 was built by Lockheed Martin Space Systems. In 2016, NASA announced plans to attempt the first ever refueling of a live satellite by refueling Landsat 7 in 2020 with the OSAM-1 mission; as of 2021, the launch date has slipped to 2025. NASA plans to decommission the satellite following the 2021 launch and activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Applied Remote Sensing
The ''Journal of Applied Remote Sensing'' is a peer-reviewed open access scientific journal published by SPIE. It covers all aspects of remote sensing and was established in 2007. The editor-in-chief is Ni-Bin Chang (University of Central Florida). Abstracting and indexing This journal is indexed by the following databases: * Science Citation Index Expanded * Current Contents/ Agriculture, Biology & Environmental Sciences * Current Contents/ Physical, Chemical & Earth Sciences * Inspec * Scopus * EI/Compendex * Astrophysics Data System According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 1.53. See also * ''ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing'' * ''Remote Sensing Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring information about Eart ...'' "Journal of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Push Broom Scanner
A push broom scanner, also known as an along-track scanner, is a device for obtaining images with spectroscopic sensors. The scanners are regularly used for passive remote sensing from space, and in spectral analysis on production lines, for example with near-infrared spectroscopy used to identify contaminated food and feed. The moving scanner line in a traditional photocopier (or a scanner or facsimile machine) is also a familiar, everyday example of a push broom scanner. Push broom scanners and the whisk broom scanners variant (also known as across-track scanners) are often contrasted with staring arrays (such as in a digital camera), which image objects without scanning, and are more familiar to most people. In orbital push broom sensors, a line of sensors arranged perpendicular to the flight direction of the spacecraft is used. Different areas of the surface are imaged as the spacecraft flies forward. A push broom scanner can gather more light than a whisk broom scanner beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
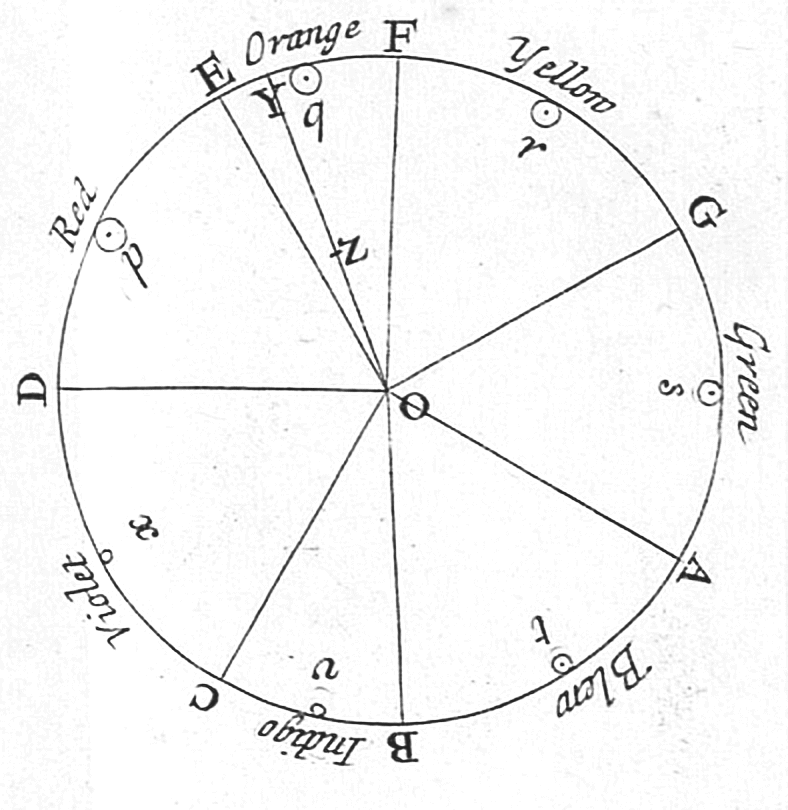
Visible Spectrum
The visible spectrum is the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visual perception, visible to the human eye. Electromagnetic radiation in this range of wavelengths is called ''visible light'' or simply light. A typical human eye will respond to wavelengths from about 380 to about 750 nanometers. In terms of frequency, this corresponds to a band in the vicinity of 400–790 Terahertz (unit), terahertz. These boundaries are not sharply defined and may vary per individual. Under optimal conditions these limits of human perception can extend to 310 nm (ultraviolet) and 1100 nm (near infrared). The optical spectrum is sometimes considered to be the same as the visible spectrum, but some authors define the term more broadly, to include the ultraviolet and infrared parts of the electromagnetic spectrum as well. The spectrum does not contain all the colors that the human visual system can distinguish. ''Excitation purity, Unsaturated colors'' such as pink, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
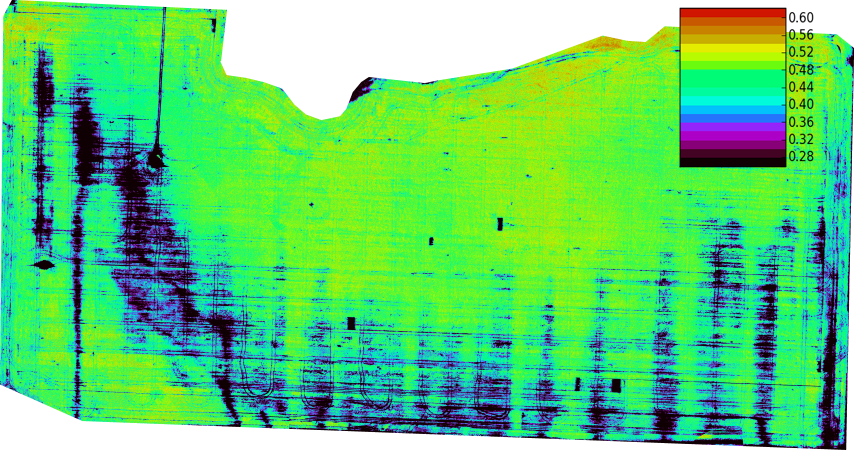
Normalized Difference Vegetation Index
The normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) is a simple graphical indicator that can be used to analyze remote sensing measurements, often from a space platform, assessing whether or not the target being observed contains live green vegetation. Brief history The exploration of outer space started in earnest with the launch of Sputnik 1 by the Soviet Union on 4 October 1957. This was the first man-made satellite orbiting the Earth. Subsequent successful launches, both in the Soviet Union (e.g., the Sputnik and Cosmos programs), and in the U.S. (e.g., the Explorer program), quickly led to the design and operation of dedicated meteorological satellites. These are orbiting platforms embarking instruments specially designed to observe the Earth's atmosphere and surface with a view to improve weather forecasting. Starting in 1960, the TIROS series of satellites embarked television cameras and radiometers. This was later (1964 onwards) followed by the Nimbus satellites and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |